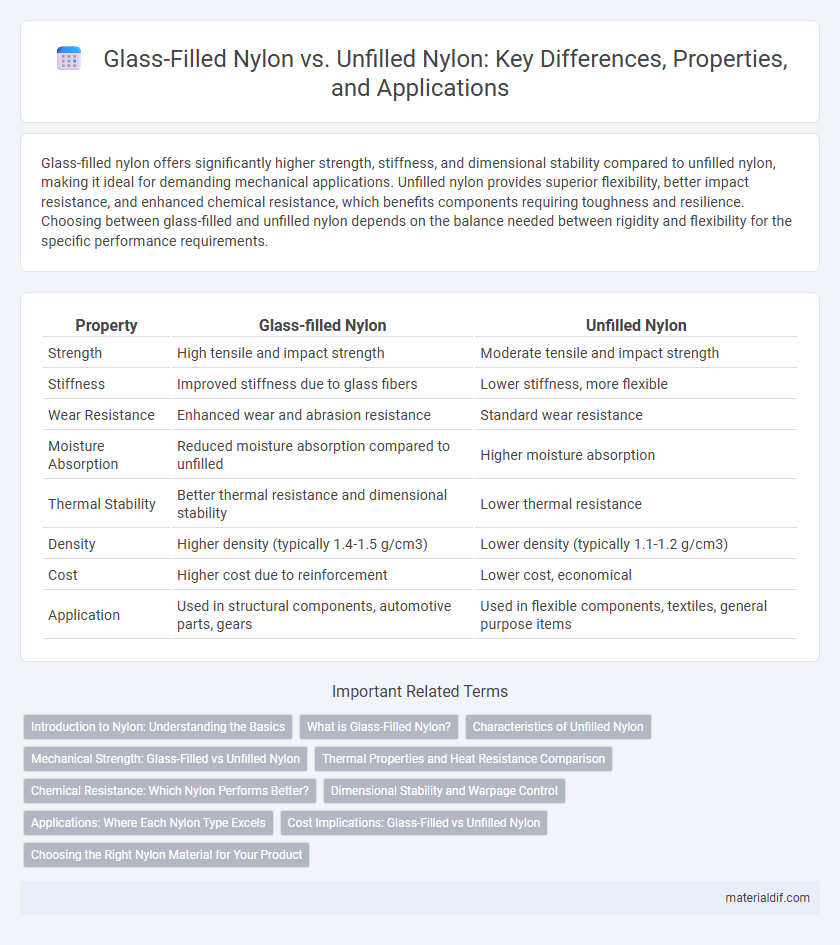
Glass-filled nylon offers significantly higher strength, stiffness, and dimensional stability compared to unfilled nylon, making it ideal for demanding mechanical applications. Unfilled nylon provides superior flexibility, better impact resistance, and enhanced chemical resistance, which benefits components requiring toughness and resilience. Choosing between glass-filled and unfilled nylon depends on the balance needed between rigidity and flexibility for the specific performance requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Glass-filled Nylon | Unfilled Nylon |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | High tensile and impact strength | Moderate tensile and impact strength |
| Stiffness | Improved stiffness due to glass fibers | Lower stiffness, more flexible |
| Wear Resistance | Enhanced wear and abrasion resistance | Standard wear resistance |
| Moisture Absorption | Reduced moisture absorption compared to unfilled | Higher moisture absorption |
| Thermal Stability | Better thermal resistance and dimensional stability | Lower thermal resistance |
| Density | Higher density (typically 1.4-1.5 g/cm3) | Lower density (typically 1.1-1.2 g/cm3) |
| Cost | Higher cost due to reinforcement | Lower cost, economical |
| Application | Used in structural components, automotive parts, gears | Used in flexible components, textiles, general purpose items |
Introduction to Nylon: Understanding the Basics
Glass-filled nylon is a composite material that combines nylon resin with glass fibers to enhance strength, stiffness, and dimensional stability compared to unfilled nylon, which consists purely of nylon polymer. Unfilled nylon offers excellent flexibility, chemical resistance, and impact absorption but struggles with higher mechanical loads and structural rigidity. Understanding these fundamental differences is crucial for selecting the right type of nylon for applications requiring varying degrees of durability and performance.
