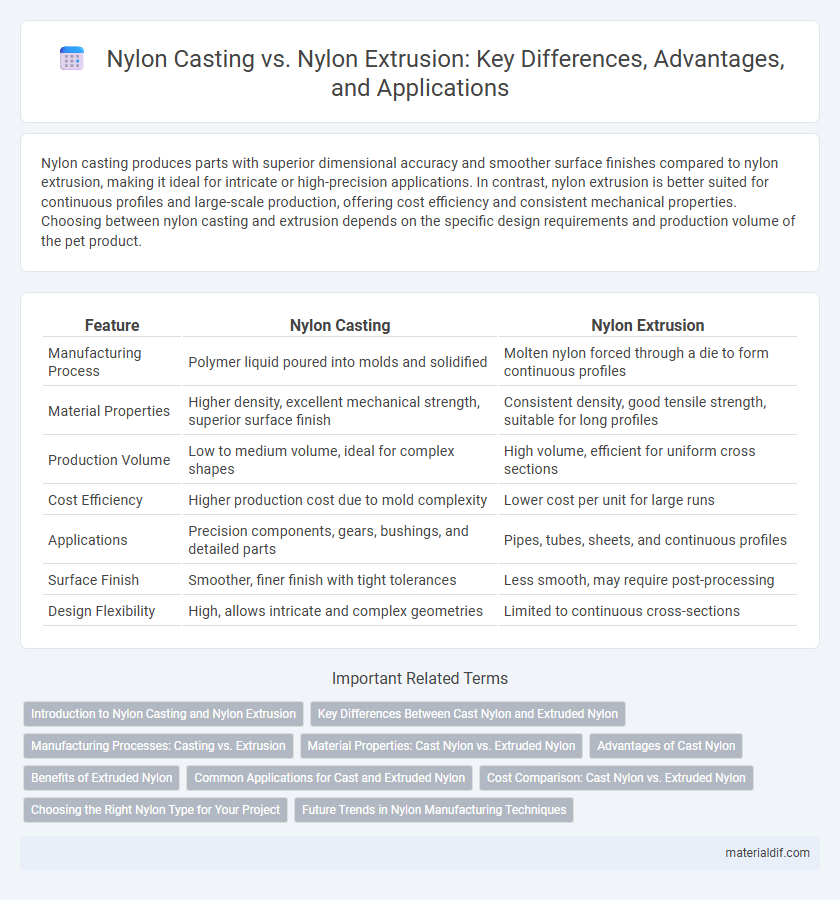
Nylon casting produces parts with superior dimensional accuracy and smoother surface finishes compared to nylon extrusion, making it ideal for intricate or high-precision applications. In contrast, nylon extrusion is better suited for continuous profiles and large-scale production, offering cost efficiency and consistent mechanical properties. Choosing between nylon casting and extrusion depends on the specific design requirements and production volume of the pet product.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Nylon Casting | Nylon Extrusion |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Polymer liquid poured into molds and solidified | Molten nylon forced through a die to form continuous profiles |
| Material Properties | Higher density, excellent mechanical strength, superior surface finish | Consistent density, good tensile strength, suitable for long profiles |
| Production Volume | Low to medium volume, ideal for complex shapes | High volume, efficient for uniform cross sections |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher production cost due to mold complexity | Lower cost per unit for large runs |
| Applications | Precision components, gears, bushings, and detailed parts | Pipes, tubes, sheets, and continuous profiles |
| Surface Finish | Smoother, finer finish with tight tolerances | Less smooth, may require post-processing |
| Design Flexibility | High, allows intricate and complex geometries | Limited to continuous cross-sections |
Introduction to Nylon Casting and Nylon Extrusion
Nylon casting involves pouring molten nylon into molds to create complex, high-precision shapes with excellent mechanical properties and surface finishes. Nylon extrusion pushes molten nylon through a die to produce continuous profiles such as rods, tubes, and sheets, offering efficient, high-volume production with consistent dimensions. Both methods utilize the thermoplastic nature of nylon but differ significantly in process output, mold complexity, and typical applications.
