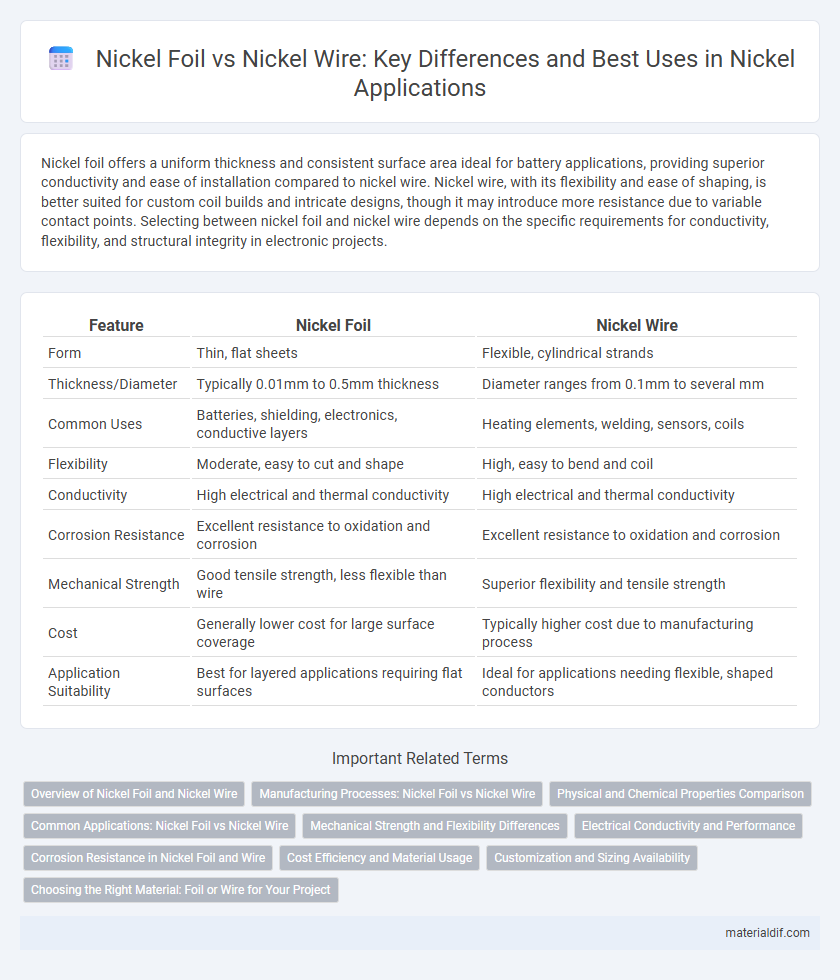
Nickel foil offers a uniform thickness and consistent surface area ideal for battery applications, providing superior conductivity and ease of installation compared to nickel wire. Nickel wire, with its flexibility and ease of shaping, is better suited for custom coil builds and intricate designs, though it may introduce more resistance due to variable contact points. Selecting between nickel foil and nickel wire depends on the specific requirements for conductivity, flexibility, and structural integrity in electronic projects.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Nickel Foil | Nickel Wire |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Thin, flat sheets | Flexible, cylindrical strands |
| Thickness/Diameter | Typically 0.01mm to 0.5mm thickness | Diameter ranges from 0.1mm to several mm |
| Common Uses | Batteries, shielding, electronics, conductive layers | Heating elements, welding, sensors, coils |
| Flexibility | Moderate, easy to cut and shape | High, easy to bend and coil |
| Conductivity | High electrical and thermal conductivity | High electrical and thermal conductivity |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent resistance to oxidation and corrosion | Excellent resistance to oxidation and corrosion |
| Mechanical Strength | Good tensile strength, less flexible than wire | Superior flexibility and tensile strength |
| Cost | Generally lower cost for large surface coverage | Typically higher cost due to manufacturing process |
| Application Suitability | Best for layered applications requiring flat surfaces | Ideal for applications needing flexible, shaped conductors |
Overview of Nickel Foil and Nickel Wire
Nickel foil offers a flat, flexible form factor ideal for applications requiring uniform surface contact and excellent corrosion resistance, while nickel wire provides strength and flexibility suited for winding, structural components, and electrical connections. Nickel foil typically comes in thin sheets with controlled thickness ranging from micrometers to millimeters, enabling precise layering in batteries, shielding, and electronics. Nickel wire varies in gauge and diameter, making it optimal for coils, resistance elements, and mechanical springs where tensile strength and conductivity are critical.
