Cupped nickel coins have a curved concave shape that enhances grip and tactile feedback, making them popular in vending machines and coin-operated devices. Flat nickel coins feature a smooth, even surface ideal for general circulation and easy stacking in coin rolls. The choice between cupped and flat nickel depends on the specific use case, balancing durability, handling, and machine compatibility.
Table of Comparison
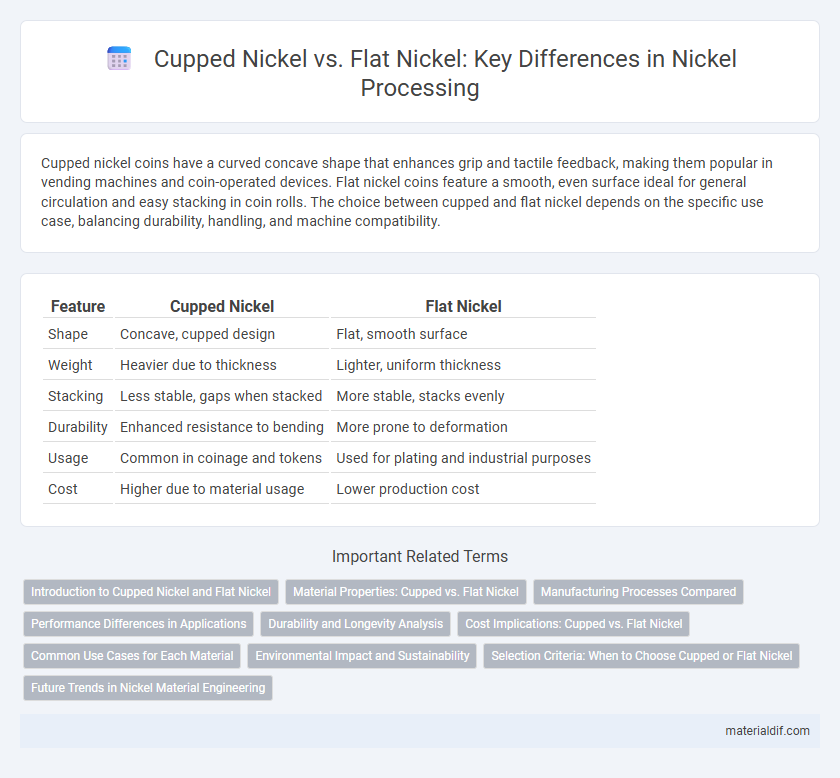
| Feature | Cupped Nickel | Flat Nickel |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Concave, cupped design | Flat, smooth surface |
| Weight | Heavier due to thickness | Lighter, uniform thickness |
| Stacking | Less stable, gaps when stacked | More stable, stacks evenly |
| Durability | Enhanced resistance to bending | More prone to deformation |
| Usage | Common in coinage and tokens | Used for plating and industrial purposes |
| Cost | Higher due to material usage | Lower production cost |
Introduction to Cupped Nickel and Flat Nickel
Cupped nickel, characterized by its concave shape, offers enhanced stacking stability and reduced surface wear compared to flat nickel, which is uniformly flat and commonly used in coinage and electronic applications. The cupped design optimizes material use and provides improved durability, making it preferable in high-friction environments. Flat nickel, however, remains a versatile choice due to its simpler manufacturing process and consistent surface area suitable for plating and coating.
Material Properties: Cupped vs. Flat Nickel
Cupped nickel exhibits enhanced mechanical strength and improved resistance to deformation compared to flat nickel due to its curved geometry distributing stress more evenly. Flat nickel, while easier to manufacture, typically shows lower tensile strength and is more prone to bending under pressure. Both forms retain similar chemical properties such as corrosion resistance, but the distinct structural differences significantly influence their performance in mechanical applications.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Cupped nickel coins are produced through a stamping process that creates a concave shape, enhancing their structural integrity and resistance to wear, whereas flat nickel coins undergo a traditional blanking and striking procedure that results in a flat, uniform surface. The cupped design requires precise die engineering and additional forming steps, increasing manufacturing complexity and cost compared to the simpler flat nickel fabrication. Material usage and metal flow during striking differ, impacting the durability and tactile feel of cupped versus flat nickel coins in circulation.
Performance Differences in Applications
Cupped nickel coins exhibit enhanced durability and resistance to wear compared to flat nickel coins, making them ideal for high-circulation environments like vending machines and public transport. The recessed center design reduces surface contact, minimizing scratches and preserving legibility over time. Flat nickel coins, while easier to stack and manufacture, typically face higher abrasion rates, impacting their longevity in rigorous handling conditions.
Durability and Longevity Analysis
Cupped nickel coins exhibit enhanced durability due to their convex shape, which distributes impact forces more evenly and reduces surface wear. Flat nickel coins, while easier to stack and handle, tend to show faster edge wear and surface scratching under repeated use. Longevity analysis indicates cupped nickels maintain structural integrity and aesthetic appearance longer in circulation, making them superior for extended usage.
Cost Implications: Cupped vs. Flat Nickel
Cupped nickel coins typically involve higher production costs due to the more complex minting process and additional material required for the raised rim, increasing overall expenses. Flat nickel fabrication is more cost-effective, benefiting from simpler stamping techniques and reduced metal usage, making it preferred for large-scale circulation. The choice between cupped and flat nickel directly impacts budget allocation in minting operations, balancing durability and aesthetics against manufacturing efficiency.
Common Use Cases for Each Material
Cupped nickel is commonly used in minting coins and collectible tokens due to its durability and ability to hold detailed designs. Flat nickel is preferred in industrial applications such as batteries, plating, and electronics, where a uniform surface and conductivity are essential. Both materials serve specialized roles, with cupped nickel excelling in currency production and flat nickel dominating technological and manufacturing sectors.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cupped nickel requires less raw material extraction due to its concave shape, reducing environmental depletion compared to flat nickel that uses more metal for the same surface area. The production of cupped nickel coins typically results in lower energy consumption and reduced carbon emissions, enhancing sustainability efforts. Recycling cupped nickel is more efficient as the material's unique shape facilitates easier collection and reprocessing, minimizing landfill waste and promoting circular economy principles.
Selection Criteria: When to Choose Cupped or Flat Nickel
Cupped nickel coins are preferred for vending machines and coin-operated devices due to their enhanced tactile grip and resistance to jamming, making them ideal in high-usage scenarios. Flat nickel coins are typically chosen for ease of stacking and storage, suited for collectors and cash handling where uniform thickness is essential. Selection depends on application needs, with cupped nickels optimizing mechanical reliability and flat nickels favoring convenience in handling and inventory management.
Future Trends in Nickel Material Engineering
Advancements in nickel material engineering indicate a growing shift towards cupped nickel designs due to their enhanced structural integrity and improved heat dissipation capabilities compared to flat nickel. Research in metallurgy highlights that cupped nickel's increased surface area facilitates better catalytic efficiency in energy storage and battery applications. Future trends prioritize optimizing cupped nickel alloys to meet the demands of electric vehicle batteries and green technology industries, promoting sustainability and performance.
Cupped nickel vs flat nickel Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com