Nylon 6 offers higher tensile strength and better abrasion resistance, making it ideal for heavy-duty pet products like collars and leashes that must endure constant wear and tear. Nylon 6/12 provides superior chemical resistance and lower water absorption, enhancing durability and flexibility in pet accessories exposed to moisture and harsh conditions. Choosing between the two depends on the specific demands of the pet product's intended use and environmental exposure.
Table of Comparison
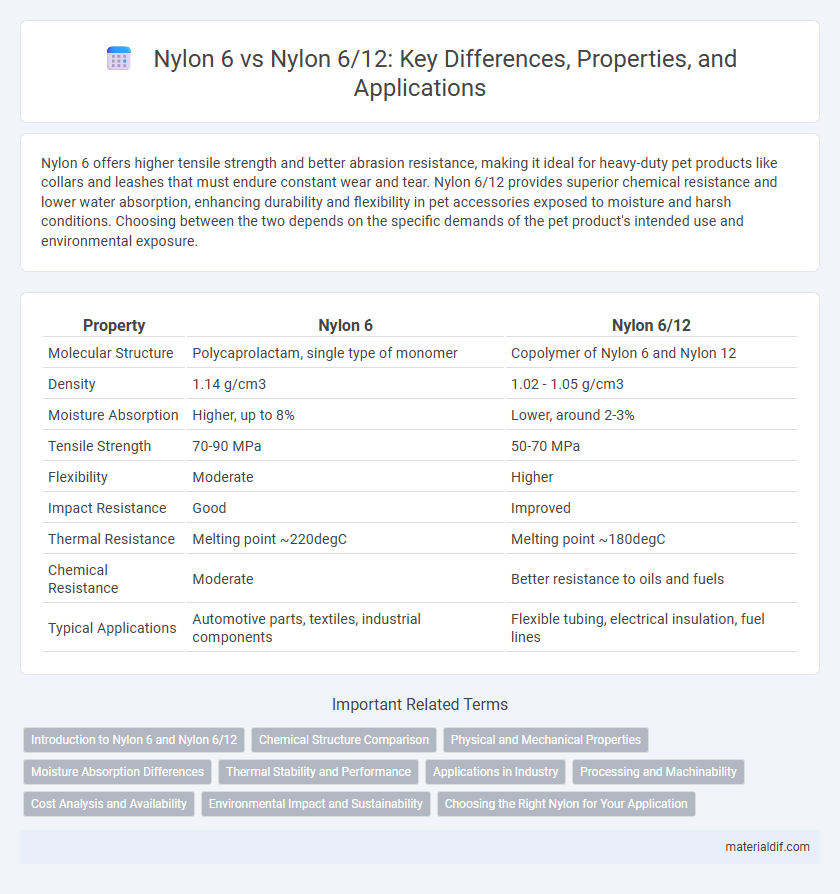
| Property | Nylon 6 | Nylon 6/12 |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Structure | Polycaprolactam, single type of monomer | Copolymer of Nylon 6 and Nylon 12 |
| Density | 1.14 g/cm3 | 1.02 - 1.05 g/cm3 |
| Moisture Absorption | Higher, up to 8% | Lower, around 2-3% |
| Tensile Strength | 70-90 MPa | 50-70 MPa |
| Flexibility | Moderate | Higher |
| Impact Resistance | Good | Improved |
| Thermal Resistance | Melting point ~220degC | Melting point ~180degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate | Better resistance to oils and fuels |
| Typical Applications | Automotive parts, textiles, industrial components | Flexible tubing, electrical insulation, fuel lines |
Introduction to Nylon 6 and Nylon 6/12
Nylon 6, a synthetic polymer derived from caprolactam, offers high tensile strength, excellent abrasion resistance, and good chemical stability, making it ideal for industrial applications and textiles. Nylon 6/12, a copolymer of Nylon 6 and Nylon 12, combines the mechanical strength of Nylon 6 with enhanced chemical resistance and lower moisture absorption, resulting in improved flexibility and dimensional stability. Both materials serve diverse uses, but Nylon 6/12 is preferred in environments requiring superior resistance to oils, fuels, and harsh chemicals.
