Heat-resistant nylon offers superior thermal stability compared to general-purpose nylon, maintaining its strength and durability at elevated temperatures up to 200degC. This specialized nylon resists deformation, melting, and degradation in harsh heat environments, making it ideal for applications requiring long-term exposure to high heat. In contrast, general-purpose nylon typically withstands lower temperatures and is suited for everyday uses without extreme thermal demands.
Table of Comparison
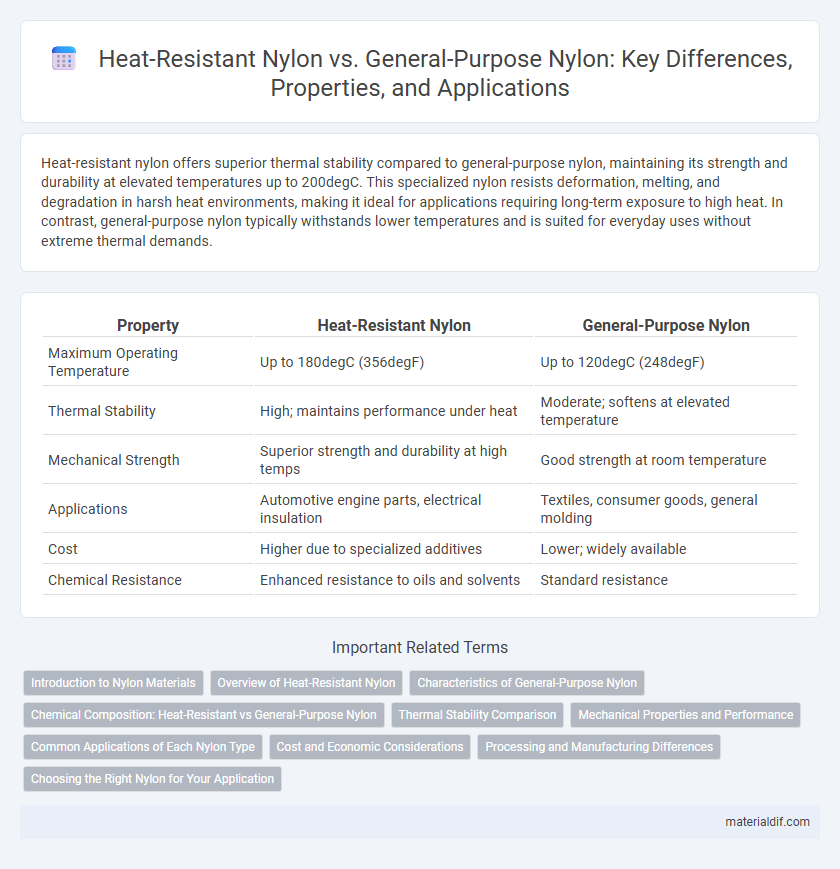
| Property | Heat-Resistant Nylon | General-Purpose Nylon |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Operating Temperature | Up to 180degC (356degF) | Up to 120degC (248degF) |
| Thermal Stability | High; maintains performance under heat | Moderate; softens at elevated temperature |
| Mechanical Strength | Superior strength and durability at high temps | Good strength at room temperature |
| Applications | Automotive engine parts, electrical insulation | Textiles, consumer goods, general molding |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized additives | Lower; widely available |
| Chemical Resistance | Enhanced resistance to oils and solvents | Standard resistance |
Introduction to Nylon Materials
Heat-resistant nylon is engineered with enhanced thermal stability, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to 180degC, making it ideal for demanding industrial applications. General-purpose nylon, typically nylon 6 or nylon 6,6, offers balanced mechanical strength and flexibility but has a lower continuous use temperature around 80-120degC. Both types share excellent chemical resistance and durability, but heat-resistant nylon's improved thermal performance expands its application in automotive, electrical, and high-heat environments.
Overview of Heat-Resistant Nylon
Heat-resistant nylon offers enhanced thermal stability, typically withstanding temperatures up to 150-180degC compared to general-purpose nylon, which deforms around 100-120degC. This specialized nylon variant incorporates heat-stabilizing additives and reinforced molecular structures, improving its performance in high-temperature applications such as automotive engine components and electrical insulators. Its superior thermal resistance reduces deformation and maintains mechanical integrity under prolonged heat exposure, making it ideal for demanding industrial environments.
