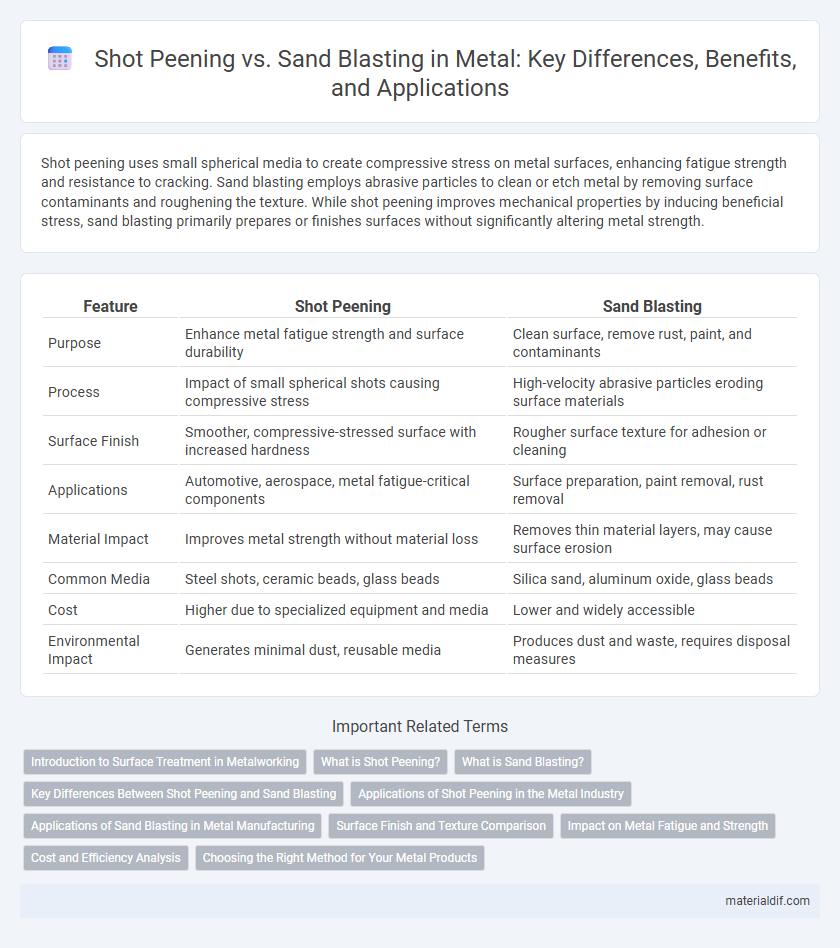
Shot peening uses small spherical media to create compressive stress on metal surfaces, enhancing fatigue strength and resistance to cracking. Sand blasting employs abrasive particles to clean or etch metal by removing surface contaminants and roughening the texture. While shot peening improves mechanical properties by inducing beneficial stress, sand blasting primarily prepares or finishes surfaces without significantly altering metal strength.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Shot Peening | Sand Blasting |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Enhance metal fatigue strength and surface durability | Clean surface, remove rust, paint, and contaminants |
| Process | Impact of small spherical shots causing compressive stress | High-velocity abrasive particles eroding surface materials |
| Surface Finish | Smoother, compressive-stressed surface with increased hardness | Rougher surface texture for adhesion or cleaning |
| Applications | Automotive, aerospace, metal fatigue-critical components | Surface preparation, paint removal, rust removal |
| Material Impact | Improves metal strength without material loss | Removes thin material layers, may cause surface erosion |
| Common Media | Steel shots, ceramic beads, glass beads | Silica sand, aluminum oxide, glass beads |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized equipment and media | Lower and widely accessible |
| Environmental Impact | Generates minimal dust, reusable media | Produces dust and waste, requires disposal measures |
Introduction to Surface Treatment in Metalworking
Shot peening and sand blasting are surface treatment techniques widely used in metalworking to enhance material properties and prepare surfaces for further processing. Shot peening involves bombarding the metal surface with small spherical media to induce compressive residual stresses, improving fatigue resistance and durability, while sand blasting uses high-pressure abrasive particles to clean or texture the surface, promoting better adhesion of coatings. Both methods are critical in optimizing the mechanical performance and longevity of metal components in automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications.
