Nickel wire offers flexibility and precise control for intricate battery builds, while nickel strip provides a flatter surface ideal for creating strong, even connections in battery packs. The choice between nickel wire and nickel strip depends on the specific requirements of the application, such as current flow and mechanical stability. Both materials ensure efficient conductivity and corrosion resistance essential for durable battery performance.
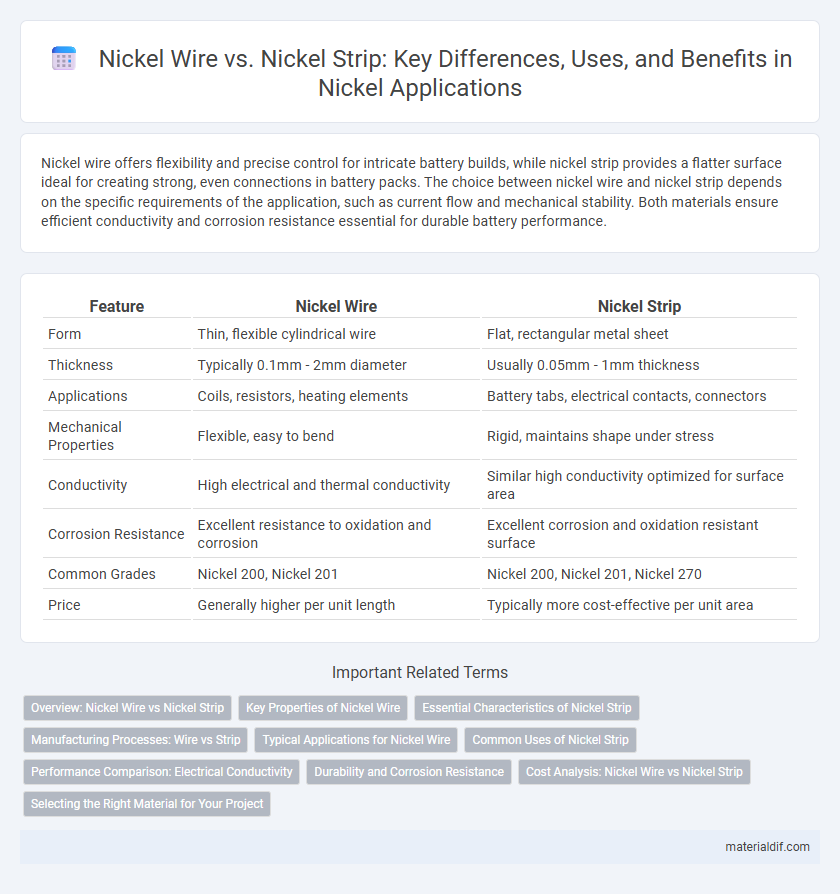
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Nickel Wire | Nickel Strip |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Thin, flexible cylindrical wire | Flat, rectangular metal sheet |
| Thickness | Typically 0.1mm - 2mm diameter | Usually 0.05mm - 1mm thickness |
| Applications | Coils, resistors, heating elements | Battery tabs, electrical contacts, connectors |
| Mechanical Properties | Flexible, easy to bend | Rigid, maintains shape under stress |
| Conductivity | High electrical and thermal conductivity | Similar high conductivity optimized for surface area |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent resistance to oxidation and corrosion | Excellent corrosion and oxidation resistant surface |
| Common Grades | Nickel 200, Nickel 201 | Nickel 200, Nickel 201, Nickel 270 |
| Price | Generally higher per unit length | Typically more cost-effective per unit area |
Overview: Nickel Wire vs Nickel Strip
Nickel wire offers high flexibility and is ideal for intricate applications requiring precise bending and detailed shaping, commonly used in electronics and heating elements. Nickel strip provides superior surface area and tensile strength, making it suitable for battery tabs, connectors, and structural reinforcements. Both forms leverage nickel's excellent corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity, but selection depends on specific mechanical and dimensional needs.
