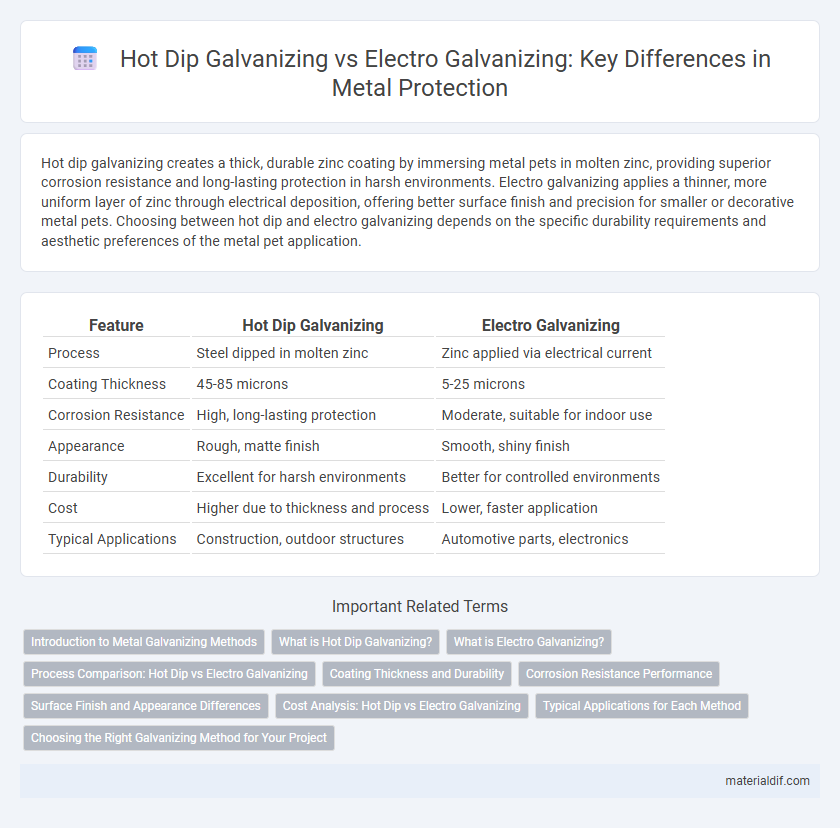
Hot dip galvanizing creates a thick, durable zinc coating by immersing metal pets in molten zinc, providing superior corrosion resistance and long-lasting protection in harsh environments. Electro galvanizing applies a thinner, more uniform layer of zinc through electrical deposition, offering better surface finish and precision for smaller or decorative metal pets. Choosing between hot dip and electro galvanizing depends on the specific durability requirements and aesthetic preferences of the metal pet application.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hot Dip Galvanizing | Electro Galvanizing |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Steel dipped in molten zinc | Zinc applied via electrical current |
| Coating Thickness | 45-85 microns | 5-25 microns |
| Corrosion Resistance | High, long-lasting protection | Moderate, suitable for indoor use |
| Appearance | Rough, matte finish | Smooth, shiny finish |
| Durability | Excellent for harsh environments | Better for controlled environments |
| Cost | Higher due to thickness and process | Lower, faster application |
| Typical Applications | Construction, outdoor structures | Automotive parts, electronics |
Introduction to Metal Galvanizing Methods
Hot dip galvanizing involves immersing steel or iron into molten zinc, creating a thick, durable coating that provides superior corrosion resistance ideal for outdoor and industrial applications. Electro galvanizing uses an electrochemical process to deposit a thin layer of zinc onto the metal surface, offering a smoother finish and enhanced aesthetic appeal but with less corrosion protection compared to hot dip galvanizing. Both methods improve metal longevity by preventing rust, making them essential techniques in metal finishing and protection industries.
What is Hot Dip Galvanizing?
Hot Dip Galvanizing is a corrosion protection method where steel or iron is submerged in molten zinc at around 450degC, creating a robust, metallurgical bond with the base metal. This process forms thick, durable zinc coatings that offer superior resistance against rust and environmental wear compared to thinner electro-galvanized layers. Its applications include industrial structures, automotive parts, and outdoor equipment requiring long-term protection in harsh conditions.
