Nylon 12 offers superior flexibility and lower moisture absorption compared to Nylon 6, making it ideal for applications requiring durable yet lightweight materials. Nylon 6 provides higher strength and stiffness, with better thermal resistance, suited for demanding engineering parts. Choosing between Nylon 12 and Nylon 6 depends on the balance needed between flexibility, mechanical performance, and environmental resistance.
Table of Comparison
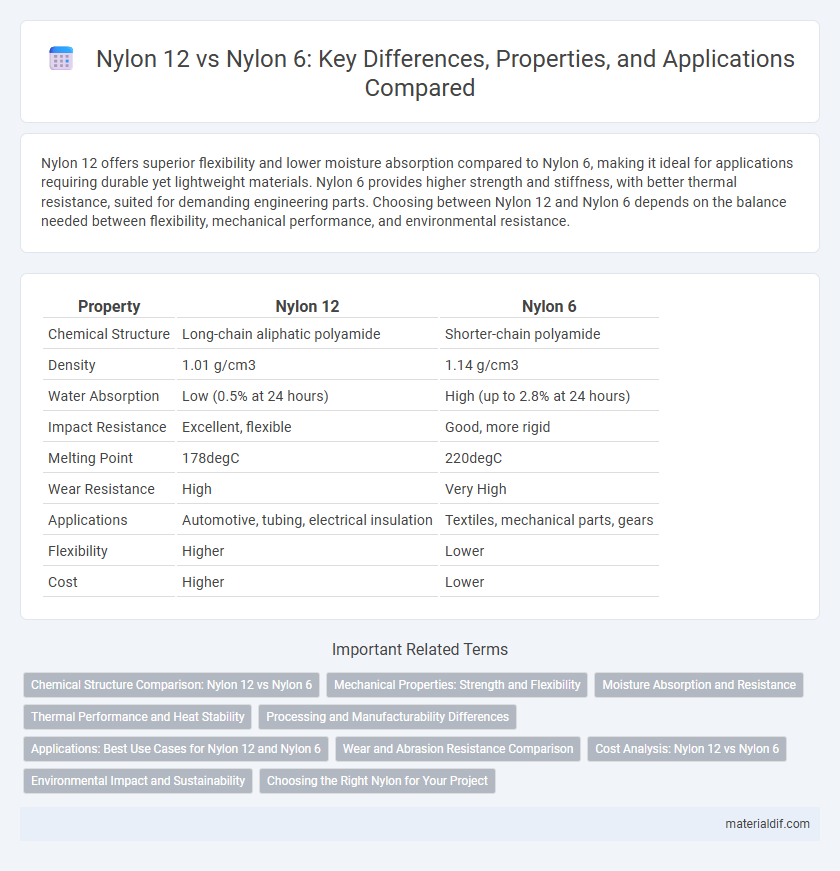
| Property | Nylon 12 | Nylon 6 |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | Long-chain aliphatic polyamide | Shorter-chain polyamide |
| Density | 1.01 g/cm3 | 1.14 g/cm3 |
| Water Absorption | Low (0.5% at 24 hours) | High (up to 2.8% at 24 hours) |
| Impact Resistance | Excellent, flexible | Good, more rigid |
| Melting Point | 178degC | 220degC |
| Wear Resistance | High | Very High |
| Applications | Automotive, tubing, electrical insulation | Textiles, mechanical parts, gears |
| Flexibility | Higher | Lower |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Chemical Structure Comparison: Nylon 12 vs Nylon 6
Nylon 12 and Nylon 6 differ significantly in chemical structure, where Nylon 12 contains 12 carbon atoms in its monomer unit derived from laurolactam, resulting in a more flexible and lower density polymer chain. In contrast, Nylon 6 is synthesized from caprolactam with 6 carbon atoms, producing a more crystalline and higher melting temperature polymer. These structural variations impact their mechanical properties, with Nylon 12 offering enhanced impact resistance and chemical resistance compared to the more rigid Nylon 6.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Flexibility
Nylon 12 exhibits lower tensile strength but higher flexibility compared to Nylon 6, making it ideal for applications requiring impact resistance and elongation. Nylon 6 offers superior tensile strength and rigidity, suitable for structural components needing high load-bearing capacity. The choice between Nylon 12 and Nylon 6 depends on balancing strength and flexibility requirements in engineering designs.
