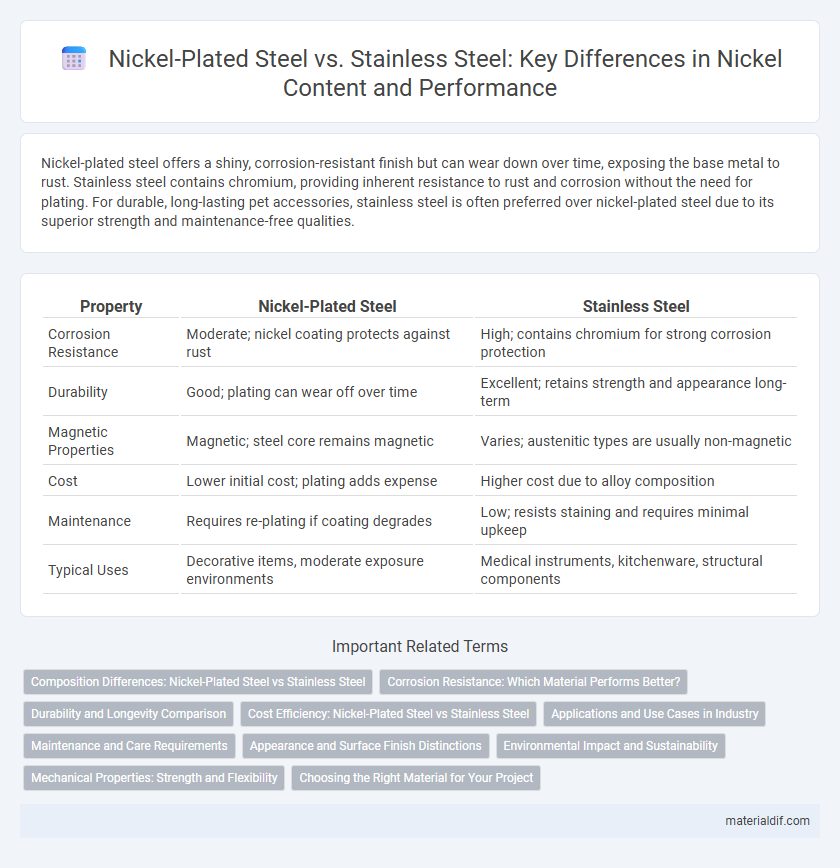
Nickel-plated steel offers a shiny, corrosion-resistant finish but can wear down over time, exposing the base metal to rust. Stainless steel contains chromium, providing inherent resistance to rust and corrosion without the need for plating. For durable, long-lasting pet accessories, stainless steel is often preferred over nickel-plated steel due to its superior strength and maintenance-free qualities.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nickel-Plated Steel | Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate; nickel coating protects against rust | High; contains chromium for strong corrosion protection |
| Durability | Good; plating can wear off over time | Excellent; retains strength and appearance long-term |
| Magnetic Properties | Magnetic; steel core remains magnetic | Varies; austenitic types are usually non-magnetic |
| Cost | Lower initial cost; plating adds expense | Higher cost due to alloy composition |
| Maintenance | Requires re-plating if coating degrades | Low; resists staining and requires minimal upkeep |
| Typical Uses | Decorative items, moderate exposure environments | Medical instruments, kitchenware, structural components |
Composition Differences: Nickel-Plated Steel vs Stainless Steel
Nickel-plated steel consists of a carbon steel base coated with a thin layer of nickel to enhance corrosion resistance and surface hardness, whereas stainless steel is an alloy primarily composed of iron, chromium (usually 10.5% or more), and varying amounts of nickel and other elements that provide intrinsic corrosion resistance throughout the material. The nickel plating on steel acts as a barrier against oxidation but can wear off, exposing the underlying steel to rust, while stainless steel's chromium content forms a passive oxide layer that self-heals and protects the entire alloy. Variations in nickel content are significant; stainless steels often contain 8% to 20% nickel, which improves ductility and corrosion resistance, unlike nickel-plated steel where nickel only serves as a surface coating.
Corrosion Resistance: Which Material Performs Better?
