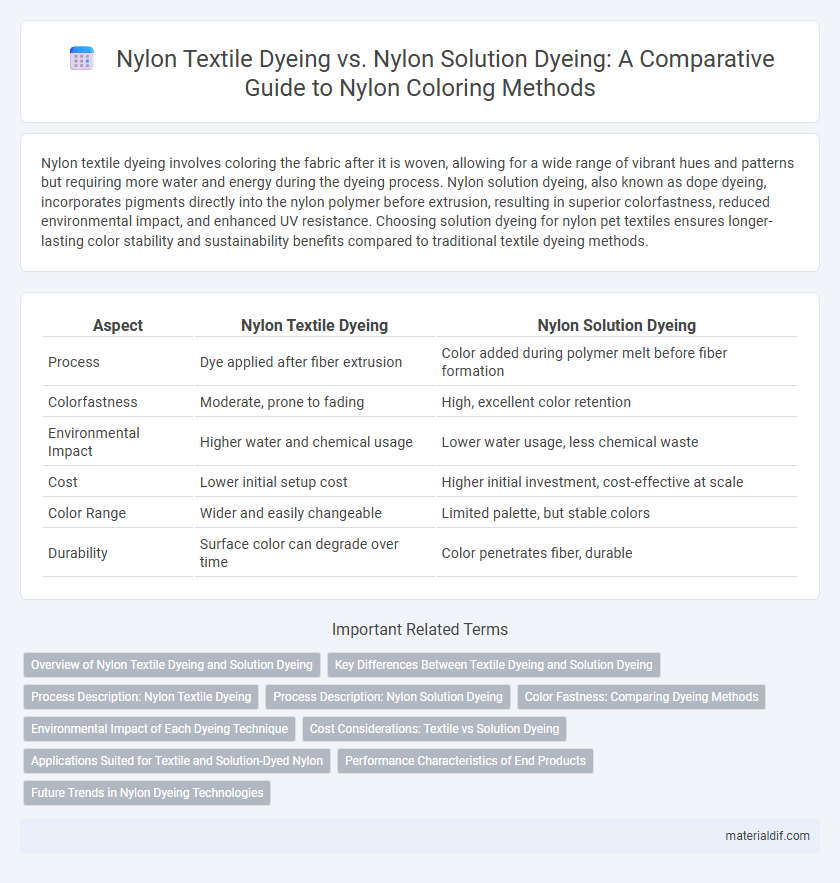
Nylon textile dyeing involves coloring the fabric after it is woven, allowing for a wide range of vibrant hues and patterns but requiring more water and energy during the dyeing process. Nylon solution dyeing, also known as dope dyeing, incorporates pigments directly into the nylon polymer before extrusion, resulting in superior colorfastness, reduced environmental impact, and enhanced UV resistance. Choosing solution dyeing for nylon pet textiles ensures longer-lasting color stability and sustainability benefits compared to traditional textile dyeing methods.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Nylon Textile Dyeing | Nylon Solution Dyeing |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Dye applied after fiber extrusion | Color added during polymer melt before fiber formation |
| Colorfastness | Moderate, prone to fading | High, excellent color retention |
| Environmental Impact | Higher water and chemical usage | Lower water usage, less chemical waste |
| Cost | Lower initial setup cost | Higher initial investment, cost-effective at scale |
| Color Range | Wider and easily changeable | Limited palette, but stable colors |
| Durability | Surface color can degrade over time | Color penetrates fiber, durable |
Overview of Nylon Textile Dyeing and Solution Dyeing
Nylon textile dyeing involves applying color to the fabric after it has been woven or knitted, offering a wide range of shade options and flexibility for customization. Solution dyeing, on the other hand, integrates color directly into the nylon polymer before fiber formation, resulting in superior colorfastness and resistance to fading from UV exposure. Both methods impact the environmental footprint, with solution dyeing generally reducing water and chemical usage compared to traditional textile dyeing processes.
Key Differences Between Textile Dyeing and Solution Dyeing
Nylon textile dyeing involves applying color to fibers after they are woven or knitted, offering a wide range of vibrant hues but often resulting in less colorfastness and higher water consumption. Nylon solution dyeing integrates pigment directly into the polymer melt before fiber extrusion, producing superior colorfastness, resistance to fading, and greater environmental sustainability. Key differences include the timing of color application, with textile dyeing occurring post-fiber formation, while solution dyeing embeds pigment during fiber production, impacting durability, cost, and ecological footprint.