What is Glass-Filled Nylon?
Glass-filled nylon is a composite material made by incorporating glass fibers into nylon resin, significantly enhancing its mechanical properties. This reinforcement increases tensile strength, stiffness, and dimensional stability compared to unfilled nylon, making it ideal for demanding industrial applications. Glass-filled nylon also offers improved heat resistance and reduced moisture absorption, which contribute to its superior performance in engineering components.
Characteristics of Unfilled Nylon
Unfilled nylon exhibits exceptional flexibility and toughness, making it ideal for applications requiring impact resistance and wearability. Its lower density compared to glass-filled nylon results in lighter components but with reduced stiffness and dimensional stability. The material also offers excellent chemical resistance and electrical insulation properties, making it suitable for versatile industrial uses.
Mechanical Strength: Glass-Filled vs Unfilled Nylon
Glass-filled nylon exhibits significantly higher mechanical strength compared to unfilled nylon due to the incorporation of glass fibers that enhance rigidity and impact resistance. The addition of glass fibers improves tensile strength and stiffness, making glass-filled nylon ideal for demanding engineering applications. Unfilled nylon, while offering greater flexibility and toughness, lacks the reinforced mechanical properties needed for high-load structural components.
Thermal Properties and Heat Resistance Comparison
Glass-filled nylon exhibits significantly enhanced thermal properties compared to unfilled nylon, with a higher heat deflection temperature (HDT) typically around 200degC versus approximately 120degC for unfilled nylon. The addition of glass fibers improves heat resistance by reducing thermal expansion and increasing dimensional stability at elevated temperatures. This makes glass-filled nylon more suitable for applications requiring sustained mechanical strength under thermal stress.
Chemical Resistance: Which Nylon Performs Better?
Glass-filled nylon offers significantly enhanced chemical resistance compared to unfilled nylon due to its composite structure, which reduces the material's susceptibility to solvents, oils, and acids. Unfilled nylon is more prone to chemical degradation, swelling, and loss of mechanical properties when exposed to harsh chemicals, limiting its use in aggressive environments. The incorporation of glass fibers in glass-filled nylon improves dimensional stability and sustains chemical resistance, making it the preferred choice for applications requiring durability against chemical exposure.
Dimensional Stability and Warpage Control
Glass-filled nylon offers superior dimensional stability compared to unfilled nylon due to the embedded glass fibers that reduce thermal expansion and shrinkage during cooling. This reinforcement significantly minimizes warpage, making glass-filled nylon ideal for precision components requiring consistent shape retention. In contrast, unfilled nylon exhibits higher susceptibility to moisture absorption and thermal deformation, leading to greater dimensional variability and potential warpage in demanding applications.
Applications: Where Each Nylon Type Excels
Glass-filled nylon offers superior strength, stiffness, and dimensional stability, making it ideal for demanding applications such as automotive components, electrical insulators, and industrial machinery parts. Unfilled nylon provides excellent flexibility, low friction, and chemical resistance, which suits applications like gears, bearings, and consumer products requiring wear resistance and ease of fabrication. Selecting between glass-filled and unfilled nylon depends on the need for mechanical strength versus flexibility and impact resistance in the specific application.
Cost Implications: Glass-Filled vs Unfilled Nylon
Glass-filled nylon incurs higher material and processing costs due to the added glass fibers, which improve strength and thermal resistance but increase the price by approximately 30-50% compared to unfilled nylon. Unfilled nylon offers a more cost-effective option for applications with less demanding mechanical and thermal requirements, resulting in lower raw material and production expenses. Manufacturers must balance these cost implications against performance needs when selecting between glass-filled and unfilled nylon for industrial components.
Choosing the Right Nylon Material for Your Product
Glass-filled nylon offers enhanced strength, rigidity, and thermal stability compared to unfilled nylon, making it ideal for high-stress applications such as automotive components and industrial machinery. Unfilled nylon provides superior flexibility, chemical resistance, and lower cost, suitable for lightweight parts and applications requiring impact absorption or electrical insulation. Selecting the right nylon material depends on balancing mechanical requirements, environmental exposure, and cost considerations to ensure optimal product performance and durability.
Glass-filled Nylon vs Unfilled Nylon Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com