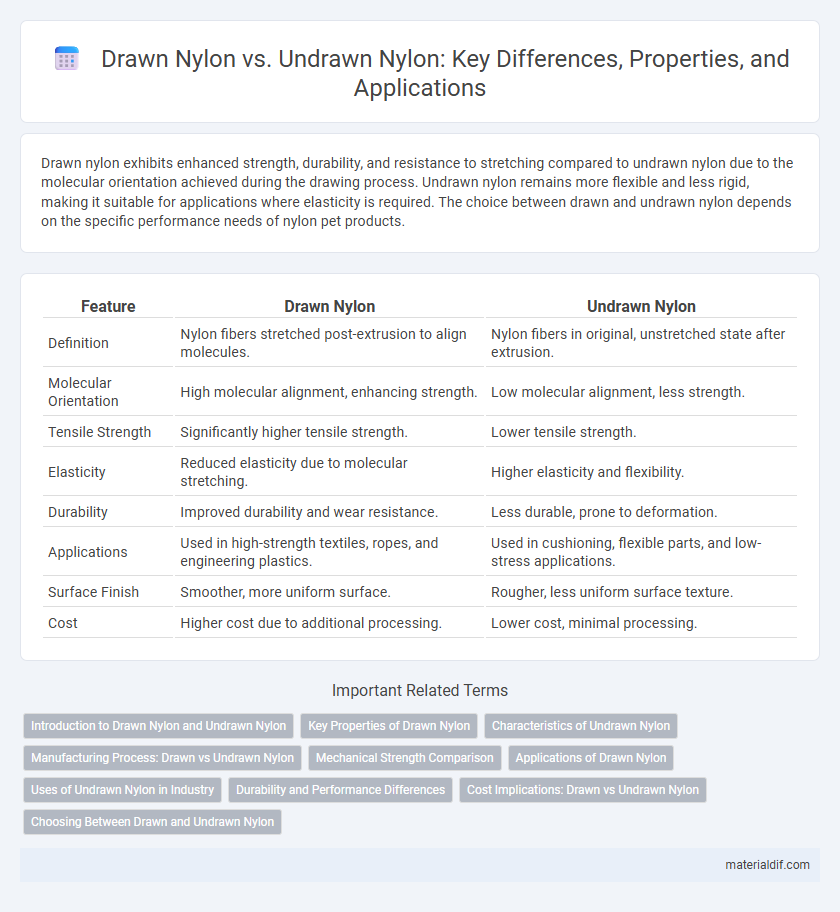
Drawn nylon exhibits enhanced strength, durability, and resistance to stretching compared to undrawn nylon due to the molecular orientation achieved during the drawing process. Undrawn nylon remains more flexible and less rigid, making it suitable for applications where elasticity is required. The choice between drawn and undrawn nylon depends on the specific performance needs of nylon pet products.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Drawn Nylon | Undrawn Nylon |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Nylon fibers stretched post-extrusion to align molecules. | Nylon fibers in original, unstretched state after extrusion. |
| Molecular Orientation | High molecular alignment, enhancing strength. | Low molecular alignment, less strength. |
| Tensile Strength | Significantly higher tensile strength. | Lower tensile strength. |
| Elasticity | Reduced elasticity due to molecular stretching. | Higher elasticity and flexibility. |
| Durability | Improved durability and wear resistance. | Less durable, prone to deformation. |
| Applications | Used in high-strength textiles, ropes, and engineering plastics. | Used in cushioning, flexible parts, and low-stress applications. |
| Surface Finish | Smoother, more uniform surface. | Rougher, less uniform surface texture. |
| Cost | Higher cost due to additional processing. | Lower cost, minimal processing. |
Introduction to Drawn Nylon and Undrawn Nylon
Drawn nylon undergoes a mechanical stretching process that aligns its polymer chains, enhancing tensile strength, durability, and resistance to abrasion, making it ideal for industrial and textile applications. Undrawn nylon lacks this orientation, resulting in a more flexible but weaker material with lower mechanical properties and decreased resistance to wear. The distinction between drawn and undrawn nylon significantly impacts performance characteristics in products such as fibers, films, and molded components.
