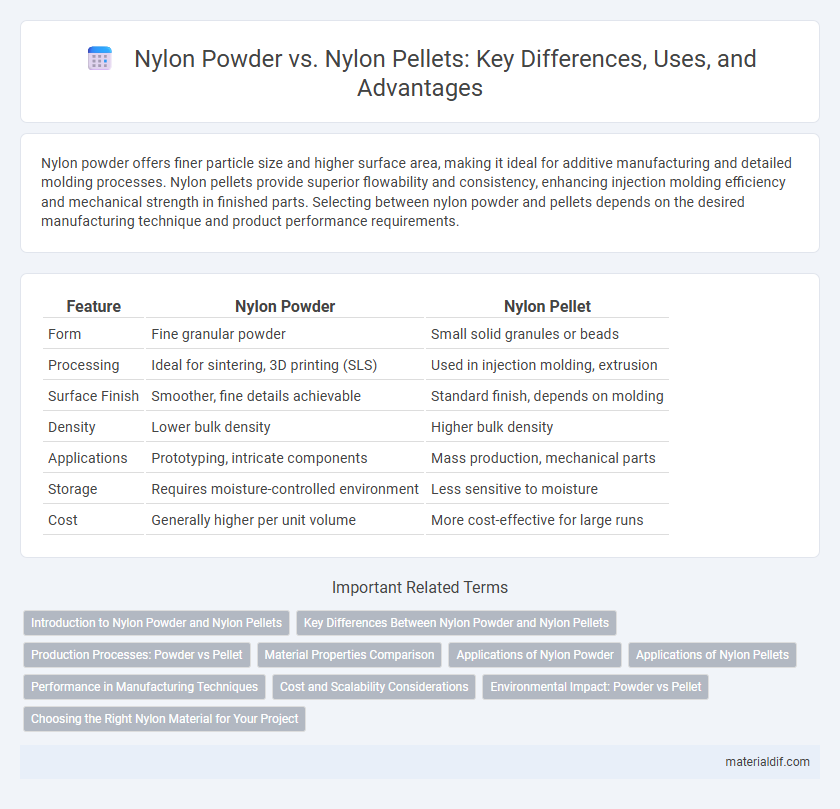
Nylon powder offers finer particle size and higher surface area, making it ideal for additive manufacturing and detailed molding processes. Nylon pellets provide superior flowability and consistency, enhancing injection molding efficiency and mechanical strength in finished parts. Selecting between nylon powder and pellets depends on the desired manufacturing technique and product performance requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Nylon Powder | Nylon Pellet |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Fine granular powder | Small solid granules or beads |
| Processing | Ideal for sintering, 3D printing (SLS) | Used in injection molding, extrusion |
| Surface Finish | Smoother, fine details achievable | Standard finish, depends on molding |
| Density | Lower bulk density | Higher bulk density |
| Applications | Prototyping, intricate components | Mass production, mechanical parts |
| Storage | Requires moisture-controlled environment | Less sensitive to moisture |
| Cost | Generally higher per unit volume | More cost-effective for large runs |
Introduction to Nylon Powder and Nylon Pellets
Nylon powder consists of fine granules used primarily in powder bed fusion 3D printing and selective laser sintering, offering superior surface finish and detail accuracy. Nylon pellets are small, cylindrical granules utilized in injection molding and extrusion processes, providing consistent melt flow and mechanical strength. Both forms are derived from polyamides, with applications driven by their particle size and processing methods.
Key Differences Between Nylon Powder and Nylon Pellets
Nylon powder consists of fine particles used primarily for selective laser sintering (SLS) 3D printing, offering high resolution and detail in complex designs. Nylon pellets are larger granules typically utilized in injection molding or extrusion processes, providing efficient melting and uniform flow for mass production. The key differences lie in particle size, application methods, and processing techniques, which influence the material's mechanical properties and surface finish in the final product.
Production Processes: Powder vs Pellet
Nylon powder is produced through a specific drying and grinding process that creates fine, uniform particles ideal for additive manufacturing and coating applications, while nylon pellets are formed by extrusion and pelletizing molten nylon, resulting in compact granules suited for injection molding and extrusion processes. Powder production typically involves techniques such as spray drying or cryogenic grinding, which preserve polymer properties and enable precise particle size distribution. In contrast, pellet production emphasizes melt processing and cutting, offering ease of handling and consistent feeding in traditional plastic processing equipment.
Material Properties Comparison
Nylon powder offers superior surface smoothness and fine detail resolution compared to nylon pellets, making it ideal for additive manufacturing and precision molding applications. Nylon pellets provide better mechanical strength and durability due to their higher density and uniform particle size, which ensures consistent melting and flow during extrusion. Both forms exhibit high abrasion resistance and chemical stability, but powder enables more intricate design capabilities, while pellets are preferred for bulk production processes.
Applications of Nylon Powder
Nylon powder is widely used in additive manufacturing processes such as selective laser sintering (SLS) for producing complex, lightweight, and durable parts in aerospace, automotive, and medical industries. Its fine particle size allows for superior surface finish and detailed geometries compared to nylon pellets, which are primarily used in injection molding and extrusion. The versatility of nylon powder enables rapid prototyping, functional testing, and small-batch production with high mechanical strength and chemical resistance.
Applications of Nylon Pellets
Nylon pellets serve as the primary raw material in injection molding, extrusion, and 3D printing processes due to their consistent size and ease of melting, enabling precise manufacturing of automotive parts, electrical components, and consumer goods. Their uniform composition ensures high mechanical strength, wear resistance, and dimensional stability, making them ideal for producing complex geometries and durable end-use products. Industries widely utilize nylon pellets for fabricating gears, bearings, and housings where toughness and thermal resistance are critical.
Performance in Manufacturing Techniques
Nylon powder offers superior surface finish and fine detail resolution in additive manufacturing processes like selective laser sintering (SLS), enabling complex geometries with minimal post-processing. Nylon pellets, commonly used in injection molding and extrusion, provide higher mechanical strength and faster production rates due to their consistent melt flow properties. Selecting between nylon powder and pellets depends on balancing precision requirements against manufacturing speed and structural performance.
Cost and Scalability Considerations
Nylon powder generally offers lower material costs and finer processing control, making it suitable for high-precision additive manufacturing applications, while nylon pellets provide greater scalability for large-scale production due to their ease of handling and compatibility with traditional injection molding processes. Pelletized nylon enables more cost-effective mass production by reducing waste and increasing throughput, whereas nylon powder incurs higher costs associated with specialized equipment and slower processing speeds. Choosing between nylon powder and pellet depends heavily on production volume and budget constraints, with pellets favored for scalability and powders preferred for intricate detail and prototyping.
Environmental Impact: Powder vs Pellet
Nylon powder generates less waste during manufacturing due to precise application in additive manufacturing, reducing material scrap and energy consumption compared to nylon pellets. Pellets often require additional energy-intensive melting and molding processes, contributing to higher carbon emissions and environmental footprint. Recycling nylon powder is more efficient when used in 3D printing, whereas pellet recycling faces challenges related to contamination and degradation of mechanical properties.
Choosing the Right Nylon Material for Your Project
Nylon powder offers finer particle size and superior surface finish for precision molding and coating applications, while nylon pellets provide ease of handling and uniform melting for injection molding and extrusion processes. Selecting the right nylon material depends on the specific manufacturing technique, desired mechanical properties, and project scale requirements. Evaluating factors like flow characteristics, processing temperature, and end-use durability ensures optimal material performance and cost-efficiency.
Nylon Powder vs Nylon Pellet Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com