What is Shot Peening?
Shot peening is a metal surface treatment process that involves bombarding the material with small spherical media to induce compressive residual stress and enhance fatigue strength. This technique improves resistance to cracking and extends the lifespan of metal components, especially in aerospace, automotive, and industrial machinery. Unlike sand blasting, which primarily cleans or etches surfaces, shot peening actively strengthens metal by altering its microstructure.
What is Sand Blasting?
Sand blasting is a surface treatment process that uses high-pressure compressed air to propel abrasive materials like sand, glass beads, or steel grit against a metal surface. This technique effectively removes rust, scale, paint, and contaminants while also creating a roughened texture that improves adhesion for coatings or paints. Unlike shot peening, which induces compressive stresses to enhance fatigue strength, sand blasting primarily serves to clean and prepare metal surfaces.
Key Differences Between Shot Peening and Sand Blasting
Shot peening involves bombarding metal surfaces with small spherical media to induce compressive stress, enhancing fatigue strength and resistance to stress corrosion cracking. Sand blasting uses abrasive particles propelled at high velocity to clean or roughen metal surfaces, primarily for surface preparation rather than strengthening. The key differences lie in their purpose: shot peening strengthens metal by creating beneficial residual stresses, while sand blasting focuses on surface cleaning and texture alteration without altering metal's internal structure.
Applications of Shot Peening in the Metal Industry
Shot peening is widely used in the metal industry to enhance fatigue strength and resistance to stress corrosion cracking in components such as automotive gears, aircraft landing gear, and turbine blades. This surface treatment introduces beneficial compressive stresses on metal surfaces, extending the lifespan of critical parts exposed to cyclic loading. Its applications also include improving the durability of springs, crankshafts, and welded structures by reducing the risk of crack initiation and propagation.
Applications of Sand Blasting in Metal Manufacturing
Sand blasting is widely used in metal manufacturing for surface preparation, including rust and scale removal from steel before painting or coating. It enhances adhesion by creating a uniform, roughened surface profile suitable for protective coatings and powder coating processes. Additionally, sand blasting is employed for cleaning castings, deburring edges, and restoring metal surfaces to improve durability and aesthetic appeal.
Surface Finish and Texture Comparison
Shot peening creates a uniformly compressed surface layer with fine, rounded indentations that enhance fatigue resistance, resulting in a smoother and more controlled surface finish compared to sand blasting. Sand blasting produces a rougher, more irregular texture by forcefully propelling abrasive particles, which is ideal for removing surface contaminants but less effective in improving metal fatigue properties. Surface hardness and microstructure integrity are better preserved through shot peening, making it optimal for applications requiring precision surface engineering.
Impact on Metal Fatigue and Strength
Shot peening improves metal fatigue resistance by creating a uniform layer of compressive residual stress on the surface, which inhibits crack initiation and propagation. Sand blasting primarily cleans and roughens the metal surface but does not significantly enhance fatigue strength or compressive stress. The controlled impact of shot peening particles results in enhanced durability and longer component life compared to sand blasting.
Cost and Efficiency Analysis
Shot peening offers superior fatigue strength improvements compared to sand blasting, but it requires higher initial equipment investment and operational expertise, leading to increased upfront costs. Sand blasting is more cost-effective for large-scale surface cleaning due to lower equipment and maintenance expenses, but it provides less consistent surface treatment and may require more frequent application. Efficiency in shot peening is maximized in high-stress components where longevity offsets costs, whereas sand blasting excels in rapid material removal and preparation for subsequent coatings.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Metal Products
Shot peening enhances metal surface strength by inducing compressive stress and improving fatigue resistance, making it ideal for automotive and aerospace components. Sand blasting effectively cleans and prepares surfaces by removing rust, paint, or contaminants, ensuring better adhesion for coatings and finishes. Selecting the appropriate method depends on whether the goal is surface strengthening or thorough cleaning of metal products.
Shot Peening vs Sand Blasting Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com