Process Description: Nylon Textile Dyeing
Nylon textile dyeing involves applying color to finished nylon fabrics through methods such as exhaust dyeing, continuous dyeing, or piece dyeing, where the fabric absorbs dyes in aqueous solutions under controlled temperature and pH conditions. This process allows for a wide range of vibrant colors and patterns on nylon textiles but requires significant water, energy, and chemical inputs. Control over dye affinity and fastness properties is critical, as nylon fibers exhibit high dye receptivity, impacting color uniformity and durability.
Process Description: Nylon Solution Dyeing
Nylon solution dyeing involves adding color pigments directly into the molten nylon polymer before fiber extrusion, resulting in deep, uniform coloration that penetrates the entire fiber cross-section. This process enhances colorfastness, resistance to fading from UV exposure, and reduces water and chemical usage compared to conventional nylon textile dyeing, where fabric is dyed post-fiber production. Solution-dyed nylon fibers are ideal for outdoor and high-performance applications due to their superior durability and vibrant, long-lasting color retention.
Color Fastness: Comparing Dyeing Methods
Nylon solution dyeing offers superior color fastness compared to traditional nylon textile dyeing due to the pigment being integrated during fiber extrusion, resulting in enhanced resistance to fading from UV exposure, washing, and abrasion. Traditional dyeing methods rely on surface absorption of dyes, which can lead to uneven color distribution and more rapid fading over time, especially under harsh environmental conditions. The durability of color in solution-dyed nylon makes it a preferred choice for outdoor and high-performance applications where long-lasting vibrant hues are critical.
Environmental Impact of Each Dyeing Technique
Nylon textile dyeing involves applying color to finished fabrics, resulting in significant water consumption, chemical discharge, and energy use, contributing to water pollution and higher carbon footprints. Nylon solution dyeing, also known as dope dyeing, reduces environmental impact by incorporating pigments during fiber production, minimizing water usage, chemical waste, and energy consumption. This process enhances colorfastness and supports sustainable manufacturing by lowering resource depletion and pollution compared to conventional textile dyeing methods.
Cost Considerations: Textile vs Solution Dyeing
Nylon textile dyeing often incurs higher costs due to the extensive use of water, energy, and chemicals during the fabric dyeing process, leading to increased environmental and operational expenses. In contrast, nylon solution dyeing integrates color pigments directly into the polymer melt, significantly reducing water consumption and minimizing waste, which results in lower overall production costs despite higher initial setup investments. Economically, solution dyeing proves more cost-effective for large volume production runs, while textile dyeing remains preferable for smaller batches with frequent color changes due to its lower upfront costs.
Applications Suited for Textile and Solution-Dyed Nylon
Textile dyeing for nylon is ideal for fashion apparel and home furnishings where a wide range of vibrant colors and patterns is required, benefiting from the fabric's dye affinity and versatility. Solution dyeing nylon excels in outdoor gear, automotive interiors, and industrial textiles due to its superior colorfastness, UV resistance, and environmental sustainability from pigment incorporation during fiber extrusion. Each dyeing method targets specific applications, maximizing performance and aesthetics based on the end-use environment and durability needs.
Performance Characteristics of End Products
Nylon textile dyeing involves applying color to finished fabrics, resulting in vibrant and customizable hues but may cause slight reductions in tensile strength and colorfastness due to dyeing processes. Nylon solution dyeing, where color pigments are added during polymer extrusion, offers superior colorfastness, UV resistance, and reduced environmental impact by minimizing water usage. End products from solution-dyed nylon exhibit enhanced durability, better resistance to fading, and longer life cycles, making them ideal for demanding applications such as outdoor gear and upholstery.
Future Trends in Nylon Dyeing Technologies
Future trends in nylon dyeing technologies emphasize sustainability and efficiency, with solution dyeing gaining traction due to its reduced water and energy consumption compared to traditional textile dyeing. Advances in bio-based colorants and low-impact coloration processes are driving innovation, enabling manufacturers to meet environmental regulations and consumer demand for eco-friendly textiles. Integration of digital dyeing techniques and smart dyeing systems promises enhanced color precision and reduced chemical waste in nylon production.
Nylon Textile Dyeing vs Nylon Solution Dyeing Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com