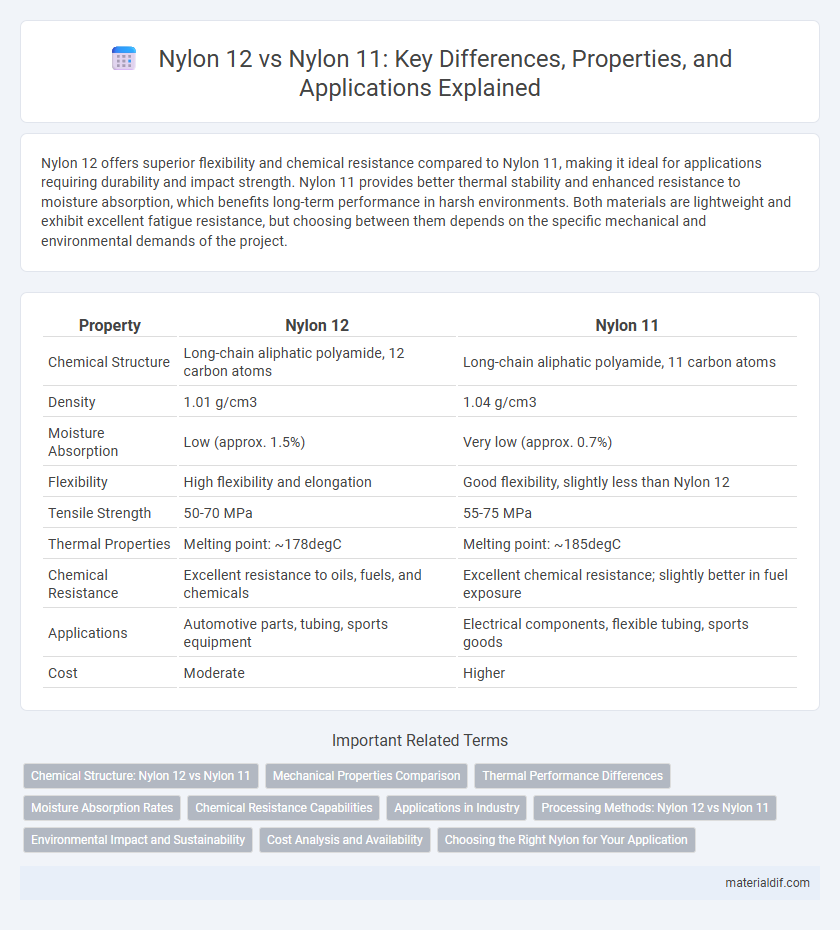
Nylon 12 offers superior flexibility and chemical resistance compared to Nylon 11, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and impact strength. Nylon 11 provides better thermal stability and enhanced resistance to moisture absorption, which benefits long-term performance in harsh environments. Both materials are lightweight and exhibit excellent fatigue resistance, but choosing between them depends on the specific mechanical and environmental demands of the project.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nylon 12 | Nylon 11 |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | Long-chain aliphatic polyamide, 12 carbon atoms | Long-chain aliphatic polyamide, 11 carbon atoms |
| Density | 1.01 g/cm3 | 1.04 g/cm3 |
| Moisture Absorption | Low (approx. 1.5%) | Very low (approx. 0.7%) |
| Flexibility | High flexibility and elongation | Good flexibility, slightly less than Nylon 12 |
| Tensile Strength | 50-70 MPa | 55-75 MPa |
| Thermal Properties | Melting point: ~178degC | Melting point: ~185degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals | Excellent chemical resistance; slightly better in fuel exposure |
| Applications | Automotive parts, tubing, sports equipment | Electrical components, flexible tubing, sports goods |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher |
Chemical Structure: Nylon 12 vs Nylon 11
Nylon 12 and Nylon 11 are polyamides with distinct monomer origins influencing their chemical structure; Nylon 12 is synthesized from laurolactam derived from petroleum, featuring a 12-carbon chain that imparts flexibility and chemical resistance. Nylon 11, sourced from 11-aminoundecanoic acid obtained from castor oil, contains an 11-carbon chain contributing to its biobased nature and enhanced environmental sustainability. The difference in carbon chain length affects properties such as moisture absorption, with Nylon 12 exhibiting lower water uptake and improved dimensional stability compared to Nylon 11.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Nylon 12 exhibits higher impact resistance and better flexibility compared to Nylon 11, making it ideal for applications requiring durability under stress. Nylon 11 offers superior tensile strength and a higher melting point, which enhances its performance in high-temperature environments. Both materials demonstrate excellent chemical resistance and low moisture absorption, but Nylon 12's lower density contributes to lighter, more flexible components.