Key Differences Between Cast Nylon and Extruded Nylon
Cast nylon offers superior mechanical properties such as higher tensile strength and better wear resistance due to its slower cooling process and controlled manufacturing environment, while extruded nylon is produced continuously, allowing for longer lengths and consistent cross-sectional shapes but with slightly lower mechanical performance. Cast nylon typically exhibits better chemical resistance and lower moisture absorption compared to extruded nylon, making it suitable for demanding applications involving aggressive environments. Extruded nylon is favored for cost-effective production of standard profiles, while cast nylon is preferred for customized, high-performance components requiring enhanced durability.
Manufacturing Processes: Casting vs. Extrusion
Nylon casting involves pouring molten nylon into molds to create complex shapes with fine surface finishes, making it ideal for custom or intricate parts. Nylon extrusion pushes heated nylon through a die, producing continuous profiles such as rods, tubes, and sheets with consistent cross-sections suitable for high-volume production. The choice between casting and extrusion depends on part complexity, production volume, and desired mechanical properties.
Material Properties: Cast Nylon vs. Extruded Nylon
Cast nylon exhibits superior mechanical strength, higher wear resistance, and better machinability compared to extruded nylon due to its slower cooling process and reduced internal stresses. Extruded nylon offers more uniform molecular orientation, resulting in improved dimensional stability and consistent surface finish. Both materials maintain excellent chemical resistance and moderate moisture absorption, but cast nylon excels in impact resistance and load-bearing applications.
Advantages of Cast Nylon
Cast nylon offers superior mechanical properties compared to extruded nylon, including higher tensile strength, better impact resistance, and enhanced wear durability. Its seamless structure provides excellent dimensional stability and uniformity, reducing the risk of warping and internal stresses common in extrusion processes. Cast nylon also allows for more complex shapes with tighter tolerances, making it ideal for precision engineering applications.
Benefits of Extruded Nylon
Extruded nylon offers superior consistency in thickness and surface finish compared to cast nylon, ensuring higher precision for machining and assembly applications. This manufacturing method provides enhanced mechanical properties such as greater tensile strength and flexibility, making extruded nylon ideal for dynamic parts like gears, rollers, and bushings. Its improved dimensional stability and reduced internal stresses result in longer-lasting components with better resistance to wear and environmental factors.
Common Applications for Cast and Extruded Nylon
Cast nylon is widely used for heavy-duty applications such as industrial gears, bearings, and wear strips due to its superior strength and abrasion resistance. Extruded nylon is commonly applied in manufacturing tubing, sheets, and rods for lightweight mechanical components, structural parts, and consumer goods. Both cast and extruded nylon serve essential roles in automotive, electrical, and construction industries, with cast nylon favored for high-stress environments and extruded nylon preferred for precision shapes and consistent thickness.
Cost Comparison: Cast Nylon vs. Extruded Nylon
Cast nylon typically incurs higher production costs than extruded nylon due to its complex manufacturing process, which involves pouring molten nylon into molds and allowing it to solidify. Extruded nylon offers cost efficiency through a continuous process of melting and shaping, reducing labor and time expenses. For applications requiring intricate shapes and superior mechanical properties, the higher investment in cast nylon is often justified despite its elevated price point.
Choosing the Right Nylon Type for Your Project
Nylon casting provides superior mechanical strength and chemical resistance, ideal for complex, high-precision parts requiring durability. Nylon extrusion offers consistent dimensional accuracy and is cost-effective for producing long continuous profiles or sheets. Choosing the right nylon type depends on project requirements such as strength, flexibility, production volume, and budget constraints.
Future Trends in Nylon Manufacturing Techniques
Nylon casting offers precise control over complex geometries, enabling innovations in medical devices and microcomponents, while nylon extrusion remains dominant for high-volume applications like fibers and automotive parts due to cost-efficiency and scalability. Emerging trends in nylon manufacturing emphasize hybrid techniques combining casting and extrusion to enhance material properties and reduce production time. Advances in additive manufacturing and bio-based nylons are driving sustainable, customizable solutions, positioning nylon production for increased flexibility and environmental impact reduction.
Nylon casting vs Nylon extrusion Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com