Nylon PA6 offers higher tensile strength and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications and parts requiring durability. Nylon PA12 provides superior flexibility, chemical resistance, and lower moisture absorption, which enhances dimensional stability in humid environments. Selecting between PA6 and PA12 depends on the specific requirements for mechanical strength versus environmental resilience in nylon pet components.
Table of Comparison
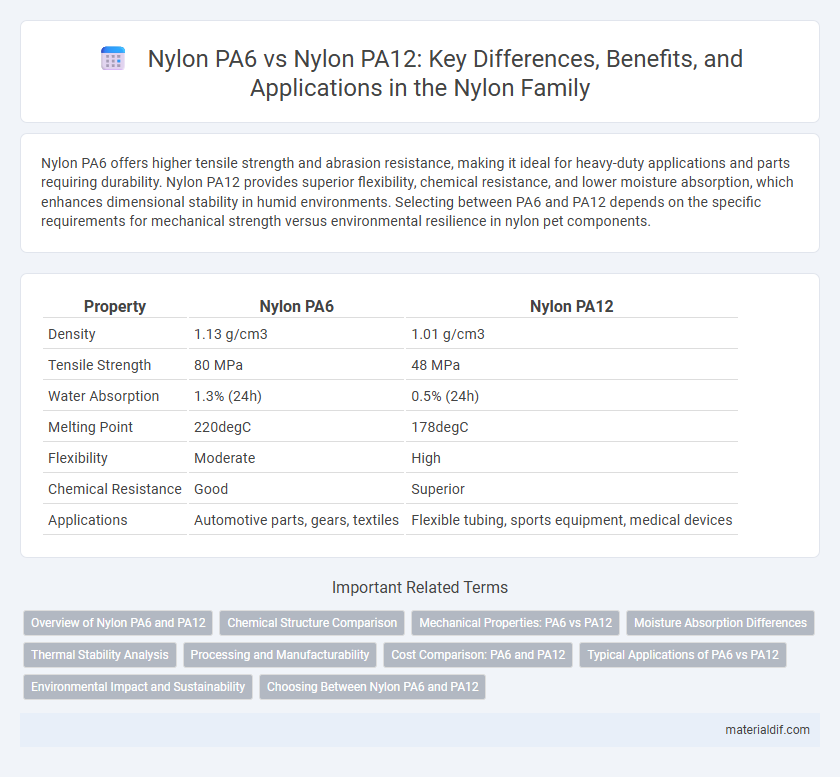
| Property | Nylon PA6 | Nylon PA12 |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 1.13 g/cm3 | 1.01 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 80 MPa | 48 MPa |
| Water Absorption | 1.3% (24h) | 0.5% (24h) |
| Melting Point | 220degC | 178degC |
| Flexibility | Moderate | High |
| Chemical Resistance | Good | Superior |
| Applications | Automotive parts, gears, textiles | Flexible tubing, sports equipment, medical devices |
Overview of Nylon PA6 and PA12
Nylon PA6 offers high tensile strength, excellent abrasion resistance, and superior mechanical properties, making it suitable for automotive and industrial applications. Nylon PA12 demonstrates enhanced chemical resistance, lower moisture absorption, and greater flexibility, often preferred for fuel lines and flexible tubing. Both materials provide durable performance but differ in processing characteristics and environmental resilience.
Chemical Structure Comparison
Nylon PA6 is a polyamide made from caprolactam with a repeating unit containing six carbon atoms, featuring amide groups that provide high strength and rigidity. Nylon PA12 consists of longer aliphatic chains with twelve carbon atoms between amide groups, resulting in greater flexibility and lower moisture absorption compared to PA6. The shorter chain length in PA6 leads to a more crystalline structure, while the extended chains in PA12 yield improved impact resistance and dimensional stability.
Mechanical Properties: PA6 vs PA12
Nylon PA6 exhibits higher tensile strength and rigidity, making it suitable for applications requiring enhanced mechanical durability and resistance to wear. Nylon PA12 offers greater flexibility and impact resistance, with superior elongation at break and better resistance to fatigue and chemicals. PA6 typically outperforms PA12 in hardness and heat resistance, while PA12 excels in dimensional stability and low moisture absorption, influencing long-term mechanical performance.
Moisture Absorption Differences
Nylon PA6 typically exhibits higher moisture absorption rates, around 2.5% to 3.5%, compared to Nylon PA12, which absorbs significantly less moisture, usually below 0.7%. This difference in moisture absorption influences dimensional stability, with Nylon PA12 maintaining better mechanical properties and less swelling in humid environments. Engineers often select Nylon PA12 for applications requiring superior moisture resistance and consistent performance.
Thermal Stability Analysis
Nylon PA6 exhibits higher melting temperatures around 220degC compared to Nylon PA12, which melts near 178degC, indicating superior thermal stability for PA6 in high-temperature applications. PA6 demonstrates greater resistance to thermal degradation and dimensional changes under continuous heat exposure, essential for mechanical parts subjected to harsh environments. Conversely, Nylon PA12 offers enhanced flexibility and lower moisture absorption but compromises on heat resistance relative to PA6.
Processing and Manufacturability
Nylon PA6 offers superior abrasion resistance and higher tensile strength, making it ideal for injection molding processes that require durability and precision. Nylon PA12 provides excellent flexibility and lower moisture absorption, which enhances its performance in extrusion and additive manufacturing techniques. Both materials exhibit good thermal stability, but PA12's lower melting point allows for easier processing and faster cycle times in manufacturing applications.
Cost Comparison: PA6 and PA12
Nylon PA6 typically costs less than Nylon PA12 due to its more straightforward manufacturing process and widespread availability, making it a cost-effective choice for many applications. PA12, while more expensive, offers superior chemical resistance and flexibility, which can justify its higher price in specialized uses. Cost differences between PA6 and PA12 are influenced by factors such as raw material prices, production complexity, and performance requirements.
Typical Applications of PA6 vs PA12
Nylon PA6 is widely used in automotive components, electrical connectors, and industrial machinery parts due to its high strength, rigidity, and good abrasion resistance. Nylon PA12 excels in flexible tubing, medical devices, and fuel lines thanks to its excellent chemical resistance, low moisture absorption, and flexibility. Both materials are chosen based on specific requirements for durability and environmental resistance in their respective applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Nylon PA6 generally has a higher environmental impact due to its production process relying on petroleum-based raw materials and higher energy consumption, while Nylon PA12 offers improved sustainability through lower greenhouse gas emissions and better recyclability. PA12's resistance to hydrolysis and chemicals extends product lifespan, reducing waste and the frequency of replacement. Innovations in bio-based feedstocks for PA12 further enhance its eco-friendly profile compared to traditional PA6.
Choosing Between Nylon PA6 and PA12
Nylon PA6 offers higher tensile strength and wear resistance, making it ideal for mechanical parts under stress, while Nylon PA12 provides superior flexibility, chemical resistance, and lower moisture absorption suited for fluid handling and automotive applications. PA6 typically has a higher melting point around 220degC compared to PA12's approximately 178degC, impacting processing conditions and thermal stability. Selecting between PA6 and PA12 depends on specific application requirements such as mechanical load, environmental exposure, and desired durability.
Nylon PA6 vs Nylon PA12 Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com