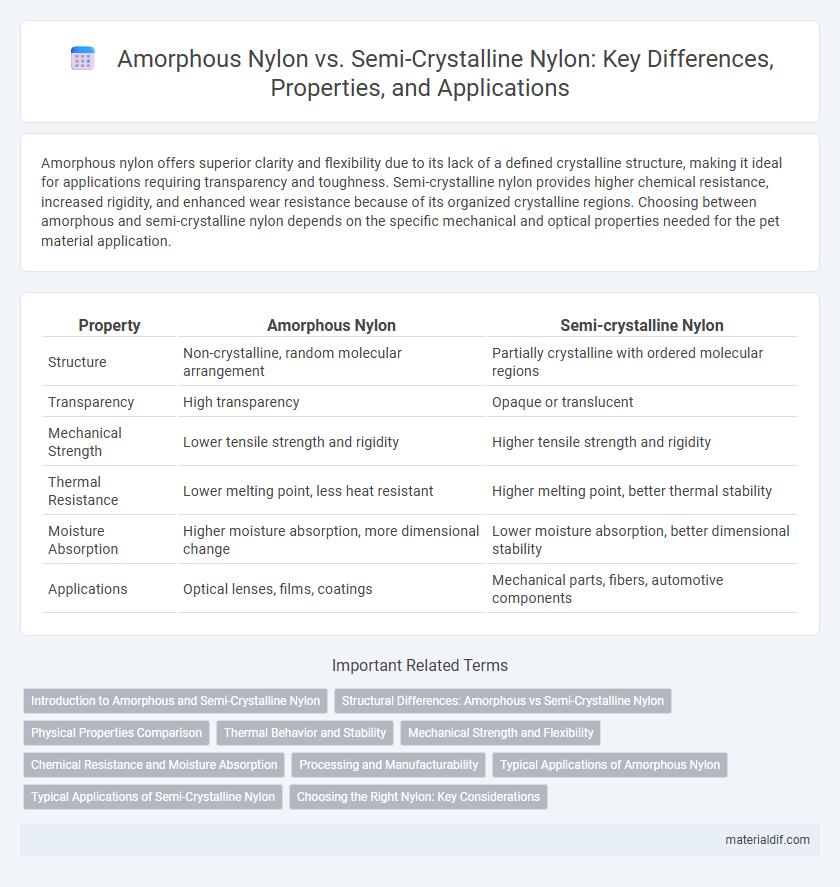
Amorphous nylon offers superior clarity and flexibility due to its lack of a defined crystalline structure, making it ideal for applications requiring transparency and toughness. Semi-crystalline nylon provides higher chemical resistance, increased rigidity, and enhanced wear resistance because of its organized crystalline regions. Choosing between amorphous and semi-crystalline nylon depends on the specific mechanical and optical properties needed for the pet material application.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Amorphous Nylon | Semi-crystalline Nylon |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Non-crystalline, random molecular arrangement | Partially crystalline with ordered molecular regions |
| Transparency | High transparency | Opaque or translucent |
| Mechanical Strength | Lower tensile strength and rigidity | Higher tensile strength and rigidity |
| Thermal Resistance | Lower melting point, less heat resistant | Higher melting point, better thermal stability |
| Moisture Absorption | Higher moisture absorption, more dimensional change | Lower moisture absorption, better dimensional stability |
| Applications | Optical lenses, films, coatings | Mechanical parts, fibers, automotive components |
Introduction to Amorphous and Semi-Crystalline Nylon
Amorphous nylon exhibits a random molecular arrangement, resulting in transparent, flexible materials with lower density and impact resistance compared to semi-crystalline nylon. Semi-crystalline nylon features ordered polymer chains, providing higher tensile strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability suitable for engineering applications. Understanding the differences in molecular structure helps optimize the selection of nylon types for specific performance requirements in automotive, electrical, and consumer goods industries.
