Flame-retardant nylon contains additives that significantly reduce its flammability, making it safer for use in environments with high fire risk. Non-flame-retardant nylon, while strong and durable, lacks these protective features and can ignite and burn more rapidly when exposed to flame. Choosing flame-retardant nylon enhances safety without compromising the material's inherent strength and flexibility.
Table of Comparison
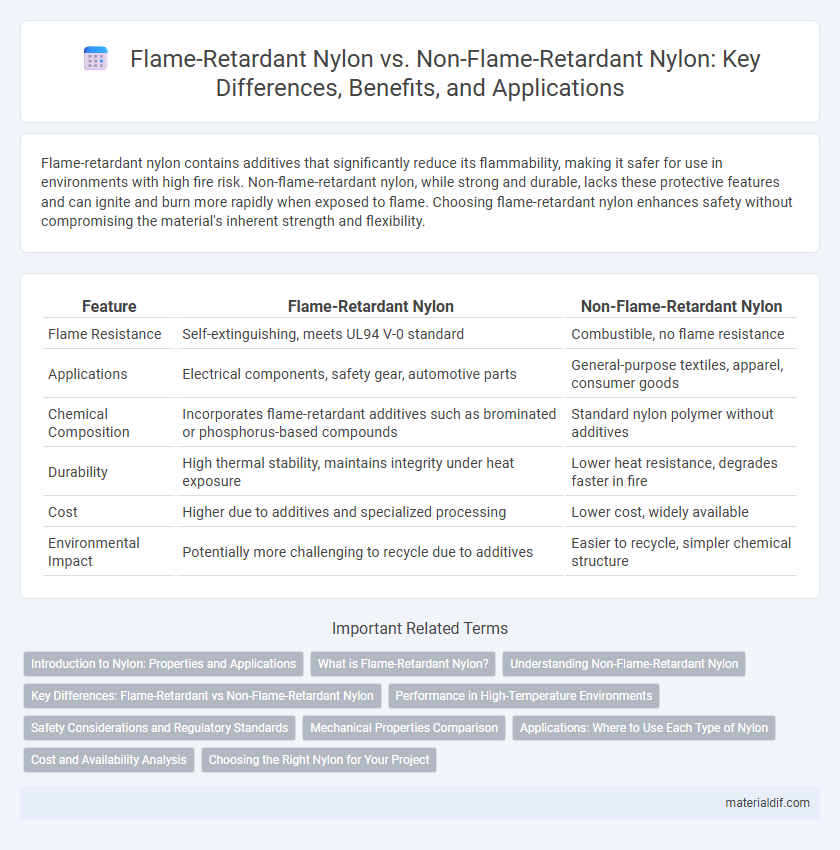
| Feature | Flame-Retardant Nylon | Non-Flame-Retardant Nylon |
|---|---|---|
| Flame Resistance | Self-extinguishing, meets UL94 V-0 standard | Combustible, no flame resistance |
| Applications | Electrical components, safety gear, automotive parts | General-purpose textiles, apparel, consumer goods |
| Chemical Composition | Incorporates flame-retardant additives such as brominated or phosphorus-based compounds | Standard nylon polymer without additives |
| Durability | High thermal stability, maintains integrity under heat exposure | Lower heat resistance, degrades faster in fire |
| Cost | Higher due to additives and specialized processing | Lower cost, widely available |
| Environmental Impact | Potentially more challenging to recycle due to additives | Easier to recycle, simpler chemical structure |
Introduction to Nylon: Properties and Applications
Flame-retardant nylon incorporates chemical additives that significantly enhance its resistance to ignition and combustion, making it ideal for electrical components and automotive parts requiring stringent fire safety standards. Non-flame-retardant nylon exhibits high tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and chemical stability, widely used in textiles, gears, and mechanical parts where fire resistance is not critical. Both types maintain nylon's inherent durability and versatility, but flame-retardant variants meet specific regulatory compliance for fire hazards in industrial and consumer applications.
What is Flame-Retardant Nylon?
