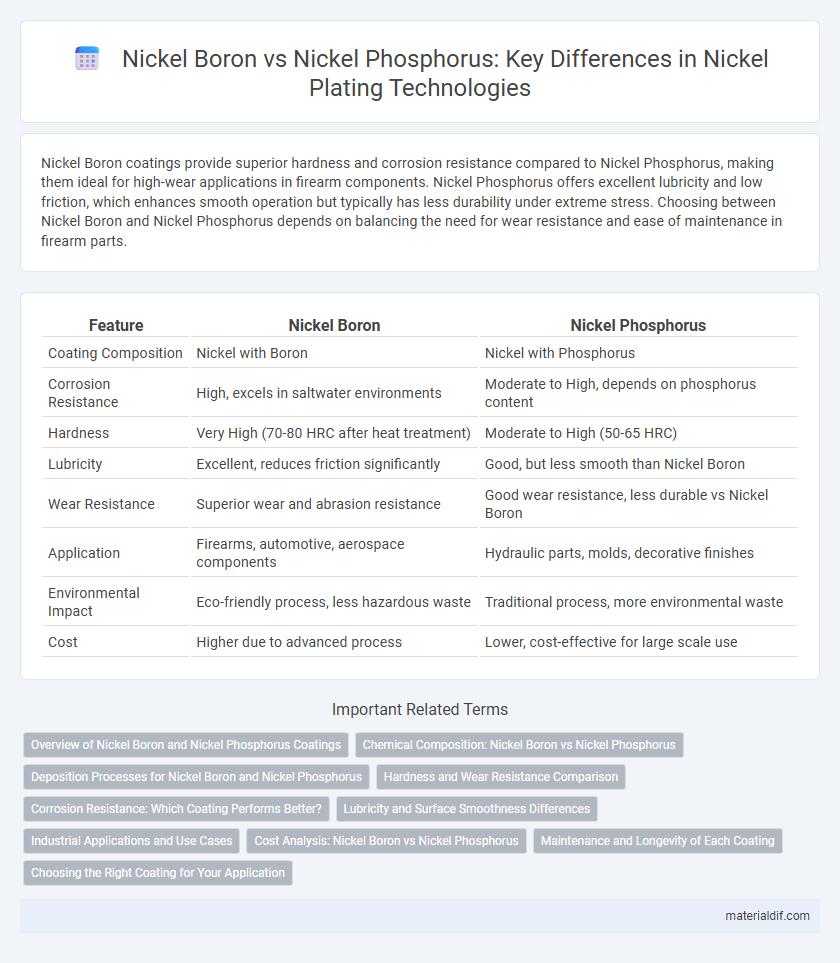
Nickel Boron coatings provide superior hardness and corrosion resistance compared to Nickel Phosphorus, making them ideal for high-wear applications in firearm components. Nickel Phosphorus offers excellent lubricity and low friction, which enhances smooth operation but typically has less durability under extreme stress. Choosing between Nickel Boron and Nickel Phosphorus depends on balancing the need for wear resistance and ease of maintenance in firearm parts.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Nickel Boron | Nickel Phosphorus |
|---|---|---|
| Coating Composition | Nickel with Boron | Nickel with Phosphorus |
| Corrosion Resistance | High, excels in saltwater environments | Moderate to High, depends on phosphorus content |
| Hardness | Very High (70-80 HRC after heat treatment) | Moderate to High (50-65 HRC) |
| Lubricity | Excellent, reduces friction significantly | Good, but less smooth than Nickel Boron |
| Wear Resistance | Superior wear and abrasion resistance | Good wear resistance, less durable vs Nickel Boron |
| Application | Firearms, automotive, aerospace components | Hydraulic parts, molds, decorative finishes |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly process, less hazardous waste | Traditional process, more environmental waste |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced process | Lower, cost-effective for large scale use |
Overview of Nickel Boron and Nickel Phosphorus Coatings
Nickel Boron coatings provide superior hardness, corrosion resistance, and reduced friction compared to traditional finishes, making them ideal for high-wear applications. In contrast, Nickel Phosphorus coatings offer excellent corrosion protection with good wear resistance and are commonly used in automotive and industrial environments. Both coatings serve different performance needs, with Nickel Boron favored for mechanical durability and Nickel Phosphorus preferred for chemical resistance and lubricity.
