Copper offers excellent electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for electrical wiring and plumbing applications. Nickel provides superior hardness and resistance to oxidation, often used in alloy formation and industrial machinery parts. Comparing copper and nickel reveals copper's advantage in conductivity, while nickel excels in strength and durability.
Table of Comparison
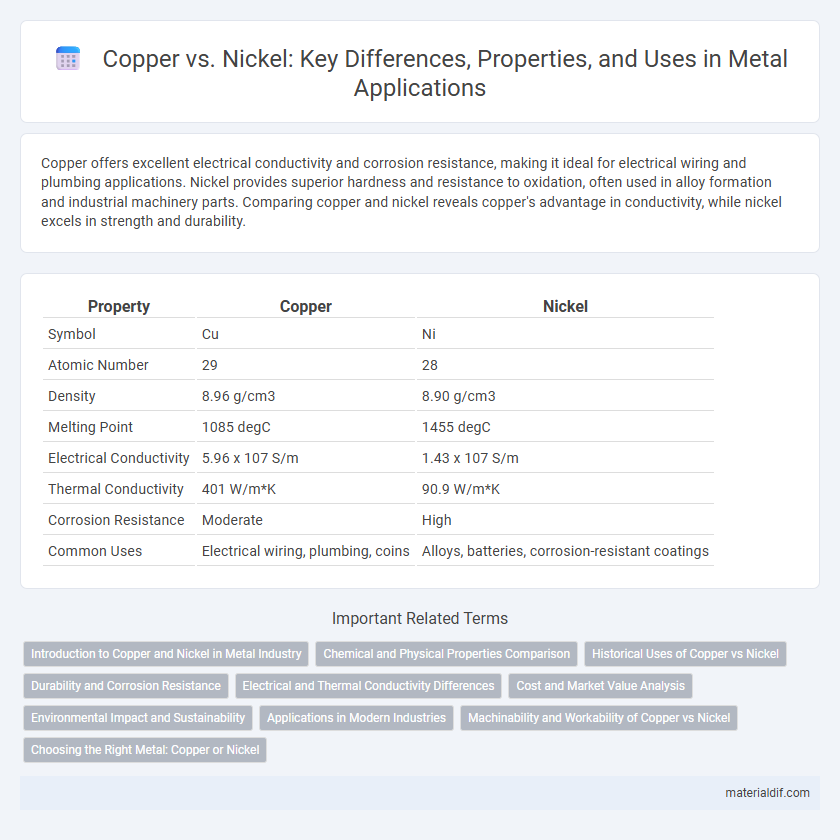
| Property | Copper | Nickel |
|---|---|---|
| Symbol | Cu | Ni |
| Atomic Number | 29 | 28 |
| Density | 8.96 g/cm3 | 8.90 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 1085 degC | 1455 degC |
| Electrical Conductivity | 5.96 x 107 S/m | 1.43 x 107 S/m |
| Thermal Conductivity | 401 W/m*K | 90.9 W/m*K |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Common Uses | Electrical wiring, plumbing, coins | Alloys, batteries, corrosion-resistant coatings |
Introduction to Copper and Nickel in Metal Industry
Copper and nickel are essential metals in the metal industry, each prized for distinct properties and applications. Copper offers exceptional electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance, making it a preferred choice for electrical wiring and plumbing systems. Nickel's strength, corrosion resistance, and heat tolerance enhance stainless steel alloys and battery technologies, driving innovation in aerospace and renewable energy sectors.
Chemical and Physical Properties Comparison
Copper exhibits excellent electrical conductivity of 5.96 x 10^7 S/m, surpassing nickel's conductivity of 1.43 x 10^7 S/m, making copper ideal for electrical applications. Nickel, with a higher melting point of 1455degC compared to copper's 1085degC, offers superior thermal stability and corrosion resistance. Both metals have distinct densities--copper at 8.96 g/cm3 and nickel at 8.90 g/cm3--impacting their use in industrial design and manufacturing.
Historical Uses of Copper vs Nickel
Copper has been used since ancient times for tools, weapons, and currency due to its excellent electrical conductivity and malleability, with evidence dating back over 10,000 years in Anatolia. Nickel's historical use began much later, prominently in the 18th century, primarily for its corrosion resistance and strength, leading to its adoption in coinage and plating. Both metals have played critical roles in industrial development, with copper dominating early civilization technologies and nickel advancing modern metallurgy and alloy production.
Durability and Corrosion Resistance
Copper exhibits excellent corrosion resistance, particularly in atmospheric and marine environments, due to its natural patina that forms over time, protecting the metal beneath. Nickel outperforms copper in terms of hardness and wear resistance, making it highly durable in abrasive conditions and ideal for plating applications that require long-lasting surfaces. Both metals demonstrate strong resistance to corrosion, but nickel's superior strength offers enhanced durability in harsher industrial and chemical environments.
Electrical and Thermal Conductivity Differences
Copper exhibits significantly higher electrical conductivity than nickel, making it the preferred choice for electrical wiring and components. Its thermal conductivity also surpasses nickel's, facilitating more efficient heat dissipation in applications such as heat exchangers and electronic devices. Nickel, while lower in conductivity, offers superior corrosion resistance and mechanical strength for specialized uses.
Cost and Market Value Analysis
Copper generally has a lower cost per pound compared to nickel, making it more economical for large-scale industrial applications. Nickel's higher market value is driven by its superior corrosion resistance and use in specialized alloys, boosting demand in aerospace and battery manufacturing sectors. Fluctuations in global supply chains, particularly from major producers in Indonesia for nickel and Chile for copper, significantly impact their respective prices and market stability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Copper mining generates significant habitat disruption and water pollution, but it is highly recyclable, reducing long-term environmental impact. Nickel extraction often involves energy-intensive processes that produce toxic waste and greenhouse gas emissions, yet advancements in sustainable mining are improving its footprint. Both metals are vital for clean energy technologies, with recycling and responsible sourcing key to minimizing ecological damage and promoting sustainability.
Applications in Modern Industries
Copper excels in electrical wiring, plumbing, and renewable energy systems due to its superior conductivity and corrosion resistance. Nickel is preferred in stainless steel production, aerospace components, and batteries, offering exceptional strength and oxidation resistance. Both metals play crucial roles in manufacturing electronics, automotive parts, and chemical processing equipment.
Machinability and Workability of Copper vs Nickel
Copper exhibits superior machinability compared to nickel due to its softer nature and lower hardness, allowing for easier cutting and shaping without excessive tool wear. Nickel, while offering greater strength and corrosion resistance, has lower workability and requires more power and specialized tooling to machine effectively. The enhanced ductility of copper also contributes to its better formability in manufacturing processes such as stamping and forging.
Choosing the Right Metal: Copper or Nickel
Copper offers excellent electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for electrical wiring and plumbing applications. Nickel provides superior strength, hardness, and resistance to oxidation, often used in stainless steel alloys and chemical processing equipment. Selecting between copper and nickel depends on balancing conductivity needs with mechanical durability and environmental exposure.
Copper vs Nickel Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com