Nickel-plated steel offers enhanced corrosion resistance compared to bare steel due to the protective nickel layer that prevents oxidation and rust. Stainless steel, particularly grades like 304 and 316, contains chromium which forms a passive oxide layer, providing superior and long-lasting corrosion resistance in various environments. In highly corrosive or marine settings, stainless steel generally outperforms nickel-plated steel by maintaining integrity and preventing corrosion without additional coatings.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Nickel-plated steel offers enhanced corrosion resistance and surface hardness compared to untreated steel, extending its lifespan in moderate environments. Stainless steel, particularly grades like 304 and 316, contains chromium and nickel alloys that provide superior rust resistance and durability in more aggressive or high-moisture conditions. Over time, stainless steel generally outperforms nickel-plated steel in longevity due to its inherent corrosion-resistant properties and ability to withstand wear without plating degradation.
Cost Efficiency: Nickel-Plated Steel vs Stainless Steel
Nickel-plated steel offers superior cost efficiency by providing corrosion resistance at a lower price compared to stainless steel, making it ideal for budget-sensitive applications. While stainless steel boasts inherent durability and requires less maintenance, its higher initial cost can be a limiting factor for large-scale projects. Choosing nickel-plated steel balances durability and affordability, especially where moderate corrosion resistance suffices.
Applications and Use Cases in Industry
Nickel-plated steel is widely used in automotive parts, electrical components, and hardware due to its enhanced corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal, making it ideal for decorative and functional surface coatings. Stainless steel, characterized by its high chromium content, is preferred in food processing, medical instruments, and construction for its durability, resistance to rust, and hygienic properties. Industries often select nickel-plated steel for cost-effective protection and lightweight applications, while stainless steel is chosen for heavy-duty, high-corrosion environments demanding long-term structural integrity.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Nickel-plated steel requires regular maintenance to prevent the nickel layer from wearing off or corroding, especially in humid or abrasive environments, necessitating frequent cleaning with non-abrasive materials and protective coatings. Stainless steel, containing chromium, offers superior corrosion resistance and minimal upkeep, often only requiring occasional cleaning to maintain its appearance and prevent staining. Proper maintenance of nickel-plated steel extends its lifespan but generally involves more effort compared to the nearly maintenance-free nature of stainless steel in similar conditions.
Appearance and Surface Finish Distinctions
Nickel-plated steel exhibits a bright, reflective finish with a uniform silver-white appearance that enhances corrosion resistance and surface hardness, making it ideal for decorative and industrial applications. Stainless steel features a naturally occurring oxide layer that provides a matte to semi-gloss finish, varying from smooth to slightly textured surfaces depending on the grade and treatment applied. The key distinction lies in nickel-plated steel's enhanced mirror-like shine compared to stainless steel's more subdued, durable surface finish.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Nickel-plated steel involves electroplating processes that consume significant energy and generate hazardous waste, contributing to environmental pollution and resource depletion. Stainless steel, primarily an alloy of iron, chromium, and nickel, offers enhanced corrosion resistance and a longer lifespan, reducing the need for frequent replacement and minimizing overall environmental impact. Recycling stainless steel is more efficient and widespread, supporting sustainability by conserving raw materials and lowering greenhouse gas emissions compared to nickel-plated steel.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Flexibility
Nickel-plated steel offers enhanced surface hardness and corrosion resistance while maintaining the high tensile strength of the underlying steel, making it suitable for applications requiring durability and moderate flexibility. Stainless steel, especially grades like 304 and 316, provides superior strength combined with excellent ductility and flexibility due to its austenitic microstructure, enabling it to withstand deformation without cracking. The choice between nickel-plated steel and stainless steel depends on the balance needed between surface wear resistance and overall mechanical flexibility in the specific engineering application.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Project
Nickel-plated steel offers enhanced corrosion resistance and a smooth, attractive finish, making it ideal for decorative applications and moderate environmental exposure. Stainless steel provides superior durability and resistance to extreme corrosion and high temperatures, suitable for industrial, marine, and harsh environments. Selecting between nickel-plated steel and stainless steel depends on project requirements such as budget, exposure conditions, and desired aesthetic longevity.
Nickel-plated steel vs Stainless steel Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com