Nylon pet collars offer superior durability and flexibility compared to polypropylene, making them ideal for active pets. While polypropylene is lightweight and resistant to moisture, nylon's strength ensures long-lasting wear and better resistance to abrasion. Choosing nylon over polypropylene enhances comfort and longevity in pet accessories.
Table of Comparison
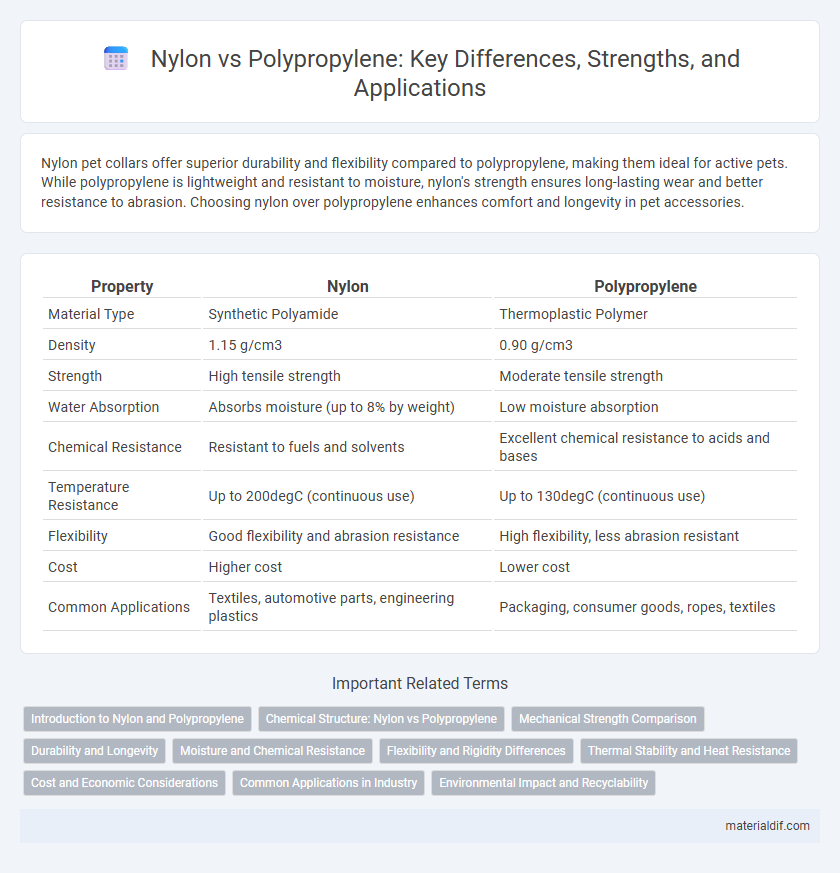
| Property | Nylon | Polypropylene |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic Polyamide | Thermoplastic Polymer |
| Density | 1.15 g/cm3 | 0.90 g/cm3 |
| Strength | High tensile strength | Moderate tensile strength |
| Water Absorption | Absorbs moisture (up to 8% by weight) | Low moisture absorption |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to fuels and solvents | Excellent chemical resistance to acids and bases |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 200degC (continuous use) | Up to 130degC (continuous use) |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility and abrasion resistance | High flexibility, less abrasion resistant |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost |
| Common Applications | Textiles, automotive parts, engineering plastics | Packaging, consumer goods, ropes, textiles |
Introduction to Nylon and Polypropylene
Nylon is a synthetic polymer known for its high tensile strength, elasticity, and resistance to abrasion, making it ideal for textiles and industrial applications. Polypropylene, another widely used thermoplastic polymer, offers excellent chemical resistance, low density, and cost-effectiveness, commonly used in packaging and automotive parts. Both materials differ significantly in mechanical properties and applications, with Nylon excelling in durability and Polypropylene favored for its versatility and moisture resistance.
Chemical Structure: Nylon vs Polypropylene
Nylon is a polyamide characterized by repeating amide linkages (-CONH-) in its backbone, providing strong hydrogen bonding that enhances its mechanical strength and thermal resistance. Polypropylene is a polyolefin consisting of a hydrocarbon chain with methyl side groups, resulting in a non-polar, chemically inert structure with lower density and moisture absorption compared to nylon. The difference in chemical structures--nylon's polar amide groups versus polypropylene's non-polar hydrocarbon chains--significantly affects their properties such as durability, moisture resistance, and chemical reactivity.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Nylon exhibits significantly higher tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to polypropylene, making it ideal for applications requiring durability under mechanical stress. Polypropylene offers greater impact resistance but generally lacks the stiffness and load-bearing capacity of nylon. The superior mechanical strength of nylon results from its hydrogen bonding between polymer chains, enhancing rigidity and resilience in demanding environments.
Durability and Longevity
Nylon exhibits superior durability compared to polypropylene due to its higher tensile strength and excellent abrasion resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring long-lasting performance. Polypropylene, while offering chemical resistance and lighter weight, tends to degrade faster under UV exposure and mechanical stress, reducing its overall lifespan. The enhanced resilience of nylon extends product longevity, especially in demanding environments such as industrial components and outdoor gear.
Moisture and Chemical Resistance
Nylon exhibits higher moisture absorption compared to polypropylene, making it less suitable for applications requiring low water uptake. Polypropylene's superior chemical resistance, especially against acids and bases, outperforms nylon, which tends to degrade in harsh chemical environments. This makes polypropylene ideal for use in damp or chemically aggressive conditions, while nylon is preferred where strength and abrasion resistance are critical despite moisture exposure.
Flexibility and Rigidity Differences
Nylon exhibits higher flexibility compared to polypropylene, making it ideal for applications requiring durability under repeated stress or bending. Polypropylene offers greater rigidity and resistance to fatigue, which suits structural components needing stiffness and shape retention. The molecular structure of nylon allows for better elasticity, whereas polypropylene's crystalline composition contributes to its firm and rigid nature.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Nylon exhibits superior thermal stability compared to polypropylene, with a melting point ranging between 220degC and 265degC, while polypropylene melts around 160degC to 170degC. This higher heat resistance makes nylon more suitable for applications involving elevated temperatures. Polypropylene's lower thermal stability limits its use in high-heat environments, whereas nylon maintains structural integrity and mechanical properties under prolonged heat exposure.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Nylon typically has a higher raw material cost compared to polypropylene, influencing its overall economic viability in large-scale manufacturing. Polypropylene offers a more cost-effective alternative due to lower production expenses and abundant availability, making it preferable for budget-sensitive applications. When evaluating long-term investment, nylon's durability and resistance often justify its premium price despite the initial higher expenditure.
Common Applications in Industry
Nylon is widely used in the automotive and textile industries for applications requiring high strength, durability, and resistance to abrasion, such as gears, bearings, and fabric fibers. Polypropylene is favored in packaging, consumer goods, and medical applications due to its lightweight, chemical resistance, and moisture barrier properties. Both polymers serve complementary roles, with nylon excelling in mechanical performance and polypropylene in cost-effective, moisture-resistant solutions.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Nylon exhibits higher environmental impact than polypropylene due to its energy-intensive production and greenhouse gas emissions. Polypropylene offers superior recyclability and lower carbon footprint, making it a more sustainable choice in packaging and textiles. Both materials are recyclable, but polypropylene's easier processing and widespread recycling infrastructure enhance its eco-friendly profile.
Nylon vs Polypropylene Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com