Cast Nylon offers superior strength, abrasion resistance, and chemical resistance, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications, while Machined Nylon provides excellent dimensional stability and precision for intricate parts. Cast Nylon's homogenous structure enhances load-bearing capacity, whereas Machined Nylon excels in creating custom shapes with tight tolerances. Choosing between Cast and Machined Nylon depends on the specific mechanical requirements and manufacturing processes of the pet product.
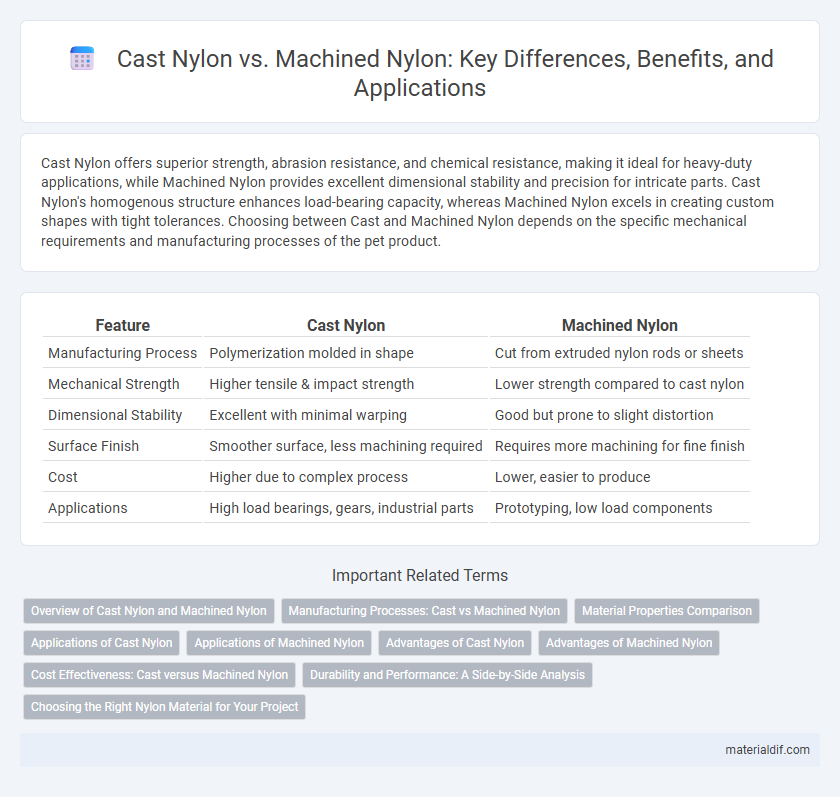
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cast Nylon | Machined Nylon |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Polymerization molded in shape | Cut from extruded nylon rods or sheets |
| Mechanical Strength | Higher tensile & impact strength | Lower strength compared to cast nylon |
| Dimensional Stability | Excellent with minimal warping | Good but prone to slight distortion |
| Surface Finish | Smoother surface, less machining required | Requires more machining for fine finish |
| Cost | Higher due to complex process | Lower, easier to produce |
| Applications | High load bearings, gears, industrial parts | Prototyping, low load components |
Overview of Cast Nylon and Machined Nylon
Cast Nylon, produced through a casting process, offers superior mechanical strength, excellent wear resistance, and a smooth surface finish ideal for precision applications. Machined Nylon, derived from extruded sheets or rods, allows for high dimensional accuracy and flexibility in custom shapes but may have slightly lower strength and wear resistance compared to cast variants. Both materials are widely used in industrial components, with Cast Nylon preferred for heavy-duty and high-performance parts while Machined Nylon suits detailed and custom-designed applications.
Manufacturing Processes: Cast vs Machined Nylon
Cast nylon is produced through a polymerization process where caprolactam monomers are cast into molds and heated to form solid, uniform sheets or blocks with excellent chemical and abrasion resistance. Machined nylon, by contrast, starts with pre-formed nylon rods or sheets, which are precisely cut, drilled, or shaped using CNC machines to achieve specific dimensions and intricate designs. The casting process allows for greater structural integrity and homogeneity, while machining offers enhanced customization and tighter tolerances for complex parts.
Material Properties Comparison
Cast nylon exhibits superior impact resistance, higher tensile strength, and better dimensional stability compared to machined nylon, making it ideal for heavy-load and wear-resistant applications. Machined nylon, derived from extruded sheets or rods, typically offers more consistent mechanical properties with tighter tolerances suitable for precision components. The material density and crystalline structure differences between cast and machined nylon significantly influence their thermal resistance and moisture absorption characteristics.
Applications of Cast Nylon
Cast Nylon excels in heavy-duty applications such as gears, wear pads, and bearings due to its superior impact resistance and dimensional stability under high stress. It is commonly used in automotive, industrial machinery, and conveyor systems where durability and resistance to abrasion are critical. This material's enhanced toughness makes it ideal for components subject to continuous mechanical wear and harsh environmental conditions.
Applications of Machined Nylon
Machined nylon excels in precision applications requiring tight tolerances and intricate shapes, making it ideal for custom gears, bushings, and wear-resistant components in automotive, aerospace, and industrial machinery. Its enhanced mechanical properties provide superior strength, durability, and dimensional stability compared to cast nylon, enabling use in high-load and high-speed environments. Industries benefit from machined nylon's adaptability in producing complex parts with consistent quality and long service life.
Advantages of Cast Nylon
Cast Nylon offers superior wear resistance and greater chemical stability compared to Machined Nylon, making it ideal for high-load and high-friction applications. Its denser molecular structure results in enhanced strength and lower moisture absorption, improving dimensional stability in varying environments. Cast Nylon also provides better surface finish and machining versatility, reducing post-processing time and costs.
Advantages of Machined Nylon
Machined nylon offers superior precision and consistency compared to cast nylon, making it ideal for applications requiring tight tolerances and intricate details. The machining process enhances mechanical properties such as strength and surface finish, resulting in components with better wear resistance and dimensional stability. Machined nylon parts also allow for greater customization and complex geometries, which are challenging to achieve with cast nylon.
Cost Effectiveness: Cast versus Machined Nylon
Cast nylon offers greater cost effectiveness for large production runs due to its low material waste and ability to form complex shapes without extensive machining. Machined nylon involves higher labor and tooling expenses, making it more suitable for prototyping or low-volume parts where precision customization is critical. Choosing cast nylon typically reduces overall manufacturing costs by minimizing post-processing and material loss compared to machined nylon components.
Durability and Performance: A Side-by-Side Analysis
Cast nylon exhibits superior durability and enhanced wear resistance compared to machined nylon due to its uniform molecular structure and reduced internal stresses. Machined nylon, while versatile and easier to customize, often experiences slightly diminished mechanical performance and can be more prone to surface imperfections. For high-load and high-wear applications, cast nylon provides better long-term performance and resistance to fatigue.
Choosing the Right Nylon Material for Your Project
Cast nylon offers superior strength, wear resistance, and dimensional stability, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications such as gears, bearings, and rollers. Machined nylon is better suited for precision components that require intricate detailing and tight tolerances, often used in custom parts and prototypes. Selecting the right nylon material depends on the specific mechanical demands and manufacturing processes of the project, ensuring optimized performance and longevity.
Cast Nylon vs Machined Nylon Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com