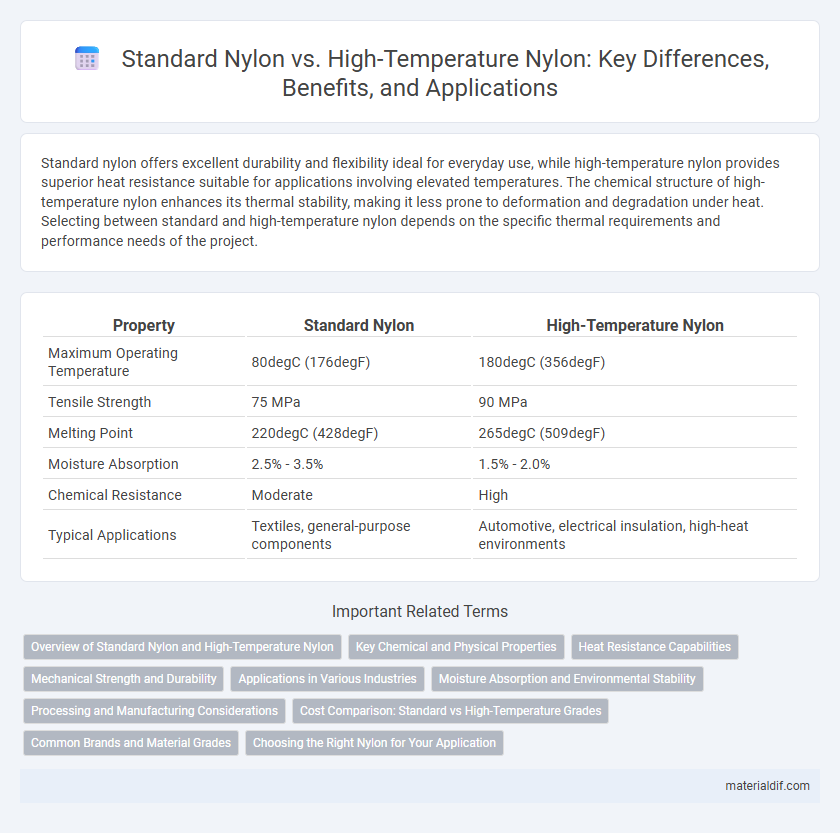
Standard nylon offers excellent durability and flexibility ideal for everyday use, while high-temperature nylon provides superior heat resistance suitable for applications involving elevated temperatures. The chemical structure of high-temperature nylon enhances its thermal stability, making it less prone to deformation and degradation under heat. Selecting between standard and high-temperature nylon depends on the specific thermal requirements and performance needs of the project.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Standard Nylon | High-Temperature Nylon |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Operating Temperature | 80degC (176degF) | 180degC (356degF) |
| Tensile Strength | 75 MPa | 90 MPa |
| Melting Point | 220degC (428degF) | 265degC (509degF) |
| Moisture Absorption | 2.5% - 3.5% | 1.5% - 2.0% |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Typical Applications | Textiles, general-purpose components | Automotive, electrical insulation, high-heat environments |
Overview of Standard Nylon and High-Temperature Nylon
Standard Nylon, commonly known as Nylon 6 or Nylon 6,6, offers excellent mechanical strength, flexibility, and abrasion resistance, making it suitable for general-purpose applications such as automotive parts, textiles, and consumer goods. High-Temperature Nylon variants, including Nylon 6T and Nylon 46, provide enhanced thermal stability, maintaining performance at elevated temperatures up to 200degC, which is critical in demanding environments like aerospace and electrical components. The chemical structure of high-temperature nylons features increased crystallinity and stronger hydrogen bonding, resulting in improved heat resistance and dimensional stability compared to standard nylon grades.
Key Chemical and Physical Properties
Standard nylon, primarily nylon 6 and 6,6, exhibits high tensile strength, excellent abrasion resistance, and good chemical stability, making it suitable for general-purpose applications. High-temperature nylon variants, such as nylon 46 and modified nylon 6, possess enhanced thermal stability with melting points exceeding 250degC, superior dimensional stability, and improved resistance to hydrolysis and oxidative degradation. The key chemical differences include molecular structure and crystallinity, which influence physical properties like thermal performance, mechanical strength, and resistance to environmental stressors.