Flame-retardant nylon is engineered with chemical additives to resist ignition and slow the spread of fire, enhancing safety in high-risk applications. Unlike non-flame-retardant nylon, which ignites and burns quickly, flame-retardant variants self-extinguish when the flame source is removed. This material is widely used in industries such as electronics, automotive, and textiles where fire resistance is critical.
Understanding Non-Flame-Retardant Nylon
Non-flame-retardant nylon is a synthetic polymer primarily composed of polyamides, valued for its strength, flexibility, and resistance to abrasion but lacks inherent resistance to ignition or flame spread. It is commonly used in textile applications, automotive components, and consumer goods where fire safety is not a critical concern. Without chemical additives or treatments that provide flame retardancy, non-flame-retardant nylon poses a higher risk of melting and burning under high temperatures or open flames.
Key Differences: Flame-Retardant vs Non-Flame-Retardant Nylon
Flame-retardant nylon incorporates chemical additives or is engineered with inherent flame-resistant properties, significantly reducing its flammability and slowing the spread of fire. Non-flame-retardant nylon lacks these modifications, making it more susceptible to ignition and rapid combustion under high heat or flame exposure. Key differences also include compliance with safety standards such as UL 94 or NFPA 701 for flame-retardant nylon, whereas non-flame-retardant variants do not meet these fire safety certifications.
Performance in High-Temperature Environments
Flame-retardant nylon exhibits superior thermal stability and maintains mechanical integrity at temperatures exceeding 200degC, making it ideal for high-temperature applications. Non-flame-retardant nylon tends to soften and degrade rapidly above 150degC, limiting its performance and safety in extreme heat environments. The inclusion of flame retardant additives in nylon significantly enhances resistance to ignition and reduces flame propagation, ensuring enhanced durability and safety under thermal stress.
Safety Considerations and Regulatory Standards
Flame-retardant nylon incorporates chemical additives that enhance its resistance to ignition and slow combustion, making it compliant with stringent regulatory standards such as UL 94 and ANSI/ISEA 107 for protective apparel. Non-flame-retardant nylon lacks these modifications, resulting in higher flammability and limited use in environments with fire safety requirements. Selecting flame-retardant nylon significantly reduces the risk of burn injuries in industrial and consumer applications, ensuring adherence to safety codes and minimizing hazard potential.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Flame-retardant nylon exhibits slightly reduced tensile strength and elongation at break compared to non-flame-retardant nylon due to the addition of flame-retardant additives that can interfere with polymer chain integrity. Despite marginal decreases in impact resistance, flame-retardant nylon maintains sufficient mechanical durability for most industrial applications. Non-flame-retardant nylon generally offers superior flexibility and higher mechanical strength, making it preferable for applications where flame resistance is not critical.
Applications: Where to Use Each Type of Nylon
Flame-retardant nylon is essential in applications requiring enhanced fire safety, such as electrical housings, automotive components, and protective gear, due to its ability to resist ignition and slow flame spread. Non-flame-retardant nylon suits general-purpose uses like textile fibers, consumer goods, and mechanical parts where fire resistance is not a critical concern. Selecting the appropriate type depends on industry regulations, safety standards, and end-use environmental conditions.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Flame-retardant nylon typically incurs higher material and processing costs due to the incorporation of specialized additives that enhance fire resistance, making it more expensive than non-flame-retardant variants. Availability of flame-retardant nylon is generally more limited, with fewer suppliers offering these specialized grades compared to the widely accessible standard nylon types. Industries requiring compliance with stringent fire safety standards often balance the premium cost against regulatory demands and safety benefits when selecting flame-retardant nylon.
Choosing the Right Nylon for Your Project
Flame-retardant nylon offers enhanced safety by resisting ignition and slowing the spread of flames, making it ideal for applications in electrical, automotive, and construction industries where fire hazards are a concern. Non-flame-retardant nylon provides superior mechanical strength, flexibility, and chemical resistance, suited for general-purpose uses like gears, bearings, and consumer goods. Selecting the appropriate nylon depends on balancing fire safety requirements with performance needs, regulatory compliance, and environmental factors specific to your project.
Flame-Retardant Nylon vs Non-Flame-Retardant Nylon Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com