Heat stabilized nylon exhibits superior thermal resistance, maintaining structural integrity and performance under elevated temperatures compared to non-stabilized nylon. This advantage makes heat stabilized nylon ideal for applications involving continuous heat exposure, preventing degradation and brittleness. Non-stabilized nylon, while suitable for lower-temperature environments, tends to degrade faster when subjected to heat, limiting its durability and lifespan.
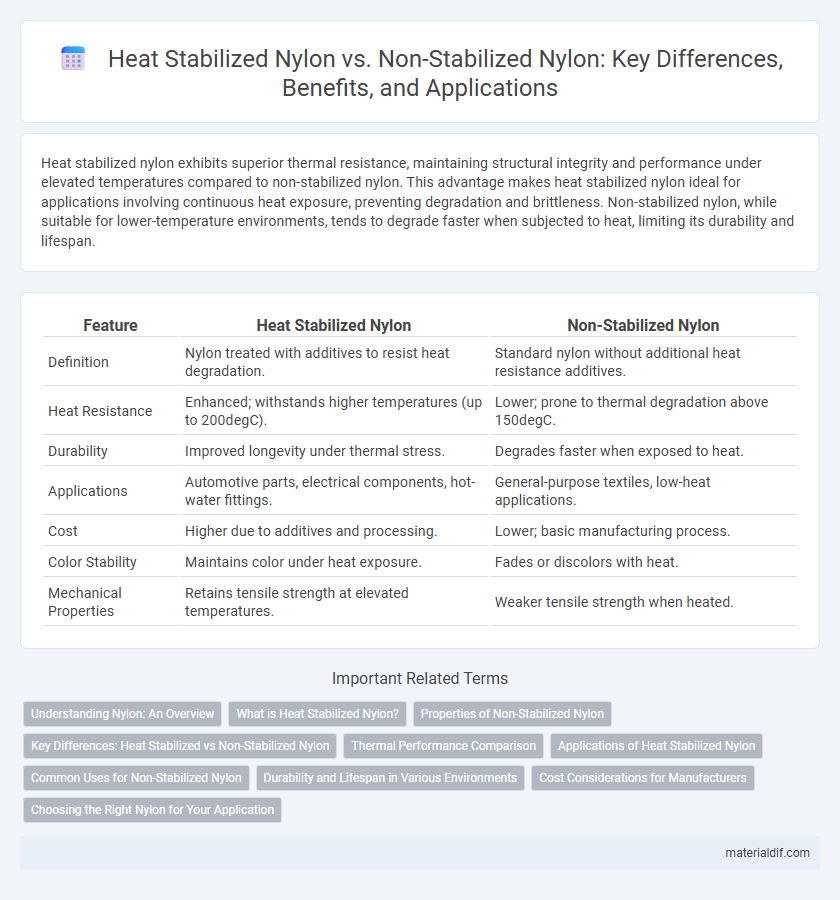
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Heat Stabilized Nylon | Non-Stabilized Nylon |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Nylon treated with additives to resist heat degradation. | Standard nylon without additional heat resistance additives. |
| Heat Resistance | Enhanced; withstands higher temperatures (up to 200degC). | Lower; prone to thermal degradation above 150degC. |
| Durability | Improved longevity under thermal stress. | Degrades faster when exposed to heat. |
| Applications | Automotive parts, electrical components, hot-water fittings. | General-purpose textiles, low-heat applications. |
| Cost | Higher due to additives and processing. | Lower; basic manufacturing process. |
| Color Stability | Maintains color under heat exposure. | Fades or discolors with heat. |
| Mechanical Properties | Retains tensile strength at elevated temperatures. | Weaker tensile strength when heated. |
Understanding Nylon: An Overview
Heat stabilized nylon contains additives that improve its resistance to thermal degradation, enabling it to maintain strength and flexibility at elevated temperatures. Non-stabilized nylon tends to degrade faster when exposed to heat, leading to loss of mechanical properties and increased brittleness. Understanding the distinctions between these types is critical for applications requiring durability under thermal stress.
What is Heat Stabilized Nylon?
