Antistatic nylon reduces static electricity buildup by dispersing electrical charges on the fabric's surface, making it ideal for environments sensitive to static discharge. Conductive nylon incorporates conductive fibers to create a fabric that actively conducts electricity, offering superior grounding and prevention of static-related hazards. Choosing between antistatic and conductive nylon depends on the level of static control required for specific applications.
Table of Comparison
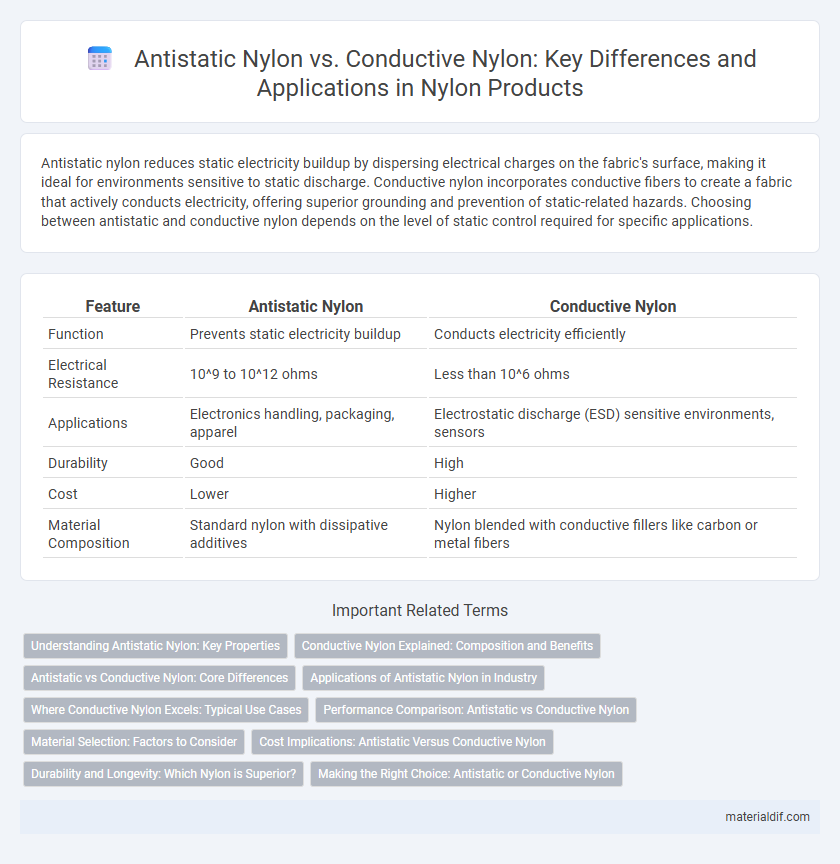
| Feature | Antistatic Nylon | Conductive Nylon |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Prevents static electricity buildup | Conducts electricity efficiently |
| Electrical Resistance | 10^9 to 10^12 ohms | Less than 10^6 ohms |
| Applications | Electronics handling, packaging, apparel | Electrostatic discharge (ESD) sensitive environments, sensors |
| Durability | Good | High |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Material Composition | Standard nylon with dissipative additives | Nylon blended with conductive fillers like carbon or metal fibers |
Understanding Antistatic Nylon: Key Properties
Antistatic nylon is engineered to prevent the buildup of static electricity by incorporating carbon black or other antistatic additives into the polymer matrix, which dissipates electrical charges. This material offers moderate conductivity, typically ranging from 10^6 to 10^9 ohm-cm, making it suitable for applications requiring static control without full electrical conduction. Unlike conductive nylon, which contains higher levels of conductive fillers like carbon fibers or metal particles for low resistivity below 10^4 ohm-cm, antistatic nylon maintains mechanical properties while reducing static hazards in electronics, packaging, and textile industries.
