E-coating provides a uniform, durable protective layer ideal for corrosion resistance on metal surfaces, using an electrically charged paint process. PVD coating offers a thin, hard, and decorative finish by depositing metal vapor onto substrates, enhancing wear resistance and aesthetic appeal. Both techniques improve metal longevity but differ in application methods and surface characteristics, with E-coating favoring protective sealing and PVD excelling in hardness and design versatility.
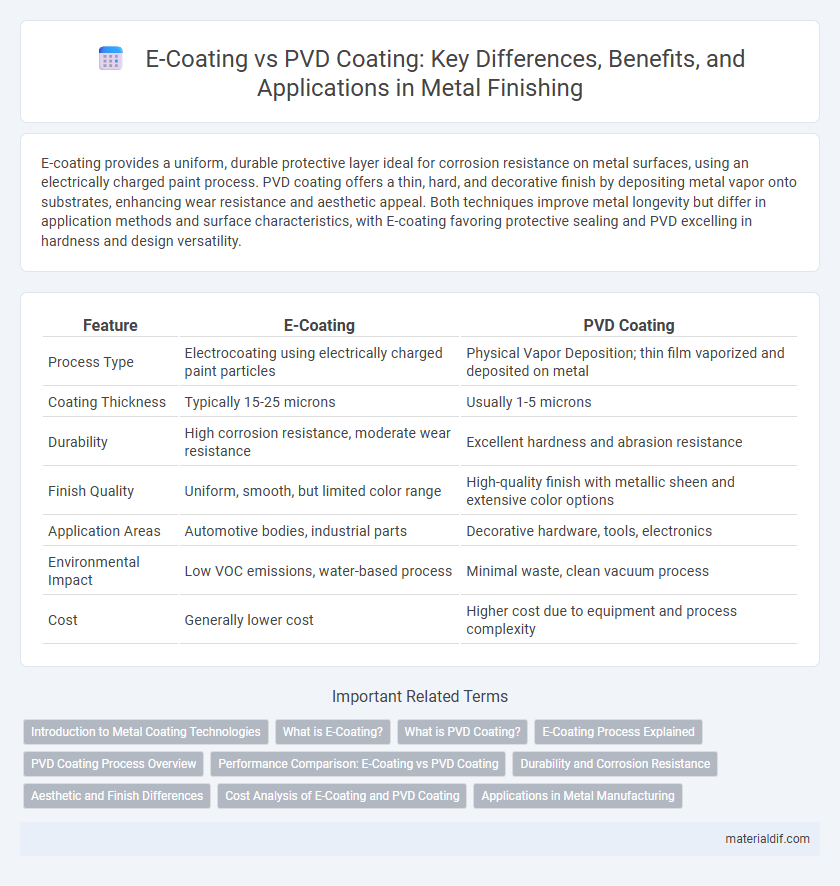
Table of Comparison
| Feature | E-Coating | PVD Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Electrocoating using electrically charged paint particles | Physical Vapor Deposition; thin film vaporized and deposited on metal |
| Coating Thickness | Typically 15-25 microns | Usually 1-5 microns |
| Durability | High corrosion resistance, moderate wear resistance | Excellent hardness and abrasion resistance |
| Finish Quality | Uniform, smooth, but limited color range | High-quality finish with metallic sheen and extensive color options |
| Application Areas | Automotive bodies, industrial parts | Decorative hardware, tools, electronics |
| Environmental Impact | Low VOC emissions, water-based process | Minimal waste, clean vacuum process |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to equipment and process complexity |
Introduction to Metal Coating Technologies
E-coating and PVD coating are advanced metal coating technologies designed to enhance corrosion resistance and surface durability. E-coating, or electrocoating, utilizes an electrically charged water-based paint to achieve uniform coverage, ideal for complex metal shapes and automotive parts. Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) coating applies thin, decorative, and wear-resistant metallic layers via vaporized material in a vacuum, commonly used in tools, architectural hardware, and electronic components.
