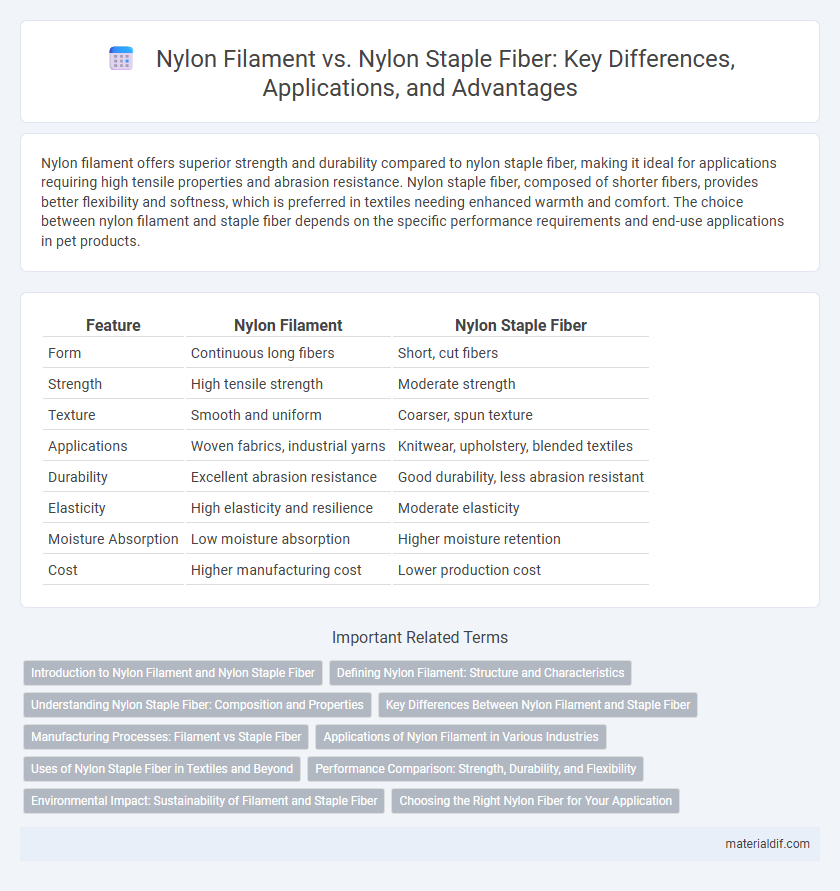
Nylon filament offers superior strength and durability compared to nylon staple fiber, making it ideal for applications requiring high tensile properties and abrasion resistance. Nylon staple fiber, composed of shorter fibers, provides better flexibility and softness, which is preferred in textiles needing enhanced warmth and comfort. The choice between nylon filament and staple fiber depends on the specific performance requirements and end-use applications in pet products.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Nylon Filament | Nylon Staple Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Continuous long fibers | Short, cut fibers |
| Strength | High tensile strength | Moderate strength |
| Texture | Smooth and uniform | Coarser, spun texture |
| Applications | Woven fabrics, industrial yarns | Knitwear, upholstery, blended textiles |
| Durability | Excellent abrasion resistance | Good durability, less abrasion resistant |
| Elasticity | High elasticity and resilience | Moderate elasticity |
| Moisture Absorption | Low moisture absorption | Higher moisture retention |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing cost | Lower production cost |
Introduction to Nylon Filament and Nylon Staple Fiber
Nylon filament consists of continuous, long fibers with uniform length, providing high strength, smooth texture, and excellent durability ideal for textile manufacturing and industrial applications. Nylon staple fiber is composed of short, cut fibers that resemble cotton or wool, offering versatility for spinning into yarns used in apparel, home textiles, and nonwoven fabrics. Both forms are derived from polyamide polymers but differ in fiber length and end-use performance characteristics.