Manufacturing Processes: Nickel Foil vs Nickel Wire
Nickel foil is produced through a rolling process that compresses nickel slabs into thin, uniform sheets, ensuring high surface quality and controlled thickness ideal for electronic and battery applications. Nickel wire manufacturing involves drawing molten nickel through progressively smaller dies to create long, durable strands with excellent flexibility and tensile strength, commonly used in electrical wiring and resistance elements. Both methods require precise temperature control and material purity, but foil emphasizes surface flatness while wire focuses on mechanical strength and elongation.
Physical and Chemical Properties Comparison
Nickel foil exhibits a thin, flat structure with excellent malleability and high corrosion resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring surface coverage and flexibility. Nickel wire, characterized by its cylindrical shape and tensile strength, provides superior conductivity and mechanical durability in electrical and industrial uses. Both forms share the same chemical stability, including resistance to oxidation and chemical corrosion, but their differing physical formats optimize them for distinct engineering and manufacturing purposes.
Common Applications: Nickel Foil vs Nickel Wire
Nickel foil is commonly used in battery manufacturing, particularly for lithium-ion batteries, due to its excellent conductivity and flexibility, making it ideal for electrode layering and electrical contacts. Nickel wire, on the other hand, is frequently employed in heating elements, resistance wires, and alloy production because of its high melting point and mechanical strength. Both materials serve crucial roles in aerospace, electronics, and chemical industries, with foil preferred for precision applications and wire favored for structural and thermal functions.
Mechanical Strength and Flexibility Differences
Nickel foil offers superior mechanical strength due to its uniform thickness and dense grain structure, making it highly resistant to deformation under stress. In contrast, nickel wire provides greater flexibility and can be easily bent or shaped without breaking, thanks to its elongated form and ability to withstand tensile strain. This distinction makes nickel foil ideal for applications requiring rigidity and durability, while nickel wire suits tasks needing adaptability and intricate bending.
Electrical Conductivity and Performance
Nickel foil offers superior electrical conductivity due to its thin, uniform structure, enabling efficient electron flow and better surface contact in electrical applications. Nickel wire, while robust and flexible, exhibits lower conductivity compared to foil because of its thicker cross-sectional area and potential for higher resistance. Performance-wise, nickel foil excels in precision electronics and battery components, whereas nickel wire is preferred for applications requiring mechanical strength and durability.
Corrosion Resistance in Nickel Foil and Wire
Nickel foil and nickel wire both exhibit excellent corrosion resistance due to their high purity and stable oxide layer, but nickel foil offers a more uniform and consistent protective barrier ideal for applications exposed to harsh chemicals or marine environments. Nickel foil's thin, flat structure ensures even coverage and minimizes corrosion sites compared to nickel wire's cylindrical form, which may develop localized corrosion at bends or welds. This makes nickel foil preferable for electronic components and surface coatings where long-term durability against oxidation and corrosion is critical.
Cost Efficiency and Material Usage
Nickel foil offers superior material utilization with minimal waste due to its thin, uniform structure compared to nickel wire, which requires additional processing like drawing and winding. The cost efficiency of nickel foil is enhanced by its ability to cover larger surface areas at lower material volumes, reducing overall raw material consumption and energy costs. In contrast, nickel wire incurs higher production expenses due to its bulkier form and increased machining requirements, making foil the preferred choice for applications prioritizing economical and efficient material use.
Customization and Sizing Availability
Nickel foil offers extensive customization options in thickness and width, making it ideal for applications requiring precise dimensional control and flexible sizing availability. Nickel wire, while also customizable, primarily varies in diameter and length, catering to uses where round cross-sections and tensile strength are critical. Manufacturers provide a broad range of sizes for both forms, but foil allows for finer adjustments to meet specific surface area and conductivity requirements.
Choosing the Right Material: Foil or Wire for Your Project
Nickel foil offers a thin, flexible option ideal for applications requiring high surface area and efficient heat dissipation, while nickel wire provides greater mechanical strength and durability for structural or electrical purposes. The choice depends on project requirements such as conductivity, flexibility, and thermal management, with foil excelling in battery electrodes and shielding, and wire preferred for resistors and connectors. Evaluating specific performance needs ensures optimal material selection for enhanced efficiency and longevity.
Nickel foil vs nickel wire Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com