Nickel-free plating offers a hypoallergenic alternative to traditional nickel-based plating, reducing the risk of allergic reactions and skin irritation. This plating method is ideal for sensitive skin, providing durable corrosion resistance without the common health concerns linked to nickel exposure. In contrast, nickel-based plating remains popular for its affordability and excellent wear resistance but may cause allergic responses in nickel-sensitive individuals.
Table of Comparison
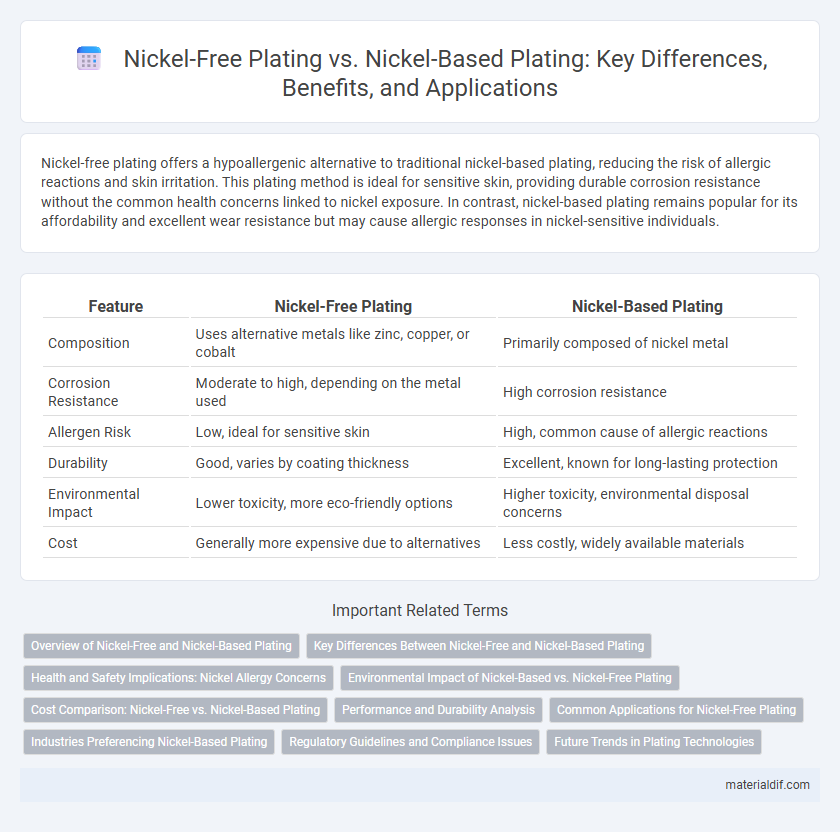
| Feature | Nickel-Free Plating | Nickel-Based Plating |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Uses alternative metals like zinc, copper, or cobalt | Primarily composed of nickel metal |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate to high, depending on the metal used | High corrosion resistance |
| Allergen Risk | Low, ideal for sensitive skin | High, common cause of allergic reactions |
| Durability | Good, varies by coating thickness | Excellent, known for long-lasting protection |
| Environmental Impact | Lower toxicity, more eco-friendly options | Higher toxicity, environmental disposal concerns |
| Cost | Generally more expensive due to alternatives | Less costly, widely available materials |
Overview of Nickel-Free and Nickel-Based Plating
Nickel-free plating offers an alternative to traditional nickel-based plating by eliminating nickel to address allergy concerns and improve environmental compliance. Nickel-based plating provides excellent corrosion resistance, hardness, and wear protection, making it the industry standard for many applications. Advances in nickel-free plating technologies, such as cobalt and zinc alloys, aim to replicate the durability and finish quality of nickel while reducing health risks and regulatory challenges.
Key Differences Between Nickel-Free and Nickel-Based Plating
Nickel-free plating eliminates the use of nickel, reducing the risk of allergic reactions and improving biocompatibility for sensitive skin applications, while nickel-based plating offers superior hardness and corrosion resistance due to nickel's inherent properties. Nickel-based plating provides enhanced durability and wear resistance, making it suitable for industrial environments, whereas nickel-free alternatives prioritize environmental safety and compliance with strict allergen regulations. Surface finish quality varies, with nickel-based plating delivering a brighter, more uniform appearance compared to some nickel-free coatings that may require additional treatments for similar aesthetics.