Heat Resistance Capabilities
Standard nylon typically exhibits heat resistance up to around 120degC (248degF), making it suitable for general-purpose applications. High-temperature nylon variants, such as Nylon 46 or reinforced polyamides, endure continuous exposure to temperatures exceeding 180degC (356degF) without significant degradation. This enhanced thermal stability allows high-temperature nylon to perform reliably in demanding environments like automotive engine components and electrical connectors.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Standard nylon offers excellent mechanical strength and durability suitable for general applications, with tensile strength typically around 70 MPa. High-temperature nylon variants, such as nylon 6/6 or those reinforced with glass fibers, exhibit enhanced mechanical strength exceeding 90 MPa and maintain superior durability at elevated temperatures up to 180degC. These high-temperature nylons resist thermal degradation and retain structural integrity under sustained mechanical loads, making them ideal for demanding industrial environments.
Applications in Various Industries
Standard nylon, known for its excellent strength and flexibility, is widely used in automotive parts, consumer goods, and textile manufacturing where moderate temperature resistance suffices. High-temperature nylon variants, such as Nylon 6T or Nylon 46, offer enhanced thermal stability, making them ideal for aerospace components, electrical connectors, and industrial machinery exposed to elevated temperatures. These specialized nylons ensure durability and performance in demanding environments, significantly expanding their application range across industries.
Moisture Absorption and Environmental Stability
Standard nylon exhibits higher moisture absorption rates, typically around 2-3% at 50% relative humidity, leading to dimensional changes and reduced mechanical performance. High-temperature nylon variants, such as polyamide 46 or reinforced grades, demonstrate significantly improved environmental stability with lower moisture uptake and enhanced resistance to thermal degradation up to 200degC. This makes high-temperature nylon ideal for applications in humid or elevated temperature conditions where maintaining structural integrity is critical.
Processing and Manufacturing Considerations
Standard Nylon offers ease of processing with lower melting points around 220degC, making it suitable for injection molding and extrusion with conventional equipment. High-Temperature Nylon requires higher processing temperatures, typically above 300degC, necessitating specialized machinery and controlled environments to prevent thermal degradation. Moisture sensitivity is critical in both types, but High-Temperature Nylon demands more rigorous drying protocols to maintain mechanical properties during manufacturing.
Cost Comparison: Standard vs High-Temperature Grades
Standard nylon typically costs less due to its simpler manufacturing process and lower heat resistance properties. High-temperature nylon grades, such as Nylon 46 or reinforced variants, command higher prices because of enhanced thermal stability and superior mechanical performance under elevated temperatures. The cost difference reflects the added value in durability and application scope, making high-temperature nylon ideal for demanding industrial uses despite its premium price.
Common Brands and Material Grades
Standard nylon, often represented by common grades like Nylon 6 and Nylon 6/6, is widely manufactured by brands such as DuPont and BASF, offering balanced mechanical properties for general applications. High-temperature nylon variants, including brands like Vydyne from Solvay and Zytel HTN from DuPont, provide enhanced thermal resistance, suitable for demanding environments up to 260degC. Material grades in high-temperature nylons integrate heat-stabilizing additives and reinforced fibers, improving dimensional stability and durability under elevated temperatures.
Choosing the Right Nylon for Your Application
Standard nylon, typically nylon 6 or nylon 6/6, offers excellent mechanical properties and chemical resistance suitable for general-purpose applications, while high-temperature nylon grades, such as nylon 6T or nylon 46, provide enhanced thermal stability and dimensional integrity for demanding environments exceeding 200degC. Selecting the right nylon depends on factors like operating temperature, mechanical load, exposure to chemicals, and environmental conditions to ensure optimal performance and longevity. High-temperature nylons are ideal for automotive, aerospace, and industrial parts requiring sustained heat resistance, whereas standard nylons suffice for everyday consumer products and equipment with moderate thermal demands.
Standard Nylon vs High-Temperature Nylon Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com