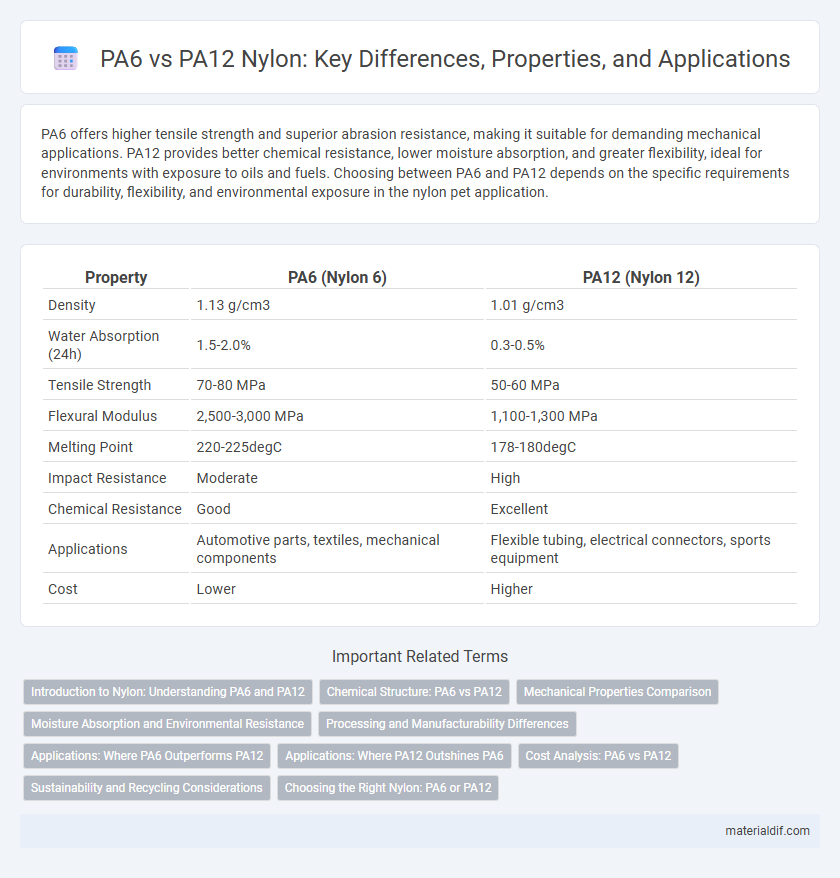
PA6 offers higher tensile strength and superior abrasion resistance, making it suitable for demanding mechanical applications. PA12 provides better chemical resistance, lower moisture absorption, and greater flexibility, ideal for environments with exposure to oils and fuels. Choosing between PA6 and PA12 depends on the specific requirements for durability, flexibility, and environmental exposure in the nylon pet application.
Table of Comparison
| Property | PA6 (Nylon 6) | PA12 (Nylon 12) |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 1.13 g/cm3 | 1.01 g/cm3 |
| Water Absorption (24h) | 1.5-2.0% | 0.3-0.5% |
| Tensile Strength | 70-80 MPa | 50-60 MPa |
| Flexural Modulus | 2,500-3,000 MPa | 1,100-1,300 MPa |
| Melting Point | 220-225degC | 178-180degC |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Chemical Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Applications | Automotive parts, textiles, mechanical components | Flexible tubing, electrical connectors, sports equipment |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Nylon: Understanding PA6 and PA12
Nylon PA6 and PA12 are prominent types of polyamide polymers widely used in engineering applications due to their strength and durability. PA6 offers higher tensile strength and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for mechanical parts, while PA12 provides superior chemical resistance and flexibility, suitable for fuel lines and flexible tubing. Understanding the specific properties of PA6 and PA12 allows engineers to select the optimal material for performance and lifecycle requirements.
