Nickel Bronze and Phosphor Bronze are both copper alloys known for their durability and resistance to corrosion, making them ideal for pet tags and accessories. Nickel Bronze offers enhanced strength and a distinctive silvery appearance, while Phosphor Bronze provides excellent elasticity and wear resistance due to its phosphorus content. Choosing between the two depends on the desired balance of aesthetic appeal and mechanical properties for pet products.
Table of Comparison
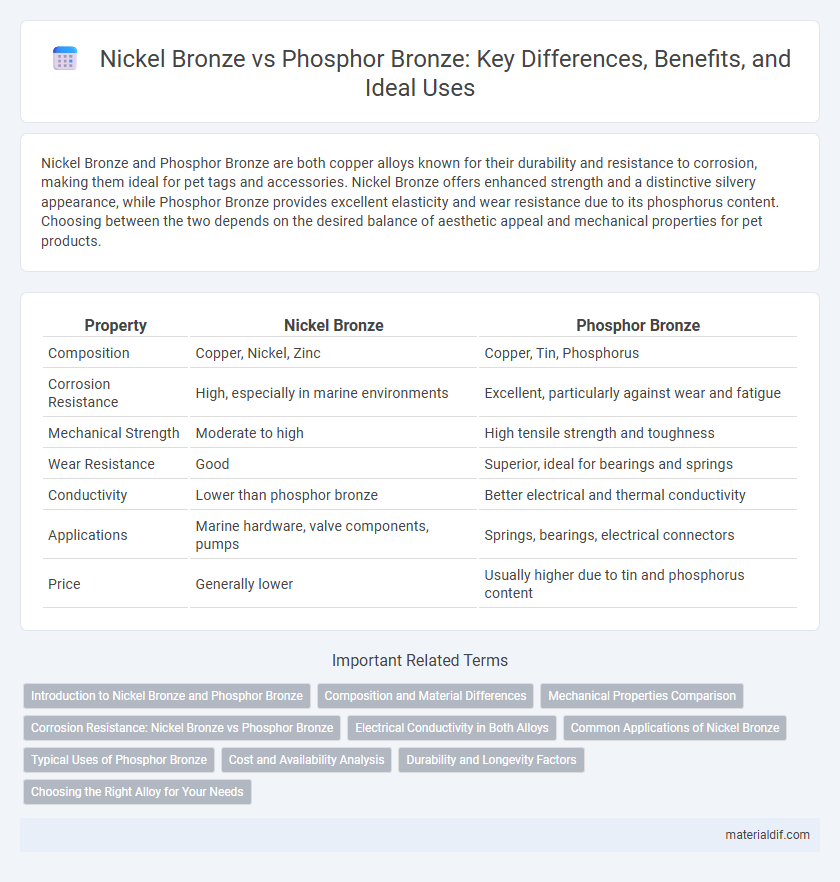
| Property | Nickel Bronze | Phosphor Bronze |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Copper, Nickel, Zinc | Copper, Tin, Phosphorus |
| Corrosion Resistance | High, especially in marine environments | Excellent, particularly against wear and fatigue |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate to high | High tensile strength and toughness |
| Wear Resistance | Good | Superior, ideal for bearings and springs |
| Conductivity | Lower than phosphor bronze | Better electrical and thermal conductivity |
| Applications | Marine hardware, valve components, pumps | Springs, bearings, electrical connectors |
| Price | Generally lower | Usually higher due to tin and phosphorus content |
Introduction to Nickel Bronze and Phosphor Bronze
Nickel bronze is a copper-based alloy enriched with nickel, offering enhanced corrosion resistance and mechanical strength, making it ideal for marine and industrial applications. Phosphor bronze, composed of copper, tin, and a small percentage of phosphorus, provides exceptional wear resistance and stiffness, commonly used in electrical components and precision instruments. Both alloys leverage copper's conductivity while tailoring properties with nickel or phosphorus to meet specific performance requirements.