What is E-Coating?
E-coating, also known as electrophoretic coating, is a water-based metal finishing process that uses electrical current to deposit a uniform, corrosion-resistant polymer film onto metal surfaces. This technique ensures consistent coverage, even on complex geometries and interior cavities, making it ideal for automotive and industrial applications. E-coating provides excellent adhesion and a durable base for subsequent topcoats, enhancing metal protection against environmental damage.
What is PVD Coating?
PVD coating, or Physical Vapor Deposition, is a vacuum-based process that deposits thin, durable metal films onto surfaces through vaporized material condensation. This technique creates hard, corrosion-resistant layers commonly used for decorative and functional metal finishes, enhancing wear resistance and lifespan. Compared to traditional coatings, PVD offers superior adhesion and environmentally friendly operation without toxic chemicals.
E-Coating Process Explained
E-coating, or electrophoretic coating, involves immersing metal parts in a water-based paint bath where an electric current deposits a uniform, corrosion-resistant polymer film. This process ensures thorough coverage, including hard-to-reach areas, resulting in enhanced durability and corrosion protection compared to traditional coatings. E-coating is widely used in automotive and industrial metal applications due to its efficiency, environmental compliance, and consistent finish quality.
PVD Coating Process Overview
PVD coating involves the physical vapor deposition process where metal ions are vaporized in a vacuum chamber and deposited onto a substrate, creating a durable, thin film with excellent wear and corrosion resistance. This method enables precise control over coating thickness and composition, resulting in superior adhesion compared to traditional e-coating techniques. PVD coatings are widely used in industries requiring high-performance surface finishes, such as automotive, aerospace, and decorative metals.
Performance Comparison: E-Coating vs PVD Coating
E-coating offers uniform corrosion resistance and excellent adhesion on complex geometries, making it ideal for automotive and industrial metal parts requiring durable, protective layers. PVD coating provides superior hardness, wear resistance, and aesthetic finishes, commonly used for decorative metals and high-performance tools where surface toughness and appearance are critical. While e-coating excels in cost-effective corrosion protection, PVD coating outperforms in mechanical durability and design versatility on metals.
Durability and Corrosion Resistance
E-coating provides uniform corrosion protection through an electrochemical deposition process, creating a durable primer layer that resists rust and chemical exposure effectively. PVD coating offers exceptional hardness and wear resistance by depositing thin metal layers via vapor phase, enhancing surface durability without adding significant thickness. Both methods improve corrosion resistance; however, e-coating excels in full-coverage protection for complex geometries, while PVD is ideal for enhancing surface hardness and scratch resistance on metal components.
Aesthetic and Finish Differences
E-coating provides a uniform, smooth finish with excellent corrosion resistance, ideal for consistent matte or satin looks on metal surfaces. PVD coating delivers a highly durable, decorative finish with vibrant colors and metallic shine that enhances surface hardness and scratch resistance. The choice between E-coating and PVD depends on desired visual appeal and functional durability in metal applications.
Cost Analysis of E-Coating and PVD Coating
E-coating generally offers a lower initial cost due to its simpler application process and minimal equipment requirements, making it ideal for large-volume metal parts. PVD coating involves higher upfront expenses driven by sophisticated vacuum technology and longer cycle times, but it delivers superior durability and aesthetic appeal. Long-term cost efficiency of PVD can offset its initial investment through enhanced wear resistance and reduced maintenance.
Applications in Metal Manufacturing
E-coating provides superior corrosion resistance and uniform coverage, making it ideal for automotive parts, electrical enclosures, and heavy machinery components. PVD coating excels in hardness, wear resistance, and aesthetic finish, commonly used for decorative hardware, cutting tools, and aerospace components. Metal manufacturers choose E-coating for protective layering in harsh environments, while PVD is preferred for enhancing durability and appearance in precision-engineered metal parts.
E-coating vs PVD Coating Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com