What is Electro Galvanizing?
Electro galvanizing is a metal finishing process that uses electrochemical deposition to apply a thin layer of zinc onto steel or iron components. This method produces a smooth, uniform coating that enhances corrosion resistance while maintaining a high-quality surface finish suitable for automotive and appliance industries. Compared to hot dip galvanizing, electro galvanizing offers precise control of coating thickness and superior aesthetics, though it provides thinner protection against harsh environmental conditions.
Process Comparison: Hot Dip vs Electro Galvanizing
Hot dip galvanizing involves immersing steel in molten zinc at approximately 450degC, creating a thick, durable zinc-iron alloy coating that offers superior corrosion resistance and long-term protection. Electro galvanizing uses an electric current to deposit a thin zinc layer at ambient temperatures, resulting in a smoother, more uniform finish but with less robust corrosion protection compared to hot dip. The choice between the two depends on application requirements: hot dip suits heavy-duty, outdoor environments, while electro galvanizing favors precision parts and indoor use.
Coating Thickness and Durability
Hot dip galvanizing creates a thicker zinc coating, typically ranging from 45 to 85 microns, which significantly enhances corrosion resistance and durability in harsh environments. Electro galvanizing produces a thinner coating, usually between 5 to 25 microns, offering a smoother finish but less protection against abrasion and long-term corrosion. The increased coating thickness of hot dip galvanizing results in superior durability for outdoor and industrial applications compared to the more aesthetic but less robust electro galvanized finish.
Corrosion Resistance Performance
Hot dip galvanizing provides superior corrosion resistance by coating steel with a thick layer of zinc, forming a robust barrier that withstands harsh environmental conditions and mechanical damage. Electro galvanizing applies a thinner zinc layer through electroplating, offering moderate protection primarily suitable for indoor or less aggressive environments. The thickness and metallurgical bond in hot dip galvanized coatings ensure longer-lasting durability against rust compared to the thinner, more sacrificial electroplated zinc layer.
Surface Finish and Appearance Differences
Hot dip galvanizing produces a thicker, more rugged zinc coating with a matte, textured surface due to the immersion process, which enhances corrosion resistance but results in a less smooth finish. Electro galvanizing offers a thinner, more uniform zinc layer with a bright, shiny, and smooth appearance ideal for aesthetic applications requiring precise surface detail. Surface finish in hot dip galvanizing tends to be rougher and more uneven compared to the glossy, consistent appearance achieved through electro galvanizing.
Cost Analysis: Hot Dip vs Electro Galvanizing
Hot dip galvanizing generally incurs higher initial costs due to its thicker zinc coating and extensive surface preparation compared to electro galvanizing, which offers a thinner, more uniform layer at a lower upfront price. Despite the greater initial investment, hot dip galvanizing provides superior long-term corrosion resistance, reducing maintenance and replacement expenses in aggressive environments. Electro galvanizing suits applications prioritizing cost-efficiency and aesthetic finish in less corrosive settings, balancing upfront savings with moderate durability.
Typical Applications for Each Method
Hot dip galvanizing is commonly used for outdoor structural steel components such as bridges, guardrails, and utility poles due to its thick, durable zinc coating that offers superior corrosion resistance in harsh environments. Electro galvanizing is preferred for automotive parts, appliances, and electronic components where a smooth, uniform finish and precise thickness control are critical for aesthetic appeal and performance. Both methods serve distinct industrial applications based on environmental exposure and coating requirements.
Choosing the Right Galvanizing Method for Your Project
Hot dip galvanizing provides a thick, durable zinc coating by immersing steel in molten zinc, ideal for outdoor structures and heavy-duty applications requiring superior corrosion resistance. Electro galvanizing applies a thinner, more uniform zinc layer through electroplating, offering better surface finish and is suitable for indoor or less corrosive environments. Selecting the right galvanizing method depends on factors like environmental exposure, required coating thickness, durability needs, and aesthetic considerations for the metal project.
Hot Dip Galvanizing vs Electro Galvanizing Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com