Defining Nylon Filament: Structure and Characteristics
Nylon filament consists of long, continuous synthetic fibers characterized by high tensile strength, flexibility, and smooth surface texture, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and elasticity. These filaments are produced through a melt-spinning process that creates uniform fibers with fewer weak points compared to staple fibers. The continuous structure of nylon filament enhances its resistance to abrasion and contributes to superior performance in textiles, industrial uses, and high-performance materials.
Understanding Nylon Staple Fiber: Composition and Properties
Nylon staple fiber consists of short-length fibers typically measuring 1.5 to 8 inches, made primarily from polyamide polymers like Nylon 6 or Nylon 6,6. Its properties include excellent tensile strength, elasticity, abrasion resistance, and moisture absorbency, making it ideal for blends in textiles, carpets, and industrial fabrics. The shorter fiber length allows greater versatility in spinning processes, resulting in softer, more flexible yarns compared to continuous nylon filaments.
Key Differences Between Nylon Filament and Staple Fiber
Nylon filament consists of continuous long strands that provide superior strength, smooth texture, and high durability, making it ideal for applications requiring consistent tensile performance such as industrial fabrics and hosiery. Nylon staple fiber, composed of shorter fiber lengths, offers enhanced bulk, softness, and easier blending with other fibers, commonly used in textile applications like apparel and upholstery for increased comfort and flexibility. Key differences center on fiber length, resulting in distinct physical properties influencing their respective uses in manufacturing and end products.
Manufacturing Processes: Filament vs Staple Fiber
Nylon filament is produced through a continuous spinning process where molten polymer is extruded through fine spinnerets to form long, continuous fibers that offer high tensile strength and uniformity. Nylon staple fiber manufacturing involves cutting these filaments into short lengths, followed by processes such as carding and blending to create a fiber mass suitable for textile spinning. The filament process emphasizes continuous fiber length for applications requiring durability, while the staple fiber method enables versatility in fabric texture and softness due to the shorter fiber segments.
Applications of Nylon Filament in Various Industries
Nylon filament fibers are extensively used in the textile and automotive industries due to their high tensile strength, elasticity, and resistance to abrasion. These continuous filaments are ideal for producing durable fabrics for activewear, upholstery, and industrial conveyor belts. In the electronics sector, nylon filament is utilized for insulation materials and protective coatings due to its excellent thermal stability and electrical resistance.
Uses of Nylon Staple Fiber in Textiles and Beyond
Nylon Staple Fiber is commonly used in textiles for producing durable, versatile fabrics such as upholstery, carpets, and activewear due to its excellent abrasion resistance and elasticity. Beyond textiles, this fiber is utilized in nonwoven materials, industrial filters, and automotive components, where strength and resilience are critical. Its short fiber length allows for blending with natural fibers, enhancing fabric texture and performance in diverse applications.
Performance Comparison: Strength, Durability, and Flexibility
Nylon filament exhibits higher tensile strength and superior durability compared to nylon staple fiber, making it ideal for applications requiring long-lasting performance and resistance to abrasion. Staple fiber offers enhanced flexibility and softness, which benefits textile products needing comfort and pliability. Both materials maintain excellent resilience and moisture resistance, but filament's continuous form provides greater uniformity and mechanical integrity.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability of Filament and Staple Fiber
Nylon filament production generally consumes less energy and generates fewer emissions compared to nylon staple fiber due to its continuous fiber processing and reduced waste. Staple fibers often require more intensive mechanical and chemical treatments, increasing the carbon footprint and environmental impact. Sustainable advancements in nylon filament recycling and closed-loop manufacturing further enhance its eco-friendly profile compared to traditional staple fiber methods.
Choosing the Right Nylon Fiber for Your Application
Nylon filament offers superior strength, smooth texture, and consistent diameter, making it ideal for high-performance textiles, industrial applications, and durable fabrics requiring excellent abrasion resistance. Nylon staple fiber, composed of shorter fibers, provides better bulk, softness, and ease of blending, suitable for knitted garments, carpets, and nonwoven products where comfort and flexibility are priorities. Selecting the right nylon fiber depends on the specific requirements of strength, texture, and end-use performance for your application.
Nylon Filament vs Nylon Staple Fiber Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com