Key Properties of Nickel Wire
Nickel wire exhibits exceptional corrosion resistance, high tensile strength, and excellent thermal stability, making it ideal for applications requiring durability under extreme conditions. Its flexibility and conductivity allow for precise electrical and mechanical uses, distinguishing it from nickel strips that prioritize surface area and structural rigidity. The wire's uniform diameter and purity ensure consistent performance in electronics, aerospace, and chemical processing industries.
Essential Characteristics of Nickel Strip
Nickel strip is characterized by its uniform thickness and superior mechanical strength, making it ideal for applications requiring consistent electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance. Unlike nickel wire, which is flexible and used for winding or intricate shapes, nickel strip offers enhanced dimensional stability and surface finish critical in battery manufacturing and electronic components. High purity and precise gauge control ensure nickel strip performs reliably in demanding environments such as fuel cells and heat exchangers.
Manufacturing Processes: Wire vs Strip
Nickel wire manufacturing involves continuous casting, hot rolling, and drawing processes that produce a flexible, cylindrical form ideal for winding and intricate electrical applications. Nickel strip production utilizes hot rolling followed by cold rolling and annealing to create flat, precise thickness sheets suitable for battery tabs and corrosion-resistant connectors. Both processes require controlled atmospheres to maintain nickel's purity and enhance mechanical properties for specific industrial uses.
Typical Applications for Nickel Wire
Nickel wire is commonly utilized in resistance heating elements, electrical contacts, and welding rods due to its excellent electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance. Its flexibility and tensile strength make it ideal for coil springs and battery electrodes in rechargeable devices. Nickel wire's ability to withstand high temperatures also suits it for use in thermocouples and aerospace components.
Common Uses of Nickel Strip
Nickel strip is commonly used in battery manufacturing, particularly in the production of nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) and nickel-cadmium (NiCd) batteries, due to its excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance. It also finds applications in electrical contacts, heating elements, and precision resistors where durable, conductive materials are essential. Compared to nickel wire, nickel strip's flat and uniform shape provides a larger surface area, making it ideal for soldering and welding tasks in various industrial processes.
Performance Comparison: Electrical Conductivity
Nickel wire offers higher flexibility and is commonly used in applications requiring intricate shaping while maintaining consistent electrical conductivity, typically around 14.3% IACS (International Annealed Copper Standard). Nickel strip provides increased surface area, enhancing heat dissipation and mechanical strength, but may exhibit slightly lower conductivity due to its broader cross-section. The choice between nickel wire and strip depends on balancing conductivity needs with mechanical and thermal performance requirements in specific electrical or thermal management applications.
Durability and Corrosion Resistance
Nickel wire offers enhanced flexibility and durability due to its braided structure, making it ideal for dynamic applications requiring frequent bending. Nickel strip provides superior corrosion resistance with a uniform surface, ensuring long-term performance in harsh environments such as chemical processing and marine exposure. Both forms maintain excellent oxidation resistance at high temperatures, but the choice depends on mechanical stress and environmental conditions.
Cost Analysis: Nickel Wire vs Nickel Strip
Nickel wire generally costs more per unit length than nickel strip due to the additional manufacturing processes such as drawing and annealing, which increase labor and energy expenses. Nickel strip is produced by rolling and slitting, resulting in lower production costs and higher material utilization, making it more cost-effective for applications requiring flat geometries. When evaluating cost, factors such as material yield, application-specific requirements, and scrap rates play critical roles in determining the most economical choice between nickel wire and nickel strip.
Selecting the Right Material for Your Project
Nickel wire offers flexibility and precise control for intricate electrical and heating applications, making it ideal for custom coil winding and fine component fabrication. Nickel strip, with its flat, uniform surface and higher mechanical strength, is better suited for structural reinforcements, battery tabs, and large-area contacts requiring consistent conductivity and durability. Selecting nickel wire or strip depends on factors like required mechanical properties, electrical conductivity, shape complexity, and application environment to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Nickel wire vs Nickel strip Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com