Composition and Material Differences
Nickel bronze typically contains a higher percentage of nickel, enhancing its corrosion resistance and mechanical strength compared to phosphor bronze, which is primarily composed of copper, tin, and a small amount of phosphorus. Phosphor bronze offers superior fatigue resistance and elasticity due to the phosphorous content, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and wear resistance. Both alloys excel in conductivity and corrosion resistance, but nickel bronze is preferred for strength-critical environments, while phosphor bronze is favored for spring components and electrical connectors.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Nickel bronze exhibits higher tensile strength and improved corrosion resistance compared to phosphor bronze, making it suitable for demanding mechanical applications. Phosphor bronze offers superior fatigue resistance and excellent elasticity, ideal for components subjected to repetitive stress. Both alloys provide good wear resistance, but nickel bronze's hardness enhances durability in abrasive environments.
Corrosion Resistance: Nickel Bronze vs Phosphor Bronze
Nickel bronze exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to phosphor bronze due to its higher nickel content, which forms a protective oxide layer that prevents rust and degradation in marine and industrial environments. Phosphor bronze, while durable and resistant to fatigue, is more susceptible to corrosion in acidic or saline conditions without additional protective coatings. The enhanced corrosion resistance of nickel bronze makes it ideal for applications requiring long-term exposure to harsh conditions, such as marine hardware and chemical processing equipment.
Electrical Conductivity in Both Alloys
Nickel bronze exhibits moderate electrical conductivity, typically around 15-25% IACS (International Annealed Copper Standard), making it suitable for applications requiring corrosion resistance combined with reasonable conductivity. Phosphor bronze offers higher electrical conductivity, often ranging between 15-30% IACS, due to its tin and phosphorus content enhancing electron flow. Both alloys are favored in electrical connectors and springs, but phosphor bronze's superior conductivity gives it an edge in high-performance electrical applications.
Common Applications of Nickel Bronze
Nickel bronze, an alloy primarily consisting of copper, nickel, and sometimes small amounts of other elements, excels in marine, electrical, and architectural applications due to its excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical strength. Commonly used in shipbuilding, heat exchangers, and electrical connectors, nickel bronze withstands harsh environments where durability and conductivity are critical. This distinguishes it from phosphor bronze, which is often preferred for its superior fatigue resistance in springs and bearings.
Typical Uses of Phosphor Bronze
Phosphor bronze is widely used in electrical connectors, springs, and bearings due to its excellent fatigue resistance, corrosion resistance, and electrical conductivity. Its typical applications include precision instruments, marine hardware, and musical instruments such as strings and reeds where durability and elasticity are crucial. Unlike nickel bronze, phosphor bronze offers superior wear resistance and is preferred in environments requiring consistent mechanical performance.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Nickel bronze generally costs more than phosphor bronze due to the higher price of nickel and its limited supply compared to the more abundant tin and phosphorus in phosphor bronze. Phosphor bronze offers better availability and lower raw material expenses, making it a cost-effective choice for applications requiring corrosion resistance and strength. Market fluctuations in nickel prices can significantly impact the overall cost of nickel bronze, whereas phosphor bronze remains relatively stable in pricing and supply.
Durability and Longevity Factors
Nickel Bronze offers superior corrosion resistance and enhanced durability due to its higher nickel content, making it ideal for marine and industrial applications requiring long-term exposure to harsh environments. Phosphor Bronze, enriched with phosphorus, provides excellent wear resistance and fatigue strength, which extends the lifespan of components subjected to frequent mechanical stress. Both alloys exhibit high longevity, but Nickel Bronze stands out in environments with chemical exposure, while Phosphor Bronze excels in applications demanding mechanical endurance.
Choosing the Right Alloy for Your Needs
Nickel bronze offers superior corrosion resistance and strength, making it ideal for marine and industrial applications where durability is critical. Phosphor bronze provides excellent fatigue resistance and electrical conductivity, suited for precision components like springs and electrical contacts. Selecting the right alloy depends on balancing environmental exposure with mechanical and electrical performance requirements.
Nickel Bronze vs Phosphor Bronze Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com