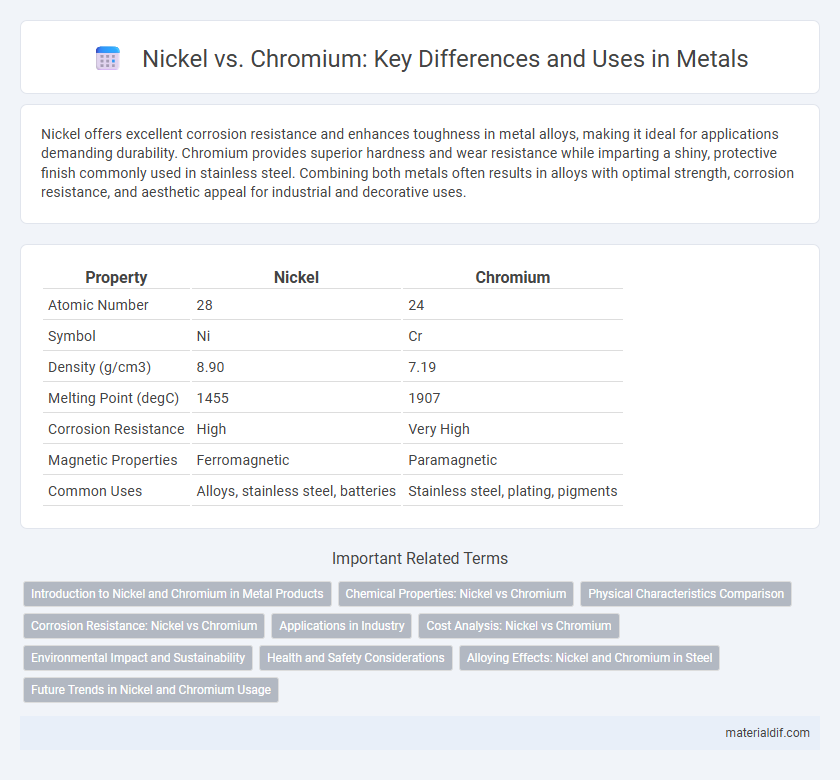
Nickel offers excellent corrosion resistance and enhances toughness in metal alloys, making it ideal for applications demanding durability. Chromium provides superior hardness and wear resistance while imparting a shiny, protective finish commonly used in stainless steel. Combining both metals often results in alloys with optimal strength, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal for industrial and decorative uses.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nickel | Chromium |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 28 | 24 |
| Symbol | Ni | Cr |
| Density (g/cm3) | 8.90 | 7.19 |
| Melting Point (degC) | 1455 | 1907 |
| Corrosion Resistance | High | Very High |
| Magnetic Properties | Ferromagnetic | Paramagnetic |
| Common Uses | Alloys, stainless steel, batteries | Stainless steel, plating, pigments |
Introduction to Nickel and Chromium in Metal Products
Nickel and chromium are essential metals widely used in alloy production to enhance corrosion resistance and durability. Nickel provides excellent toughness and resistance to oxidation, making it ideal for stainless steel and industrial applications. Chromium contributes to hardness and a shiny finish, significantly improving metal surface protection and wear resistance.
Chemical Properties: Nickel vs Chromium
Nickel exhibits a lower reactivity compared to chromium, resisting oxidation due to its stable electron configuration, while chromium readily forms a protective oxide layer that enhances its corrosion resistance. Both metals have multiple oxidation states, with nickel primarily showing +2 and +3 states, and chromium exhibiting a wider range from +2 to +6, influencing their diverse chemical behaviors. Chromium's amphoteric nature allows it to react with both acids and bases, whereas nickel is mainly reactive with acids, defining their applications in chemical and industrial processes.
Physical Characteristics Comparison
Nickel exhibits a silver-white color with a slight golden hue, a melting point of 1455degC, and high corrosion resistance, making it ideal for alloys and plating. Chromium has a distinctive shiny, steely-gray appearance, a higher melting point of 1907degC, and exceptional hardness and oxidation resistance, commonly used in stainless steel production. Both metals possess excellent magnetic properties, though nickel is more ductile, while chromium is brittle at room temperature.
Corrosion Resistance: Nickel vs Chromium
Nickel offers superior corrosion resistance in acidic and alkaline environments, making it ideal for harsh chemical applications. Chromium forms a robust oxide layer that provides excellent protection against oxidation and surface corrosion, especially in stainless steel alloys. The combination of nickel and chromium in alloys enhances overall corrosion resistance, balancing toughness and environmental durability.
Applications in Industry
Nickel is extensively used in stainless steel production, enhancing corrosion resistance and toughness, making it ideal for chemical processing plants and aerospace components. Chromium is crucial for creating hard, wear-resistant surfaces in automotive parts and decorative coatings due to its exceptional hardness and oxidation resistance. Both metals play vital roles in industrial alloys, with nickel offering superior thermal stability and chromium providing enhanced surface durability.
Cost Analysis: Nickel vs Chromium
Nickel typically exhibits a higher cost than chromium due to its greater extraction and refining expenses, making it less economical for large-scale applications. Chromium offers a cost advantage, especially in stainless steel production, due to its abundant availability and lower price per ton. The price difference impacts material selection in industries where budget constraints prioritize durable yet affordable metals.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Nickel mining generates significant environmental challenges including habitat destruction, water pollution from tailings, and high energy consumption, impacting ecosystem sustainability. Chromium extraction, particularly for hexavalent chromium, poses toxic risks to soil and groundwater, demanding stringent waste management to minimize contamination. Sustainable practices for both metals emphasize recycling, cleaner extraction technologies, and reducing carbon footprints to mitigate long-term ecological damage.
Health and Safety Considerations
Nickel exposure often causes allergic reactions and contact dermatitis in sensitive individuals, requiring strict handling precautions to minimize skin contact and inhalation of dust or fumes. Chromium, particularly hexavalent chromium, is recognized as a potent carcinogen and respiratory hazard, necessitating robust ventilation controls and personal protective equipment in industrial settings. Both metals demand rigorous workplace safety standards to prevent chronic health effects and ensure worker safety.
Alloying Effects: Nickel and Chromium in Steel
Nickel enhances steel's toughness, corrosion resistance, and ductility by stabilizing the austenitic phase, making it ideal for stainless alloys used in harsh environments. Chromium significantly improves hardness, wear resistance, and oxidation resistance by forming a passive oxide layer on the steel surface, crucial for stainless and tool steels. Combining nickel and chromium in steel alloys creates a balanced microstructure that optimizes strength, corrosion resistance, and heat resistance for diverse industrial applications.
Future Trends in Nickel and Chromium Usage
Nickel usage is projected to grow significantly due to increased demand in electric vehicle batteries and stainless steel production, driven by the global shift toward renewable energy and sustainability. Chromium continues to be essential for corrosion-resistant alloys, with future trends emphasizing its role in advanced stainless steel grades and environmentally friendly manufacturing processes. Innovations in recycling technologies for both metals are expected to enhance resource efficiency and reduce supply chain vulnerabilities.
Nickel vs Chromium Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com