Chemical Composition: Nickel Boron vs Nickel Phosphorus
Nickel Boron coatings consist primarily of nickel combined with a small percentage of boron, typically enhancing hardness and wear resistance through a crystalline structure. Nickel Phosphorus coatings feature nickel with varying phosphorus content, which influences corrosion resistance and hardness by creating an amorphous or semi-amorphous layer depending on phosphorus concentration. The chemical composition difference between Nickel Boron and Nickel Phosphorus directly affects their physical properties and suitability for applications requiring specific wear and corrosion characteristics.
Deposition Processes for Nickel Boron and Nickel Phosphorus
Nickel Boron is commonly deposited through electroless plating, which utilizes a reducing agent like sodium hypophosphite to deposit a uniform, hard coating with excellent wear resistance and low friction properties. Nickel Phosphorus is also applied via electroless plating, but the process relies on the autocatalytic reduction of nickel ions by hypophosphite ions, producing coatings with varying phosphorus content that influence hardness and corrosion resistance. Both deposition methods enable conformal coatings on complex geometries, but the chemistry and deposition rates differ, impacting the microstructure and performance of the final layer.
Hardness and Wear Resistance Comparison
Nickel Boron coatings exhibit superior hardness, typically ranging from 1200 to 1400 Vickers, compared to Nickel Phosphorus's 600 to 900 Vickers, resulting in enhanced wear resistance and durability. The boron content creates a harder, more abrasion-resistant surface ideal for high-friction applications, while Nickel Phosphorus provides moderate hardness with excellent corrosion resistance. Industrial components requiring extended lifespan under stress often favor Nickel Boron for its outstanding wear performance.
Corrosion Resistance: Which Coating Performs Better?
Nickel Boron coatings offer superior corrosion resistance due to their harder, denser structure that forms a more effective barrier against environmental factors. Nickel Phosphorus coatings perform well but typically exhibit lower resistance to acidic and alkaline corrosion compared to Nickel Boron. For applications demanding enhanced durability and protection in harsh environments, Nickel Boron is generally the preferred choice.
Lubricity and Surface Smoothness Differences
Nickel Boron coatings exhibit superior lubricity and surface smoothness compared to Nickel Phosphorus, making them highly effective in reducing friction and wear in mechanical applications. The crystalline structure of Nickel Boron creates a harder, smoother surface ideal for precision parts requiring minimal friction. In contrast, Nickel Phosphorus coatings tend to have a more amorphous texture that provides good corrosion resistance but slightly less lubricity and surface uniformity.
Industrial Applications and Use Cases
Nickel Boron coatings exhibit superior hardness and wear resistance, making them ideal for industrial applications such as automotive parts, aerospace components, and cutting tools that require enhanced durability and low friction. Nickel Phosphorus coatings offer excellent corrosion resistance and uniform deposition, which benefits industries like electronics, chemical processing, and hydraulic systems where protection against oxidation and chemical exposure is critical. The choice between Nickel Boron and Nickel Phosphorus depends on specific use cases, with Nickel Boron favored for mechanical strength and Nickel Phosphorus preferred for corrosion protection in harsh environments.
Cost Analysis: Nickel Boron vs Nickel Phosphorus
Nickel Boron coatings generally exhibit higher upfront costs compared to Nickel Phosphorus due to more complex deposition processes and raw material expenses. Despite the initial investment, Nickel Boron offers superior wear resistance and hardness, potentially reducing long-term maintenance costs in industrial applications. Nickel Phosphorus remains a cost-effective choice for corrosion protection and moderate wear environments, balancing affordability and functional performance in budget-sensitive projects.
Maintenance and Longevity of Each Coating
Nickel Boron coatings exhibit superior hardness and wear resistance, significantly reducing the need for frequent maintenance compared to Nickel Phosphorus. The dense, uniform layer of Nickel Phosphorus offers excellent corrosion resistance but tends to degrade faster under high-friction conditions, impacting longevity. Maintenance intervals for Nickel Boron-coated components can extend by up to 30% due to their enhanced durability and lower susceptibility to galling and abrasion.
Choosing the Right Coating for Your Application
Nickel boron coatings offer superior hardness and wear resistance, making them ideal for high-friction applications such as firearm components and cutting tools. Nickel phosphorus coatings provide excellent corrosion resistance and are often selected for applications requiring chemical stability, like in automotive and electronics industries. Selecting the right coating depends on balancing factors such as hardness, corrosion resistance, and the specific environmental conditions of the application.
Nickel Boron vs Nickel Phosphorus Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com