Nickel sheet and nickel plate differ primarily in thickness and application flexibility, with nickel sheets being thinner and more suitable for precision components and lightweight structures. Nickel plates are thicker, offering enhanced strength and durability, making them ideal for heavy-duty industrial uses and structural support. Both materials provide excellent corrosion resistance and high-temperature stability, ensuring long-lasting performance in various environments.
Table of Comparison
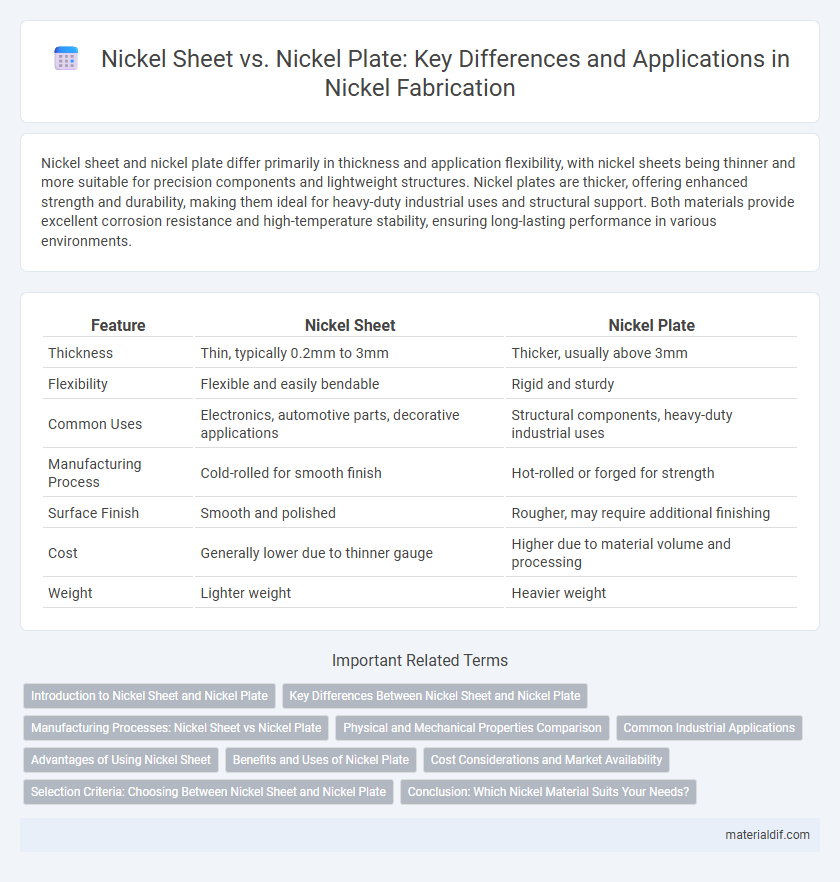
| Feature | Nickel Sheet | Nickel Plate |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | Thin, typically 0.2mm to 3mm | Thicker, usually above 3mm |
| Flexibility | Flexible and easily bendable | Rigid and sturdy |
| Common Uses | Electronics, automotive parts, decorative applications | Structural components, heavy-duty industrial uses |
| Manufacturing Process | Cold-rolled for smooth finish | Hot-rolled or forged for strength |
| Surface Finish | Smooth and polished | Rougher, may require additional finishing |
| Cost | Generally lower due to thinner gauge | Higher due to material volume and processing |
| Weight | Lighter weight | Heavier weight |
Introduction to Nickel Sheet and Nickel Plate
Nickel sheet and nickel plate are both versatile forms of nickel metal used in industrial applications requiring corrosion resistance and high strength. Nickel sheet is thinner and typically supplied in rolls or flat sheets, making it suitable for precise fabrication, while nickel plate is thicker and designed for heavy-duty structural uses. The difference in thickness and form factor impacts their mechanical properties and ideal application environments.