Conductive Nylon Explained: Composition and Benefits
Conductive nylon is engineered by integrating conductive fillers such as carbon black, metal fibers, or carbon nanotubes into the nylon matrix, creating a material that efficiently dissipates static electricity. This composition enhances electrical conductivity while preserving nylon's inherent strength, flexibility, and durability, making it ideal for applications in electronics, automotive parts, and anti-static gloves. Its benefits include improved safety in static-sensitive environments, reduced risk of electrostatic discharge damage, and compliance with industry standards for electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding.
Antistatic vs Conductive Nylon: Core Differences
Antistatic nylon reduces surface static buildup by dissipating charges more slowly, ideal for environments with moderate static control needs. Conductive nylon incorporates conductive fibers to provide rapid, continuous electrical discharge, suitable for high-static or sensitive electronic applications. Both materials enhance safety and functionality but differ in conductivity levels and typical usage scenarios.
Applications of Antistatic Nylon in Industry
Antistatic nylon is extensively used in the electronics and automotive industries to prevent static discharge that could damage sensitive components or ignite flammable materials. Its ability to dissipate static electricity makes it ideal for manufacturing protective clothing, conveyor belts, and packaging materials in cleanroom environments. The textile and packaging sectors also leverage antistatic nylon for enhanced safety and reliability in handling and transporting electronic devices.
Where Conductive Nylon Excels: Typical Use Cases
Conductive nylon excels in applications requiring efficient dissipation of static electricity, such as in electronic component housings, cleanroom environments, and automotive parts sensitive to electrostatic discharge. Its embedded conductive fibers provide superior grounding capabilities compared to antistatic nylon, making it ideal for industries like aerospace and electronics manufacturing. Conductive nylon also enhances safety by reducing the risk of static sparks in explosive or flammable atmospheres.
Performance Comparison: Antistatic vs Conductive Nylon
Antistatic nylon reduces static electricity buildup by incorporating additives that dissipate charges on the surface, making it suitable for environments requiring minimal static interference. Conductive nylon contains conductive fibers such as carbon or metal, allowing it to carry electrical current and offer superior grounding capabilities compared to antistatic variants. Performance comparison shows conductive nylon delivers enhanced electrical conductivity and durability in high-demand applications, while antistatic nylon excels in cost-effective, moderate static control scenarios.
Material Selection: Factors to Consider
When selecting between antistatic nylon and conductive nylon, key factors include electrical conductivity requirements, environmental conditions, and application sensitivity to static discharge. Antistatic nylon offers moderate static control by dissipating charge buildup, suitable for environments with low to medium static risks. Conductive nylon integrates conductive fibers for high conductivity, ideal for applications demanding rapid static discharge and robust electromagnetic interference shielding.
Cost Implications: Antistatic Versus Conductive Nylon
Antistatic nylon generally offers lower cost implications compared to conductive nylon due to simpler manufacturing processes and less expensive additives. Conductive nylon requires specialized conductive fillers such as carbon black or metal fibers, increasing raw material and production expenses significantly. Choosing between antistatic and conductive nylon depends on balancing budget constraints and performance needs for static dissipation.
Durability and Longevity: Which Nylon is Superior?
Antistatic nylon is engineered with additives that reduce static electricity buildup without compromising fiber strength, offering moderate durability suitable for various industrial applications. Conductive nylon incorporates conductive fillers like carbon or metal fibers, enhancing electrical conductivity but potentially impacting fiber flexibility and increasing wear over time. When comparing longevity, antistatic nylon generally provides superior durability due to its balanced properties, whereas conductive nylon may experience faster degradation in high-friction environments.
Making the Right Choice: Antistatic or Conductive Nylon
Antistatic nylon is engineered to prevent static electricity buildup by dissipating low levels of charge, ideal for environments sensitive to static discharge but not requiring full conductivity. Conductive nylon incorporates conductive fibers or coatings to provide a continuous electrical path, suitable for applications needing electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding or static grounding. Choosing between antistatic and conductive nylon depends on the specific electrostatic protection requirements, environmental conditions, and industry standards for safety and functionality.
Antistatic nylon vs Conductive nylon Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com