Chemical Structure: PA6 vs PA12
PA6, or Polyamide 6, consists of repeating units derived from caprolactam, featuring a six-carbon backbone with an amide group, which results in higher crystallinity and rigidity. PA12, or Polyamide 12, is synthesized from laurolactam with a twelve-carbon chain, offering increased flexibility and lower moisture absorption due to its longer aliphatic segment. The fundamental chemical structure difference between PA6 and PA12 significantly influences their mechanical properties, thermal stability, and chemical resistance in industrial applications.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
PA6 exhibits higher tensile strength and rigidity compared to PA12, making it suitable for load-bearing applications requiring durability. PA12 offers superior impact resistance and flexibility, ideal for parts subject to repeated stress and bending. Both nylons provide excellent chemical resistance, but PA6 generally performs better under higher mechanical loads.
Moisture Absorption and Environmental Resistance
PA12 demonstrates significantly lower moisture absorption compared to PA6, typically around 0.5% versus 2.5%, making PA12 more dimensionally stable in humid environments. PA12 also offers superior environmental resistance, including enhanced resistance to chemicals, UV exposure, and hydrolysis, extending its lifespan in harsh conditions. These properties make PA12 preferable for applications requiring consistent mechanical performance and durability under moisture and environmental stress.
Processing and Manufacturability Differences
PA6 offers better mechanical strength and rigidity, making it suitable for injection molding with faster cycle times and easier processing due to its semi-crystalline structure. PA12 exhibits superior flexibility and chemical resistance, enabling extrusion and blow molding processes with lower moisture absorption and less warping during manufacturing. The differences in melting temperatures--PA6 around 220degC and PA12 between 175-180degC--significantly influence their thermal processing windows and tooling requirements.
Applications: Where PA6 Outperforms PA12
PA6 excels in applications demanding higher mechanical strength and rigidity, such as automotive engine components, industrial gears, and electrical connectors, due to its superior tensile strength and abrasion resistance. Its higher melting point and better stiffness make PA6 preferable for parts exposed to elevated temperatures and mechanical stress. PA6's inherent moisture absorption enhances dimensional stability in humid environments, making it ideal for structural and load-bearing applications over PA12.
Applications: Where PA12 Outshines PA6
PA12 outperforms PA6 in automotive fuel lines and flexible tubing due to its superior chemical resistance and low moisture absorption, ensuring durability and long-term performance in harsh environments. In electrical and electronic components, PA12's excellent dimensional stability and low dielectric constant make it the preferred choice for precise, insulated parts. Additionally, PA12 is favored in sports equipment such as protective gear and inflatable structures for its high flexibility and impact resistance.
Cost Analysis: PA6 vs PA12
PA6 typically offers a lower raw material cost compared to PA12, making it a more economical choice for high-volume production. However, PA12 provides superior flexibility and chemical resistance, potentially reducing long-term maintenance and replacement expenses. Factoring in processing costs, PA6 requires higher energy input due to its higher melting point, while PA12's lower processing temperature can lead to cost savings in manufacturing.
Sustainability and Recycling Considerations
PA6 and PA12 both offer distinct sustainability profiles, with PA12 typically exhibiting lower density and enhanced chemical resistance, leading to longer product lifespans and reduced material usage. Recycling PA6 is well-established through mechanical and chemical recycling processes, but it often faces challenges due to its higher moisture absorption and crystallinity compared to PA12. PA12's superior moisture resistance and lower processing temperatures contribute to energy-efficient recyclability, making it a preferred option for applications emphasizing environmental impact reduction.
Choosing the Right Nylon: PA6 or PA12
PA6 offers higher tensile strength and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and impact resistance, while PA12 provides superior chemical resistance and flexibility, suitable for low-moisture environments and complex geometries. Choosing between PA6 and PA12 depends on operational demands such as temperature tolerance, mechanical stress, and exposure to chemicals or moisture. PA12's lower water absorption enhances dimensional stability, whereas PA6 benefits from higher stiffness and cost-effectiveness in general-purpose uses.
PA6 vs PA12 Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com