Nylon 11 offers superior flexibility and excellent chemical resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring durability under stress and exposure to harsh environments. Nylon 12 provides better impact resistance and dimensional stability, which is preferable for precision components and parts subject to mechanical wear. Both materials are lightweight and corrosion-resistant, but the choice depends on the specific performance requirements of the project.
Table of Comparison
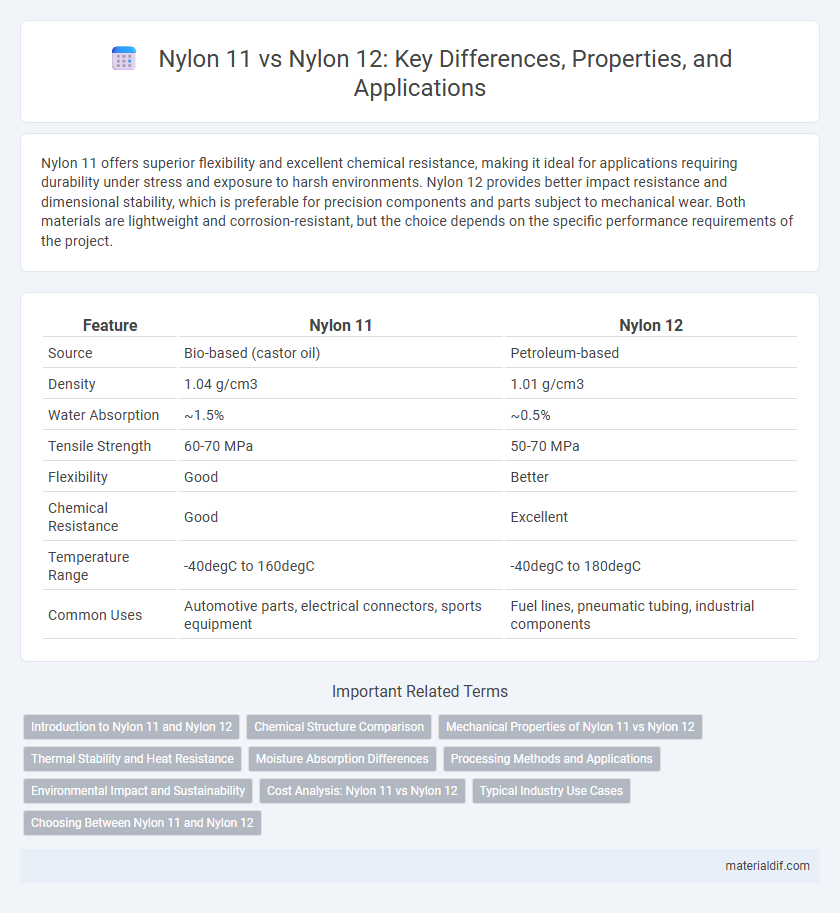
| Feature | Nylon 11 | Nylon 12 |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Bio-based (castor oil) | Petroleum-based |
| Density | 1.04 g/cm3 | 1.01 g/cm3 |
| Water Absorption | ~1.5% | ~0.5% |
| Tensile Strength | 60-70 MPa | 50-70 MPa |
| Flexibility | Good | Better |
| Chemical Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 160degC | -40degC to 180degC |
| Common Uses | Automotive parts, electrical connectors, sports equipment | Fuel lines, pneumatic tubing, industrial components |
Introduction to Nylon 11 and Nylon 12
Nylon 11 and Nylon 12 are both biopolyamides derived from renewable sources, primarily castor oil, offering eco-friendly alternatives to traditional petroleum-based nylons. Nylon 11 features higher rigidity and thermal resistance, making it suitable for applications requiring durability and heat stability such as automotive fuel lines and electrical cables. Nylon 12 provides greater flexibility and lower moisture absorption, advantageous for medical devices, flexible tubing, and protective coatings.