Key Properties of Drawn Nylon
Drawn nylon exhibits enhanced tensile strength, improved dimensional stability, and superior abrasion resistance compared to undrawn nylon due to the molecular chains being aligned during the drawing process. This orientation results in increased crystallinity, contributing to higher stiffness and better resistance to deformation under load. Additionally, drawn nylon offers greater chemical resistance and reduced moisture absorption, making it suitable for high-performance applications where durability and stability are critical.
Characteristics of Undrawn Nylon
Undrawn nylon exhibits a more amorphous molecular structure, resulting in lower tensile strength and reduced crystallinity compared to drawn nylon. It maintains higher elasticity and flexibility, making it suitable for applications requiring stretch and resilience rather than rigidity. The surface of undrawn nylon fibers appears rougher and less oriented, contributing to increased moisture absorption and dye affinity.
Manufacturing Process: Drawn vs Undrawn Nylon
Drawn nylon undergoes a manufacturing process where the polymer fibers are stretched and aligned, enhancing tensile strength and elasticity, while undrawn nylon remains in its original, non-stretched form with lower mechanical properties. The drawing process involves heating and controlled elongation, which improves crystallinity and molecular orientation, resulting in superior durability and resistance to deformation. Undrawn nylon, produced without fiber stretching, is more flexible but lacks the enhanced performance characteristics found in drawn nylon fibers.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Drawn nylon exhibits significantly higher mechanical strength compared to undrawn nylon due to molecular chain alignment during the drawing process, which enhances tensile strength and elasticity. Undrawn nylon fibers retain a more amorphous structure, resulting in lower tensile strength and reduced durability under mechanical stress. This fundamental difference makes drawn nylon preferable in applications requiring robust performance and resistance to wear and tear.
Applications of Drawn Nylon
Drawn nylon exhibits enhanced tensile strength, dimensional stability, and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for applications such as high-performance fibers in textiles, industrial cords, and fishing lines. Its improved molecular orientation facilitates superior mechanical properties compared to undrawn nylon, which is typically softer and less durable. Industries rely on drawn nylon for products requiring durability and structural integrity under stress, including conveyor belts and automotive components.
Uses of Undrawn Nylon in Industry
Undrawn nylon exhibits high elasticity and lower tensile strength, making it ideal for applications requiring flexibility such as sewing threads, textiles, and film production. Its ability to stretch without breaking is utilized in industrial packaging and expandable fabrics. Undrawn nylon also serves as a precursor in manufacturing processes where subsequent drawing enhances mechanical properties for specific end uses.
Durability and Performance Differences
Drawn nylon exhibits enhanced durability and superior mechanical performance due to the molecular alignment achieved during the drawing process, resulting in increased tensile strength and resistance to wear. Undrawn nylon retains a more amorphous structure, leading to lower tensile strength and reduced abrasion resistance, making it less suitable for high-stress applications. The increased crystallinity in drawn nylon also improves its dimensional stability and fatigue resistance, critical factors in engineered components and textile industries.
Cost Implications: Drawn vs Undrawn Nylon
Drawn nylon undergoes a stretching process that realigns polymer chains, significantly enhancing tensile strength and durability compared to undrawn nylon. This additional manufacturing step increases production costs, resulting in higher prices for drawn nylon products relative to undrawn variants. Choosing undrawn nylon can reduce initial expenses but may compromise mechanical performance in demanding applications.
Choosing Between Drawn and Undrawn Nylon
Drawn nylon exhibits enhanced tensile strength, elasticity, and resistance to abrasion compared to undrawn nylon due to molecular alignment during the drawing process. Undrawn nylon maintains greater flexibility and softness, making it suitable for applications requiring more pliability and less mechanical stress. Selecting between drawn and undrawn nylon depends on the specific performance requirements, such as durability needs favoring drawn nylon and comfort or elasticity needs favoring undrawn nylon.
Drawn Nylon vs Undrawn Nylon Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com