Nylon PA11 and Nylon PA12 are both durable, flexible materials commonly used in pet products such as collars and harnesses, with PA11 offering superior environmental sustainability due to its bio-based origins. PA11 exhibits higher impact resistance and better chemical resistance, making it ideal for outdoor and rugged pet accessories. PA12 provides excellent dimensional stability and moisture resistance, ensuring long-lasting performance in various weather conditions.
Table of Comparison
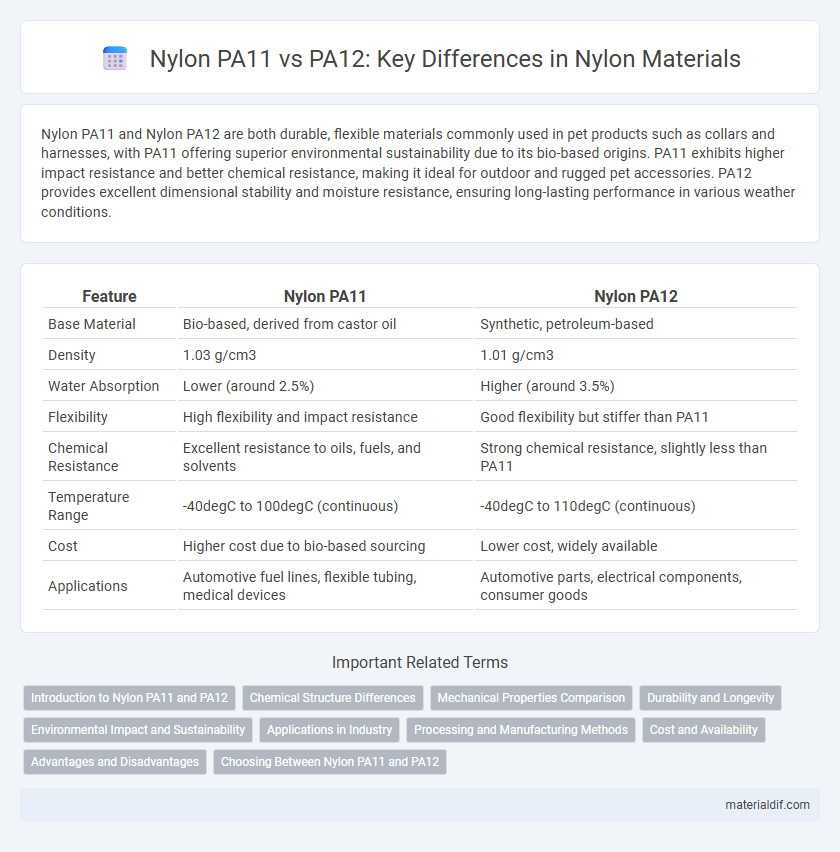
| Feature | Nylon PA11 | Nylon PA12 |
|---|---|---|
| Base Material | Bio-based, derived from castor oil | Synthetic, petroleum-based |
| Density | 1.03 g/cm3 | 1.01 g/cm3 |
| Water Absorption | Lower (around 2.5%) | Higher (around 3.5%) |
| Flexibility | High flexibility and impact resistance | Good flexibility but stiffer than PA11 |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and solvents | Strong chemical resistance, slightly less than PA11 |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 100degC (continuous) | -40degC to 110degC (continuous) |
| Cost | Higher cost due to bio-based sourcing | Lower cost, widely available |
| Applications | Automotive fuel lines, flexible tubing, medical devices | Automotive parts, electrical components, consumer goods |
Introduction to Nylon PA11 and PA12
Nylon PA11 and Nylon PA12 are both polyamide materials widely used in engineering applications due to their excellent mechanical properties and chemical resistance. Nylon PA11 is derived from renewable resources like castor oil, offering enhanced flexibility and impact resistance, making it suitable for automotive and aerospace industries. Nylon PA12, synthesized from petroleum, features lower moisture absorption and superior dimensional stability, favored in 3D printing and industrial manufacturing for precision parts.