Thermal Performance Differences
Nylon 12 exhibits superior thermal stability with a higher melting point around 178degC compared to Nylon 11's melting point near 190degC, making Nylon 11 better suited for applications requiring elevated temperature resistance. Nylon 11 offers enhanced heat deflection temperature and improved durability under prolonged thermal stress, while Nylon 12 provides better dimensional stability at moderate temperatures. These characteristics influence their selection in industries like automotive and aerospace, where temperature performance is critical.
Moisture Absorption Rates
Nylon 12 exhibits significantly lower moisture absorption rates compared to Nylon 11, making it more suitable for applications requiring dimensional stability in humid environments. While Nylon 11 absorbs around 1.6% moisture after 24 hours, Nylon 12 absorbs less than 0.5%, reducing swelling and mechanical property degradation. This characteristic enhances Nylon 12's performance in automotive and medical device industries where moisture resistance is critical.
Chemical Resistance Capabilities
Nylon 12 offers superior chemical resistance compared to Nylon 11, particularly against oils, fuels, and solvents, making it ideal for automotive and industrial applications. Its lower moisture absorption also enhances resistance to hydrolysis and dimensional stability in aggressive environments. Nylon 11, while slightly less resistant, provides excellent performance in moderate chemical exposure and is valued for its flexibility and impact strength.
Applications in Industry
Nylon 12 offers excellent chemical resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for automotive fuel lines, industrial tubing, and electrical insulation applications. Nylon 11, derived from renewable castor oil, is favored in medical devices, flexible pneumatic tubing, and corrosion-resistant industrial components due to its biocompatibility and durability. Both materials serve critical roles in aerospace, sports equipment, and consumer goods, with Nylon 12 excelling in environments requiring low moisture absorption and Nylon 11 preferred for sustainable, high-performance uses.
Processing Methods: Nylon 12 vs Nylon 11
Nylon 12 and Nylon 11 differ notably in processing methods, where Nylon 12 excels in injection molding due to its lower melting point and superior flow characteristics, enabling quicker cycle times and finer detail in parts. Nylon 11, derived from renewable sources, is preferred in extrusion and blow molding processes because of its higher thermal stability and impact resistance, making it ideal for flexible tubing and films. Both materials are also compatible with advanced techniques like 3D printing, but Nylon 12's enhanced printability supports more intricate and durable prototypes.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Nylon 12, derived from laurolactam, offers greater chemical resistance and durability but relies more heavily on petrochemical sources compared to Nylon 11, which is synthesized from castor oil, a renewable resource. Nylon 11's bio-based origin significantly reduces carbon footprint and enhances biodegradability, making it a more sustainable choice for eco-conscious applications. The environmental impact of Nylon 12 is higher due to its fossil fuel dependency and lower recyclability in comparison to the greener profile of Nylon 11.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Nylon 12 generally offers better cost efficiency due to its lower raw material and processing expenses compared to Nylon 11, making it a preferred choice for budget-sensitive applications. Nylon 11 is typically more expensive because it is derived from renewable resources, resulting in higher production costs and limited large-scale availability. Despite its higher price, Nylon 11 is favored in specialized industries requiring superior chemical resistance and biocompatibility, but Nylon 12's broader availability supports more widespread industrial use.
Choosing the Right Nylon for Your Application
Nylon 12 offers superior flexibility, chemical resistance, and low moisture absorption, making it ideal for automotive and consumer electronics applications requiring durability and dimensional stability. Nylon 11, derived from renewable sources, provides excellent impact resistance and better performance in low-temperature environments, thus preferred in medical devices and sports equipment. Selecting between Nylon 11 and Nylon 12 depends on application-specific factors such as mechanical requirements, environmental exposure, and sustainability priorities.
Nylon 12 vs Nylon 11 Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com