Health and Safety Implications: Nickel Allergy Concerns
Nickel-free plating eliminates the risk of nickel allergy, a common cause of skin irritation and dermatitis affecting up to 10% of the population. Nickel-based plating, while durable and corrosion-resistant, can release nickel ions upon prolonged skin contact, triggering allergic reactions and posing significant health concerns. Opting for nickel-free alternatives enhances safety in consumer goods, especially for individuals with hypersensitivity.
Environmental Impact of Nickel-Based vs. Nickel-Free Plating
Nickel-based plating releases hazardous nickel compounds into the environment, contributing to soil and water pollution and posing health risks to workers and ecosystems due to nickel's toxicity and potential carcinogenicity. Nickel-free plating alternatives, often utilizing materials like zinc, tin, or organic coatings, significantly reduce these environmental hazards by minimizing metal leaching and occupational exposure. Choosing nickel-free plating supports sustainable manufacturing practices by lowering ecological footprints and enhancing regulatory compliance regarding heavy metal emissions.
Cost Comparison: Nickel-Free vs. Nickel-Based Plating
Nickel-free plating generally incurs higher upfront costs due to specialized materials like zinc or copper alloys, but it offers long-term savings by reducing allergic reactions and environmental compliance expenses. Nickel-based plating is more cost-effective initially, with widely available materials and established processes, yet it may lead to higher costs over time from skin sensitivity issues and stricter regulation on nickel use. Evaluating total lifecycle costs reveals nickel-free plating as a strategic investment for industries prioritizing sustainability and consumer safety.
Performance and Durability Analysis
Nickel-free plating offers enhanced corrosion resistance and hypoallergenic properties, making it ideal for sensitive skin applications where durability and environmental safety are critical. Nickel-based plating demonstrates superior hardness and wear resistance, providing long-lasting performance in high-friction environments but may cause allergic reactions for some users. Performance trade-offs depend on the specific use case, with nickel-free coatings prioritizing biocompatibility and nickel-based finishes excelling in mechanical durability.
Common Applications for Nickel-Free Plating
Nickel-free plating is widely used in medical devices, electronics, and jewelry to prevent allergic reactions and ensure biocompatibility. This plating method offers excellent corrosion resistance and durability without the risk of nickel-induced skin sensitization, making it ideal for wearable items and surgical instruments. Common applications include watches, eyeglass frames, and pacemakers where safety and hypoallergenic properties are critical.
Industries Preferencing Nickel-Based Plating
Industries such as automotive, electronics, and aerospace prefer nickel-based plating for its superior corrosion resistance, hardness, and wear protection in harsh environments. Nickel-based plating offers excellent adhesion and solderability, making it crucial for circuit boards and electronic connectors. Despite the rise of nickel-free alternatives to reduce allergy risks, nickel plating remains dominant where durability and performance are prioritized.
Regulatory Guidelines and Compliance Issues
Nickel-Free plating solutions comply more readily with stringent regulatory guidelines such as the EU's REACH and RoHS directives, which restrict nickel content due to its allergenic and environmental risks. Nickel-Based plating, while offering superior corrosion resistance and durability, faces increasing compliance challenges in consumer products subject to biocompatibility and occupational exposure limits. Manufacturers must carefully navigate these regulations to meet safety standards and avoid costly recalls or market restrictions.
Future Trends in Plating Technologies
Nickel-free plating technologies are gaining traction due to increasing regulatory restrictions on nickel exposure and growing demand for hypoallergenic surface coatings in electronics and automotive sectors. Innovations in advanced ceramics and composite materials are driving the development of nickel-free alternatives that offer comparable corrosion resistance and durability to traditional nickel-based plating. Emerging trends highlight the integration of environmentally friendly processes and nanotechnology to enhance performance while reducing toxic byproducts in plating applications.
Nickel-Free Plating vs Nickel-Based Plating Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com