Chemical Structure Comparison
Nylon 11 and Nylon 12 are both polyamides derived from diamine and dicarboxylic acid monomers, differing primarily in the length of their carbon chains; Nylon 11 is synthesized from 11-carbon monomers, while Nylon 12 originates from 12-carbon monomers. This slight variation in chemical structure imparts Nylon 12 with enhanced flexibility, lower glass transition temperature, and better moisture resistance compared to Nylon 11. The additional methylene group in Nylon 12 reduces intermolecular hydrogen bonding strength, impacting crystallinity and mechanical performance relative to Nylon 11.
Mechanical Properties of Nylon 11 vs Nylon 12
Nylon 11 exhibits higher tensile strength and impact resistance compared to Nylon 12, making it more suitable for applications requiring durability under stress. Nylon 12 offers greater flexibility and elongation at break, providing enhanced fatigue resistance and improved performance in dynamic environments. Both polymers demonstrate excellent chemical resistance, but Nylon 11 maintains better dimensional stability under varying temperature conditions.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Nylon 11 exhibits superior thermal stability with a higher melting point around 185degC compared to Nylon 12's melting point of approximately 178degC, making it more suitable for applications with elevated temperature demands. Nylon 11's heat resistance allows it to maintain mechanical properties under prolonged exposure to heat, whereas Nylon 12 tends to soften faster under thermal stress. This makes Nylon 11 preferable in industries such as automotive and aerospace where consistent performance at higher temperatures is crucial.
Moisture Absorption Differences
Nylon 11 exhibits significantly lower moisture absorption compared to Nylon 12, typically absorbing around 1.5% water by weight after 24 hours, whereas Nylon 12 can absorb up to 2.5%. This difference in hygroscopic behavior impacts dimensional stability and mechanical properties in humid environments, making Nylon 11 more suitable for applications requiring consistent performance under moisture exposure. Lower water uptake in Nylon 11 results in reduced swelling and better retention of tensile strength, essential factors in automotive, electronics, and industrial uses.
Processing Methods and Applications
Nylon 11 and Nylon 12 differ primarily in their processing methods, with Nylon 11 commonly processed through injection molding and extrusion due to its renewable origin and flexibility, while Nylon 12 offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it suitable for advanced techniques like powder bed fusion and injection molding. Nylon 11 is widely used in automotive fuel lines, flexible tubing, and sports equipment, leveraging its excellent impact resistance and environmental sustainability. Nylon 12 finds extensive applications in aerospace, electronics, and medical devices, where precision molding and durability under harsh conditions are critical.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Nylon 11 is derived from renewable castor oil, making it more sustainable and environmentally friendly compared to Nylon 12, which is primarily petroleum-based. The biobased origin of Nylon 11 reduces carbon footprint and reliance on fossil fuels, contributing to lower greenhouse gas emissions during production. Both materials are recyclable, but Nylon 11's renewable feedstock positions it as a preferred choice in eco-conscious applications and sustainable product development.
Cost Analysis: Nylon 11 vs Nylon 12
Nylon 11 typically incurs higher raw material costs due to its bio-based origin from castor oil, making it more sustainable but pricier than Nylon 12, which is derived from petrochemicals. Manufacturing expenses for Nylon 12 are generally lower, benefiting from established large-scale production processes and economies of scale. When evaluating cost efficiency in applications such as automotive and sports equipment, Nylon 12 often presents a more budget-friendly option without significant compromises in mechanical performance.
Typical Industry Use Cases
Nylon 11 excels in automotive fuel lines, pneumatic tubing, and flexible cable sheathing due to its superior chemical resistance and low moisture absorption. Nylon 12 is preferred in electrical connectors, sports equipment, and industrial tubing for its excellent impact strength and dimensional stability at varying temperatures. Both nylons are widely utilized in 3D printing; however, Nylon 12 offers better warpage reduction, making it ideal for complex geometries.
Choosing Between Nylon 11 and Nylon 12
Nylon 11 offers superior impact resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for applications requiring durability under dynamic stress. Nylon 12 features lower moisture absorption and better chemical resistance, which suits environments exposed to harsh chemicals or moisture. Selecting between Nylon 11 and Nylon 12 depends on prioritizing mechanical toughness versus environmental resilience for optimal material performance.
Nylon 11 vs Nylon 12 Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com