Moisture Absorption and Resistance
Nylon 12 exhibits significantly lower moisture absorption compared to Nylon 6, with levels around 0.5% versus 2-3%, enhancing its dimensional stability and mechanical properties in humid environments. Nylon 12's superior resistance to water uptake reduces swelling and maintains toughness over time, making it ideal for demanding applications requiring consistent performance. In contrast, Nylon 6 absorbs more moisture, which can lead to dimensional changes and decreased strength under prolonged exposure to moisture.
Thermal Performance and Heat Stability
Nylon 12 exhibits superior thermal performance compared to Nylon 6, with a higher melting temperature around 178degC versus 220degC for Nylon 6, but Nylon 6 offers greater heat stability under prolonged exposure to elevated temperatures. Nylon 12's lower glass transition temperature and enhanced flexibility result in better dimensional stability in varying thermal environments, making it ideal for applications requiring resistance to thermal cycling and impact. Nylon 6, with its higher crystallinity and heat resistance, excels in high-temperature applications demanding long-term mechanical strength and structural integrity.
Processing and Manufacturability Differences
Nylon 12 offers lower moisture absorption and better chemical resistance compared to Nylon 6, enhancing its dimensional stability during processing and reducing the risk of hydrolytic degradation in manufacturing. It processes at lower temperatures, which minimizes thermal degradation and improves energy efficiency, whereas Nylon 6 requires higher processing temperatures and more drying time to avoid mold defects. The reduced shrinkage and improved flow properties of Nylon 12 enable easier injection molding and more precise tolerances in complex parts compared to Nylon 6.
Applications: Best Use Cases for Nylon 12 and Nylon 6
Nylon 12 excels in applications requiring low moisture absorption, chemical resistance, and flexibility, making it ideal for automotive fuel lines, flexible tubing, and electrical cable jackets. Nylon 6 offers superior strength, wear resistance, and thermal stability, commonly used in gears, bearings, and industrial machinery components. Choosing between Nylon 12 and Nylon 6 depends on specific requirements such as environmental exposure, mechanical stress, and flexibility needs.
Wear and Abrasion Resistance Comparison
Nylon 12 exhibits superior wear and abrasion resistance compared to Nylon 6, attributed to its lower moisture absorption and greater flexibility. The denser molecular structure of Nylon 6 increases its hardness but also makes it more susceptible to surface wear under friction. For applications requiring enhanced durability and reduced material degradation, Nylon 12 generally outperforms Nylon 6 in maintaining integrity during prolonged abrasive conditions.
Cost Analysis: Nylon 12 vs Nylon 6
Nylon 12 generally incurs higher production costs compared to Nylon 6 due to its more complex polymerization process and raw material expenses. While Nylon 6 offers cost efficiency through widespread availability and mature manufacturing techniques, Nylon 12 provides superior chemical resistance and flexibility justifying its premium price in specialized applications. Evaluating the total cost of ownership requires balancing Nylon 12's enhanced performance properties against Nylon 6's affordability for high-volume industrial use.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Nylon 12 demonstrates a lower environmental footprint than Nylon 6 due to its reduced energy consumption and lower greenhouse gas emissions during production. Biobased sources for Nylon 12 contribute to improved sustainability, whereas Nylon 6 relies primarily on petroleum-derived raw materials. The enhanced recyclability and longer lifecycle of Nylon 12 further promote eco-friendly applications in industries aiming to reduce plastic waste.
Choosing the Right Nylon for Your Project
Nylon 12 offers excellent chemical resistance and low moisture absorption, making it ideal for applications requiring dimensional stability and flexibility. Nylon 6 provides higher strength and rigidity, suitable for parts subjected to mechanical stress and impact. Selecting between Nylon 12 and Nylon 6 depends on project requirements such as environmental exposure, mechanical load, and desired durability.
Nylon 12 vs Nylon 6 Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com