Heat stabilized nylon is a type of nylon polymer treated with heat stabilizers to enhance its resistance to thermal degradation, improving durability under high-temperature conditions. This treatment prevents discoloration, loss of mechanical properties, and deformation caused by prolonged exposure to heat. Heat stabilized nylon is commonly used in automotive parts, electrical components, and industrial applications requiring consistent performance at elevated temperatures.
Properties of Non-Stabilized Nylon
Non-stabilized nylon exhibits excellent mechanical strength and flexibility but is more susceptible to thermal degradation and discoloration when exposed to high temperatures. This type of nylon absorbs moisture readily, which can lead to dimensional changes and reduced electrical insulation properties. Its lower heat resistance limits applications in environments with prolonged heat exposure, unlike heat stabilized variants designed for enhanced thermal performance.
Key Differences: Heat Stabilized vs Non-Stabilized Nylon
Heat stabilized nylon exhibits enhanced thermal resistance, maintaining mechanical properties and dimensional stability at elevated temperatures compared to non-stabilized nylon, which tends to degrade and lose strength when exposed to heat. The incorporation of heat stabilizers reduces oxidation and thermal degradation, extending the service life of heat stabilized nylon in high-temperature applications such as automotive components and electrical insulation. Non-stabilized nylon, while cost-effective and mechanically robust at ambient conditions, is prone to discoloration, brittleness, and structural failure under prolonged thermal stress.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Heat stabilized nylon demonstrates significantly enhanced thermal resistance, maintaining structural integrity and mechanical properties at temperatures up to 180degC, compared to non-stabilized nylon which typically degrades above 120degC. The incorporation of heat stabilizers in nylon formulations reduces thermal oxidation and prevents discoloration, extending the material's lifespan in high-temperature applications. Non-stabilized nylon exhibits increased brittleness and loss of tensile strength under sustained heat exposure, limiting its use in demanding thermal environments.
Applications of Heat Stabilized Nylon
Heat stabilized nylon is essential in automotive and electrical applications where high temperature resistance and reduced thermal degradation are critical for long-term performance. Its enhanced stability allows it to maintain mechanical strength and dimensional accuracy in engines, electrical connectors, and housings exposed to continuous heat. Industries such as aerospace and consumer electronics rely on heat stabilized nylon for durable components operating under elevated thermal conditions.
Common Uses for Non-Stabilized Nylon
Non-stabilized nylon is commonly used in applications where heat exposure is minimal, such as textile fibers for clothing, carpets, and upholstery, benefiting from its excellent strength and abrasion resistance. It is also frequently utilized in consumer goods like brushes, fishing lines, and ropes, where flexibility and durability are important but high-temperature resistance is not critical. These non-heat stabilized nylons perform well in environments below 120degC, making them suitable for everyday products that do not require thermal stability.
Durability and Lifespan in Various Environments
Heat stabilized nylon exhibits superior durability and extended lifespan compared to non-stabilized nylon when exposed to high-temperature and UV-intensive environments. The heat stabilization process enhances thermal resistance, reducing degradation and maintaining mechanical properties under harsh conditions. Non-stabilized nylon tends to degrade faster, becoming brittle and losing strength in prolonged heat or sunlight exposure, limiting its application in demanding industrial uses.
Cost Considerations for Manufacturers
Heat stabilized nylon offers enhanced resistance to thermal degradation, leading to increased durability in high-temperature applications, but it commands a higher material cost compared to non-stabilized nylon. Manufacturers must weigh the upfront expense against potential savings from reduced product failure rates and lower maintenance requirements. Non-stabilized nylon presents a cost-effective option for less demanding environments, yet it may incur higher long-term costs due to faster aging and decreased performance under heat exposure.
Choosing the Right Nylon for Your Application
Heat stabilized nylon offers superior resistance to thermal degradation and maintains mechanical properties at elevated temperatures, making it ideal for applications involving continuous heat exposure or thermal cycling. Non-stabilized nylon is suitable for environments with minimal heat stress, offering cost-effectiveness and good general-purpose performance. Selecting the right nylon depends on factors like operating temperature, mechanical load, and environmental exposure, ensuring optimal durability and functionality in the intended application.
Heat Stabilized Nylon vs Non-Stabilized Nylon Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com