Characteristics of General-Purpose Nylon
General-purpose nylon offers excellent balance between mechanical strength, flexibility, and chemical resistance, making it suitable for a wide range of everyday applications including automotive parts, textiles, and consumer goods. It demonstrates good wear resistance and impact toughness but has a lower melting point and thermal stability compared to heat-resistant nylon variants. Moisture absorption can affect its dimensional stability and mechanical properties under prolonged exposure to humid environments.
Chemical Composition: Heat-Resistant vs General-Purpose Nylon
Heat-resistant nylon typically contains enhanced molecular structures such as increased crystalline regions and incorporation of heat-stabilizing additives like aromatic polyamides, which improve thermal stability up to 200degC or higher. General-purpose nylon, commonly nylon 6 or nylon 6,6, features a simpler linear polyamide chain with lower crystalline content, resulting in melting points around 215-265degC but reduced long-term heat resistance. The chemical composition differences include variations in monomer types, crystalline structure, and the presence of stabilizers, directly influencing their thermal endurance and mechanical properties.
Thermal Stability Comparison
Heat-resistant nylon demonstrates superior thermal stability with a continuous use temperature typically ranging from 120degC to 180degC, compared to general-purpose nylon which usually withstands up to 90degC to 110degC. This enhanced thermal resistance is due to specialized additives and higher crystallinity in heat-resistant nylon, enabling it to maintain mechanical properties under prolonged exposure to elevated temperatures. General-purpose nylon, while versatile and cost-effective, experiences significant degradation and loss of strength when subjected to high-temperature environments.
Mechanical Properties and Performance
Heat-resistant nylon exhibits superior mechanical properties compared to general-purpose nylon, including higher tensile strength, improved dimensional stability, and enhanced resistance to thermal degradation at elevated temperatures. Its performance in high-temperature applications ensures retention of rigidity and impact resistance, whereas general-purpose nylon may soften or deform under similar conditions. These characteristics make heat-resistant nylon ideal for demanding engineering applications requiring durability and consistent mechanical behavior under heat stress.
Common Applications of Each Nylon Type
Heat-resistant nylon is commonly used in automotive components, electrical connectors, and industrial machinery parts that require durability under high temperatures. General-purpose nylon finds a wide range of applications in textiles, consumer goods, and packaging materials where moderate strength and flexibility are sufficient. Both types serve crucial roles in manufacturing, with heat-resistant nylon favored for extreme conditions and general-purpose nylon suitable for everyday use.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Heat-resistant nylon typically incurs higher production costs due to its enhanced thermal stability and specialized additives, resulting in a greater initial investment compared to general-purpose nylon. General-purpose nylon offers a more cost-effective solution for applications with lower temperature demands, making it economically advantageous for large-scale manufacturing where heat resistance is not critical. Balancing application requirements with budget constraints ensures optimal material selection, minimizing overall lifecycle costs while maintaining performance.
Processing and Manufacturing Differences
Heat-resistant nylon requires specialized processing techniques such as controlled cooling and annealing to enhance thermal stability, whereas general-purpose nylon uses standard injection molding with less stringent temperature controls. Manufacturing heat-resistant nylon involves higher melting points and compound additives to improve heat endurance, while general-purpose variants prioritize ease of molding and cost efficiency. These differences result in heat-resistant nylon having superior dimensional stability and mechanical properties at elevated temperatures compared to general-purpose nylon.
Choosing the Right Nylon for Your Application
Heat-resistant nylon offers superior thermal stability withstanding temperatures up to 260degC, making it ideal for high-temperature applications in automotive and electrical industries. General-purpose nylon provides excellent strength and abrasion resistance suitable for everyday uses such as consumer goods and mechanical parts. Selecting the right nylon depends on the specific thermal requirements, mechanical stresses, and environmental exposure of your application.
Heat-Resistant Nylon vs General-Purpose Nylon Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com