Heat-stabilized nylon offers enhanced resistance to high temperatures, making it ideal for applications requiring durability under thermal stress. Unlike standard nylon, it maintains its mechanical properties and dimensional stability when exposed to heat, reducing the risk of deformation or degradation. This improvement extends the lifespan and performance of finished products, especially in industrial and automotive settings.
Table of Comparison
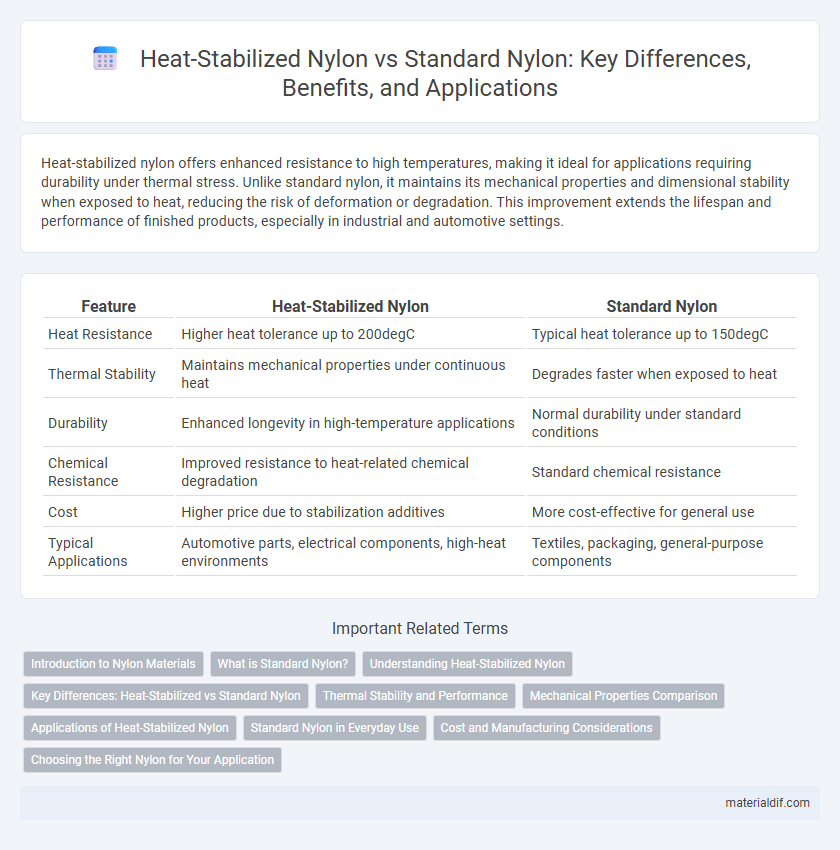
| Feature | Heat-Stabilized Nylon | Standard Nylon |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | Higher heat tolerance up to 200degC | Typical heat tolerance up to 150degC |
| Thermal Stability | Maintains mechanical properties under continuous heat | Degrades faster when exposed to heat |
| Durability | Enhanced longevity in high-temperature applications | Normal durability under standard conditions |
| Chemical Resistance | Improved resistance to heat-related chemical degradation | Standard chemical resistance |
| Cost | Higher price due to stabilization additives | More cost-effective for general use |
| Typical Applications | Automotive parts, electrical components, high-heat environments | Textiles, packaging, general-purpose components |
Introduction to Nylon Materials
Heat-stabilized nylon offers enhanced thermal resistance compared to standard nylon, making it suitable for applications involving elevated temperatures. Standard nylon, while durable and flexible, tends to degrade or lose mechanical properties under prolonged heat exposure. The improved heat stability in heat-stabilized nylon results from additives or modified polymer structures that prevent thermal decomposition.
What is Standard Nylon?
Standard nylon is a synthetic polymer widely used in textiles and engineering due to its strength, flexibility, and abrasion resistance. It typically exhibits moderate thermal stability, which can limit its performance in high-temperature applications where heat-stabilized variants are preferred. Standard nylon's properties include good chemical resistance and durability, making it suitable for everyday use but less effective under prolonged heat exposure.
Understanding Heat-Stabilized Nylon
Heat-stabilized nylon is engineered to withstand higher temperatures without degrading, making it ideal for applications requiring thermal resistance beyond standard nylon's limits. Unlike standard nylon, which softens and loses mechanical integrity when exposed to heat, heat-stabilized variants incorporate additives or modified polymers that enhance thermal stability. This improved heat resistance ensures longer service life and reliable performance in automotive, electrical, and industrial components exposed to elevated temperatures.
Key Differences: Heat-Stabilized vs Standard Nylon
Heat-stabilized nylon exhibits enhanced thermal resistance, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to 220degC, compared to standard nylon which typically degrades around 150degC. The improved heat stability of heat-stabilized nylon reduces deformation, discoloration, and loss of mechanical properties during prolonged exposure to elevated temperatures. Standard nylon is more prone to thermal degradation, limiting its use in high-heat applications such as automotive engine components and industrial machinery.
Thermal Stability and Performance
Heat-stabilized nylon exhibits enhanced thermal stability, maintaining its mechanical properties at temperatures up to 260degC, compared to standard nylon which typically degrades above 180degC. This improvement reduces thermal decomposition and yellowing, extending the material's lifespan in high-temperature applications such as automotive and electrical components. Consequently, heat-stabilized nylon delivers superior performance under thermal stress, ensuring reliability and durability in demanding environments.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Heat-stabilized nylon exhibits enhanced mechanical properties compared to standard nylon, including increased tensile strength and improved resistance to deformation at elevated temperatures. This stabilization process reduces thermal degradation, maintaining the polymer's flexibility and impact resistance under prolonged heat exposure. As a result, heat-stabilized nylon offers superior dimensional stability and durability in high-temperature applications.
Applications of Heat-Stabilized Nylon
Heat-stabilized nylon offers enhanced thermal resistance and reduced degradation at elevated temperatures, making it ideal for automotive under-the-hood components, electrical connectors, and industrial machinery parts exposed to continuous heat. Its improved dimensional stability and wear resistance extend the lifespan of components in aerospace and electronics, where standard nylon would fail. Industries requiring high-performance materials under thermal stress prioritize heat-stabilized nylon for reliable, long-term application.
Standard Nylon in Everyday Use
Standard nylon, known for its excellent strength and elasticity, is widely utilized in everyday applications such as textiles, packaging, and automotive parts. Its natural resistance to abrasion and chemicals makes it a practical choice for durable clothing, ropes, and gears without additional heat stabilization. However, standard nylon may degrade more quickly under prolonged exposure to high temperatures compared to heat-stabilized variants, limiting its use in extreme thermal environments.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Heat-stabilized nylon exhibits enhanced thermal resistance compared to standard nylon, allowing for higher processing temperatures and improved dimensional stability. Manufacturing costs for heat-stabilized nylon are typically higher due to specialized additives and more controlled production processes required to achieve its heat resistance. The increased material expense is often balanced by reduced product failure rates and extended service life in high-temperature applications.
Choosing the Right Nylon for Your Application
Heat-stabilized nylon offers enhanced resistance to high temperatures and reduced thermal degradation compared to standard nylon, making it ideal for applications requiring durability under heat stress. Standard nylon provides excellent mechanical properties and chemical resistance at lower cost but is more prone to deformation and brittleness when exposed to continuous elevated temperatures. Selecting the right nylon depends on your application's thermal demands, mechanical requirements, and exposure environment to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Heat-Stabilized Nylon vs Standard Nylon Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com