Structural Differences: Amorphous vs Semi-Crystalline Nylon
Amorphous nylon lacks a well-defined crystalline structure, resulting in a random, disordered molecular arrangement that enhances transparency and impact resistance. Semi-crystalline nylon exhibits a highly ordered, tightly packed crystalline phase interspersed with amorphous regions, providing superior mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability. These structural differences influence the material's performance, with amorphous nylon favored for optical clarity and flexibility, while semi-crystalline nylon is preferred for durability and high-stress applications.
Physical Properties Comparison
Amorphous nylon exhibits lower density and higher impact resistance compared to semi-crystalline nylon, which features greater tensile strength and stiffness due to its ordered molecular structure. Semi-crystalline nylon's melting point ranges between 210degC and 260degC, offering superior thermal stability relative to the lower softening temperature found in amorphous variants. Moisture absorption is higher in amorphous nylon, influencing its dimensional stability, whereas semi-crystalline nylon maintains better resistance to wear and chemical exposure.
Thermal Behavior and Stability
Amorphous nylon exhibits lower thermal stability and a broader glass transition temperature (Tg) compared to semi-crystalline nylon, which has a well-defined melting point due to its ordered crystalline regions. The semi-crystalline structure enhances thermal resistance and dimensional stability under heat, making it suitable for high-temperature applications. In contrast, amorphous nylon's random molecular arrangement results in increased toughness but reduced resistance to thermal degradation.
Mechanical Strength and Flexibility
Amorphous nylon offers superior flexibility due to its random molecular structure, making it ideal for applications requiring high impact resistance and elasticity. Semi-crystalline nylon exhibits greater mechanical strength and rigidity because of its ordered crystalline regions, providing enhanced tensile strength and dimensional stability. Balancing flexibility and strength, semi-crystalline variants are preferred in load-bearing components, while amorphous types excel in dynamic, flexible parts.
Chemical Resistance and Moisture Absorption
Amorphous nylon exhibits lower crystallinity, resulting in higher moisture absorption and reduced chemical resistance compared to semi-crystalline nylon. Semi-crystalline nylon possesses a tightly packed molecular structure that enhances its resistance to chemicals such as acids and alkalis while minimizing water uptake. This makes semi-crystalline nylon preferable for applications requiring durability in harsh chemical environments and dimensional stability under humid conditions.
Processing and Manufacturability
Amorphous nylon exhibits superior clarity and flexibility, allowing easier molding and extrusion with faster cycle times due to its lower melting point and lack of crystalline structures. Semi-crystalline nylon offers enhanced mechanical strength and chemical resistance, requiring higher processing temperatures and precise cooling rates to achieve optimal crystallinity. Manufacturers often select amorphous nylon for applications demanding complex shapes and transparency, while semi-crystalline nylon suits components needing durability and wear resistance.
Typical Applications of Amorphous Nylon
Amorphous nylon is widely used in optical lenses, automotive fuel system components, and electrical insulation due to its transparency and excellent chemical resistance. Its non-crystalline structure ensures high impact strength and dimensional stability, making it suitable for applications requiring toughness and precision. Typical applications also include packaging films and flexible tubing where flexibility and clarity are critical.
Typical Applications of Semi-Crystalline Nylon
Semi-crystalline nylons are widely used in automotive parts, electrical connectors, and industrial machinery due to their high mechanical strength and excellent chemical resistance. Their semi-crystalline structure provides superior toughness, thermal stability, and wear resistance, making them suitable for gears, bearings, and fuel system components. These properties enable semi-crystalline nylons to perform effectively in demanding environments requiring durability and dimensional stability.
Choosing the Right Nylon: Key Considerations
Amorphous nylon offers superior transparency and impact resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring optical clarity and toughness, while semi-crystalline nylon provides higher stiffness, chemical resistance, and thermal stability suitable for structural components. Factors such as mechanical requirements, environmental exposure, and processing methods guide the selection between amorphous and semi-crystalline types. Evaluating properties like crystallinity level, moisture absorption, and dimensional stability ensures optimal performance tailored to specific industrial needs.
Amorphous nylon vs Semi-crystalline nylon Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com