Key Differences Between Nickel Sheet and Nickel Plate
Nickel sheet is thinner and more flexible than nickel plate, making it ideal for applications requiring precise forming and easier handling. Nickel plate, being thicker and more rigid, provides superior strength and durability for heavy-duty uses such as structural components and industrial machinery. The choice between nickel sheet and nickel plate depends on the specific requirements of thickness, mechanical strength, and flexibility in the intended application.
Manufacturing Processes: Nickel Sheet vs Nickel Plate
Nickel sheets are produced through cold rolling or hot rolling processes that create thin, uniform metal layers with precise thickness control for applications requiring flexibility and detailed fabrication. Nickel plates undergo hot rolling and are subsequently annealed and pickled to enhance structural integrity and corrosion resistance, ideal for heavy-duty and industrial uses. The manufacturing differences result in sheets being thinner and more malleable, while plates remain thicker and stronger to withstand mechanical stress.
Physical and Mechanical Properties Comparison
Nickel sheets typically measure less than 6 mm in thickness and offer superior flexibility and ease of fabrication compared to nickel plates, which are thicker and provide enhanced strength and structural support. The mechanical properties of nickel sheets include a tensile strength range of approximately 310-450 MPa and excellent ductility, while nickel plates demonstrate higher tensile strength up to 550 MPa and increased hardness, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications. In terms of physical properties, both nickel sheets and plates share similar corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity, but plates exhibit better load-bearing capacity due to their increased thickness and density.
Common Industrial Applications
Nickel sheets are commonly used in applications requiring flexibility and precision, such as in electronics, battery production, and chemical processing equipment due to their uniform thickness and smooth surface. Nickel plates, being thicker and more rigid, find widespread use in heavy-duty industrial applications including machinery parts, heat exchangers, and structural components that demand enhanced strength and corrosion resistance. Both forms benefit from nickel's excellent resistance to oxidation and high temperatures, making them essential in aerospace, marine, and energy industries.
Advantages of Using Nickel Sheet
Nickel sheet offers superior flexibility and ease of fabrication compared to nickel plate, making it ideal for custom applications requiring precise bending or shaping. Its uniform thickness and smooth surface enhance corrosion resistance and durability in high-temperature environments. Nickel sheet's reduced weight compared to thicker plates also improves handling and installation efficiency in industrial and architectural uses.
Benefits and Uses of Nickel Plate
Nickel plate offers superior strength and thickness compared to nickel sheet, making it ideal for heavy-duty industrial applications such as aerospace, chemical processing, and marine environments where durability and corrosion resistance are critical. Its enhanced mechanical properties provide excellent wear resistance and high-temperature stability, ensuring long-lasting performance under extreme conditions. Common uses include fabrication of structural components, heat exchangers, and protective cladding that demand robust and reliable material characteristics.
Cost Considerations and Market Availability
Nickel sheets typically cost less than nickel plates due to thinner gauges and easier manufacturing processes, making sheets more budget-friendly for applications requiring flexibility. Market availability favors nickel sheets because they are produced in larger volumes and stocked widely by suppliers, whereas nickel plates, being thicker and used for specialized industrial needs, often involve longer lead times and higher prices. When balancing budget constraints and procurement timelines, selecting nickel sheets is generally more cost-effective and accessible for standard projects.
Selection Criteria: Choosing Between Nickel Sheet and Nickel Plate
Nickel sheet offers more flexibility and is typically thinner, making it ideal for applications requiring precise forming and welding, such as electronics and aerospace components. Nickel plate, being thicker and more robust, is suited for heavy-duty uses like chemical processing equipment and marine hardware where strength and corrosion resistance are critical. Selection between nickel sheet and nickel plate should consider factors such as thickness requirements, mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, and the intended fabrication process.
Conclusion: Which Nickel Material Suits Your Needs?
Nickel sheet offers flexibility and ease of fabrication, making it ideal for applications requiring intricate shapes or lightweight components, while nickel plate possesses greater thickness and strength suited for heavy-duty industrial uses. Consider the specific requirements such as durability, corrosion resistance, and dimensional precision when choosing between nickel sheet and plate. Evaluating the balance of mechanical properties and application environment ensures the selection of the most suitable nickel material.
Nickel Sheet vs Nickel Plate Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com