Chemical Structure Differences
Nylon PA11 is derived from castor oil, featuring a longer aliphatic chain with 11 carbon atoms between amide groups, resulting in greater flexibility and impact resistance. Nylon PA12 contains 12 carbon atoms in its repeating unit, providing a slightly denser molecular structure that enhances chemical resistance and dimensional stability. These chemical structure differences influence their respective performance in applications requiring elasticity versus barrier properties.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Nylon PA11 offers higher impact resistance and better elongation at break compared to Nylon PA12, making it suitable for applications requiring flexibility and toughness. Nylon PA12 generally exhibits superior tensile strength and stiffness, providing enhanced load-bearing capacity and dimensional stability. Both materials demonstrate excellent chemical resistance, but PA12's mechanical properties make it favored in automotive and industrial parts demanding rigidity.
Durability and Longevity
Nylon PA11 offers enhanced flexibility and impact resistance, making it highly durable in dynamic applications, while Nylon PA12 provides superior chemical resistance and dimensional stability, contributing to longer service life in harsh environments. PA11's bio-based origin also delivers excellent fatigue resistance, ensuring prolonged usability under repeated stress. PA12 excels in maintaining mechanical properties over time, particularly in automotive and aerospace components where longevity is critical.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Nylon PA11 is derived from renewable resources such as castor oil, offering a lower carbon footprint compared to Nylon PA12, which is typically petroleum-based. PA11 demonstrates superior biodegradability and reduced environmental toxicity, making it a more sustainable choice for applications demanding eco-friendly materials. The production of PA11 generates fewer greenhouse gas emissions and relies less on fossil fuels, aligning with sustainability goals and circular economy principles.
Applications in Industry
Nylon PA11 is widely used in automotive and aerospace industries for fuel lines and flexible tubing due to its excellent chemical resistance and low moisture absorption. Nylon PA12 finds extensive applications in electrical and medical industries, favored for its superior dimensional stability and resistance to impact and abrasion. Both materials are crucial in 3D printing for producing durable, lightweight parts with tailored mechanical properties.
Processing and Manufacturing Methods
Nylon PA11 is derived from renewable castor oil and offers superior flexibility and impact resistance, making it well-suited for additive manufacturing techniques like selective laser sintering (SLS) and injection molding with lower processing temperatures around 190-220degC. Nylon PA12, synthesized from petrochemicals, is favored in industrial applications due to its higher density and dimensional stability, optimal for SLS and extrusion processes with processing temperatures near 210-230degC. Both materials require controlled drying before processing to prevent moisture absorption, but PA12's enhanced flow properties often result in faster cycle times and higher part accuracy in manufacturing.
Cost and Availability
Nylon PA11 typically costs more than Nylon PA12 due to its bio-based origin from castor oil, which offers better sustainability credentials but limits production scale. Nylon PA12 is more widely available and produced in larger volumes, resulting in lower prices and easier procurement across global markets. Both materials are popular in industrial applications, but PA12's cost-effectiveness and availability make it more common for cost-sensitive manufacturing.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Nylon PA11 offers superior flexibility, chemical resistance, and environmental friendliness due to its bio-based origin, making it ideal for applications in automotive and medical industries. Nylon PA12 provides higher moisture resistance, dimensional stability, and better low-temperature performance, which suits aerospace and industrial parts requiring consistent mechanical properties. However, PA11 tends to absorb more moisture leading to potential dimensional changes, while PA12's petrochemical base makes it less sustainable and slightly more expensive.
Choosing Between Nylon PA11 and PA12
Choosing between Nylon PA11 and PA12 depends on application-specific requirements such as flexibility, chemical resistance, and environmental impact. Nylon PA11, derived from renewable resources, offers superior flexibility and impact resistance ideal for automotive and sporting goods, while PA12 provides enhanced chemical resistance and dimensional stability suited for industrial and electrical components. Evaluating factors like mechanical performance, cost, and sustainability helps determine the optimal nylon type for manufacturing needs.
Nylon PA11 vs Nylon PA12 Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com