Chemical Structure Comparison
Nylon 6 features a polymer chain derived from caprolactam, consisting of repeated amide groups with a single type of monomer unit, resulting in a more crystalline and rigid structure. Nylon 6/12 is a copolymer made from hexamethylene diamine and a mix of adipic acid and laurolactam, incorporating both 6 and 12 carbon atoms in its repeating units, which decreases crystallinity and increases flexibility. The chemical structure differences impact melting point, moisture absorption, and mechanical properties, with Nylon 6 generally exhibiting higher tensile strength and Nylon 6/12 offering enhanced chemical resistance.
Physical and Mechanical Properties
Nylon 6 exhibits higher tensile strength and stiffness compared to Nylon 6/12, making it suitable for applications requiring durability and rigidity. Nylon 6/12 offers superior chemical resistance and lower moisture absorption, enhancing dimensional stability in humid environments. Both materials provide good impact resistance, but Nylon 6/12's flexibility is advantageous for components subjected to repeated stress or flexing.
Moisture Absorption Differences
Nylon 6 exhibits higher moisture absorption compared to Nylon 6/12 due to its more hydrophilic amide groups and tighter molecular structure. Nylon 6/12 has a longer aliphatic chain, reducing water uptake and enhancing dimensional stability in humid conditions. This lower moisture absorption in Nylon 6/12 improves mechanical performance and electrical properties in moisture-sensitive applications.
Thermal Stability and Performance
Nylon 6 exhibits higher thermal stability with a melting point around 220degC, making it suitable for high-temperature applications. Nylon 6/12 offers improved impact resistance and lower moisture absorption, enhancing performance in environments with fluctuating temperatures and humidity. The choice between Nylon 6 and Nylon 6/12 depends on balancing thermal stability requirements against mechanical flexibility and environmental exposure.
Applications in Industry
Nylon 6 is widely used in automotive parts, electrical components, and industrial machinery due to its high strength and excellent abrasion resistance. Nylon 6/12 offers superior chemical resistance and lower moisture absorption, making it ideal for fuel lines, hydraulic hoses, and packaging films. Both materials are essential in manufacturing, but Nylon 6/12's enhanced flexibility and durability expand its applications in harsh chemical environments.
Processing and Machinability
Nylon 6 offers superior machinability due to its higher melting point and rigidity, making it ideal for precision molding and extrusion processes. Nylon 6/12 provides enhanced processing flexibility with lower moisture absorption and improved dimensional stability during machining. These properties result in smoother finishes and reduced tool wear for Nylon 6/12 in applications requiring high impact resistance and low friction.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Nylon 6 typically offers lower production costs compared to Nylon 6/12 due to its simpler polymerization process and widespread manufacturing infrastructure, making it more readily available in bulk quantities. Nylon 6/12, while often more expensive, provides better chemical resistance and lower moisture absorption, which can justify the higher price in specialized applications. Market availability for Nylon 6/12 is more limited, with fewer suppliers and higher lead times compared to the extensively produced and distributed Nylon 6.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Nylon 6/12 generally presents lower environmental impact than Nylon 6 due to its higher resistance to chemicals and moisture, which extends product lifespan and reduces waste. The production of Nylon 6/12 results in less water and energy consumption compared to Nylon 6, improving sustainability metrics. Biodegradability remains limited for both, but Nylon 6/12's reduced need for frequent replacement contributes to a smaller overall ecological footprint.
Choosing the Right Nylon for Your Application
Nylon 6 offers high tensile strength and excellent abrasion resistance, making it ideal for demanding mechanical applications like gears and bearings. Nylon 6/12 provides superior chemical resistance and lower moisture absorption, which suits environments exposed to oils and harsh chemicals. Selecting the right nylon depends on balancing strength, flexibility, and environmental exposure to optimize performance and durability.
Nylon 6 vs Nylon 6/12 Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com