Galvanized steel is coated with a layer of zinc to enhance corrosion resistance, making it ideal for outdoor and industrial applications where exposure to moisture is common. Cold rolled steel undergoes a finishing process that improves its surface finish, strength, and dimensional accuracy, making it suitable for precision components and structural use. While galvanized steel excels in durability against rust, cold rolled steel offers superior formability and aesthetic appeal for manufacturing high-quality metal products.
Table of Comparison
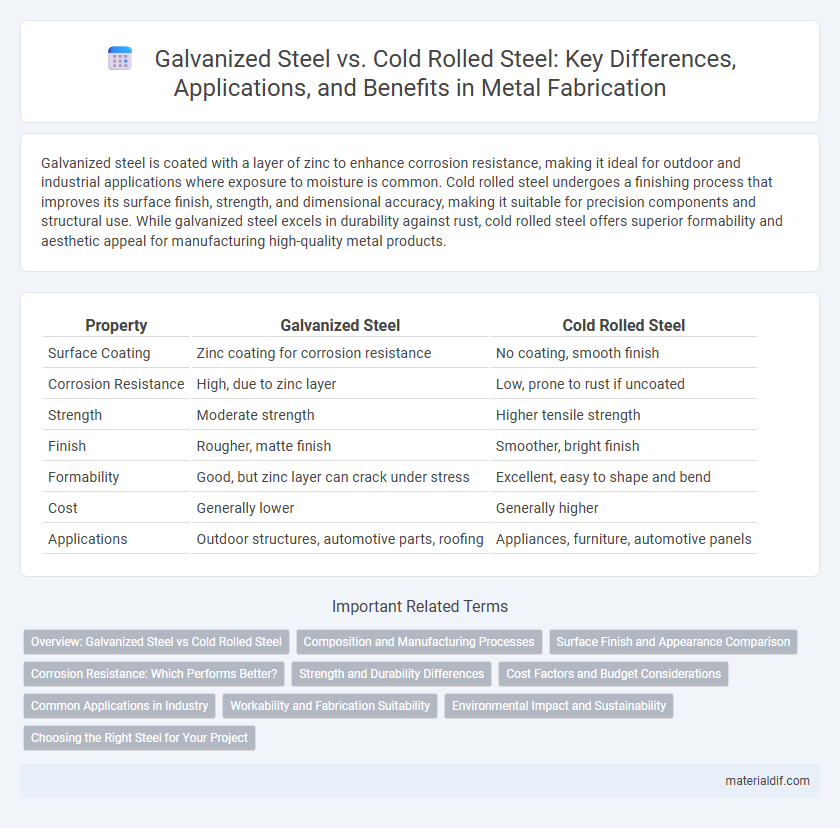
| Property | Galvanized Steel | Cold Rolled Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Coating | Zinc coating for corrosion resistance | No coating, smooth finish |
| Corrosion Resistance | High, due to zinc layer | Low, prone to rust if uncoated |
| Strength | Moderate strength | Higher tensile strength |
| Finish | Rougher, matte finish | Smoother, bright finish |
| Formability | Good, but zinc layer can crack under stress | Excellent, easy to shape and bend |
| Cost | Generally lower | Generally higher |
| Applications | Outdoor structures, automotive parts, roofing | Appliances, furniture, automotive panels |
Overview: Galvanized Steel vs Cold Rolled Steel
Galvanized steel features a zinc coating that enhances corrosion resistance, making it ideal for outdoor and industrial applications. Cold rolled steel undergoes a cold forming process that improves surface finish, strength, and dimensional accuracy, commonly used in automotive and appliance manufacturing. Selecting between galvanized and cold rolled steel depends on specific needs for durability, rust protection, and precision in metalworking projects.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Galvanized steel is composed of carbon steel coated with a layer of zinc through a hot-dip or electro-galvanizing process, which enhances corrosion resistance. Cold rolled steel undergoes a refining process where hot rolled steel is further rolled at room temperature, improving surface finish and mechanical properties without any coating. The manufacturing of galvanized steel involves protective zinc layering to prevent rust, whereas cold rolled steel is produced through precise mechanical deformation to achieve tighter tolerances and improved strength.
Surface Finish and Appearance Comparison
Galvanized steel features a distinct matte gray surface with a slightly spangled pattern due to the zinc coating, providing corrosion resistance and a rougher texture ideal for outdoor applications. Cold rolled steel, produced through a mechanical rolling process, boasts a smooth, shiny, and uniform surface finish that enhances its appearance for indoor use and applications requiring precise paint adhesion. The visible differences in surface texture and shine make galvanized steel more suited for durability-focused projects, while cold rolled steel excels in aesthetic-driven designs.
Corrosion Resistance: Which Performs Better?
Galvanized steel outperforms cold rolled steel in corrosion resistance due to its protective zinc coating that prevents rust and extends the material's lifespan in harsh environments. Cold rolled steel, while offering superior surface finish and strength, lacks inherent corrosion protection and typically requires additional treatments or coatings to withstand moisture exposure. The zinc layer on galvanized steel reacts with oxygen and moisture, forming a tough barrier that guards against corrosion, making it the preferred choice for outdoor and industrial applications.
Strength and Durability Differences
Galvanized steel features a protective zinc coating that significantly enhances its corrosion resistance, making it more durable in harsh environments compared to cold rolled steel. Cold rolled steel, processed at room temperature, exhibits superior tensile strength and a smoother finish but lacks the corrosion protection inherent in galvanized steel. While galvanized steel excels in outdoor applications requiring longevity against rust, cold rolled steel is preferred for structural components demanding high strength and precision.
Cost Factors and Budget Considerations
Galvanized steel typically incurs higher costs due to the zinc coating process, which provides enhanced corrosion resistance and longer lifespan, making it ideal for outdoor or harsh environments. Cold rolled steel is more affordable upfront, offering a smooth finish and precise dimensions, but lacks the protective coating, potentially increasing maintenance expenses over time. Budget considerations should weigh initial material costs against long-term durability and environmental exposure to determine the most cost-effective choice.
Common Applications in Industry
Galvanized steel is widely used in outdoor construction, automotive bodies, and electrical equipment due to its corrosion-resistant zinc coating, making it ideal for environments exposed to moisture. Cold rolled steel is preferred in manufacturing precision parts, appliances, and furniture, where a smooth surface finish and high strength are critical for aesthetic and structural integrity. Both materials serve key roles in industrial production but are selected based on specific application requirements related to durability and surface quality.
Workability and Fabrication Suitability
Galvanized steel offers excellent corrosion resistance due to its zinc coating, making it ideal for outdoor and harsh environment applications, but its workability can be limited by the coating which may crack or peel during bending or welding. Cold rolled steel provides superior surface finish and dimensional accuracy, enhancing its ease of fabrication and suitability for precise forming, stamping, and welding processes. Selecting between these metals depends on the balance between environmental exposure requirements and the complexity of the fabrication tasks involved.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Galvanized steel features a zinc coating that enhances corrosion resistance and extends product lifespan, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing environmental waste. Cold rolled steel, produced through a mechanical process without coatings, generally consumes less energy during manufacturing, contributing to lower carbon emissions. The recyclability of both materials supports sustainable practices, but galvanized steel's longer durability often results in a smaller environmental footprint over its lifecycle.
Choosing the Right Steel for Your Project
Galvanized steel offers superior corrosion resistance due to its zinc coating, making it ideal for outdoor or moisture-exposed applications where durability is critical. Cold rolled steel provides a smoother surface finish and higher tensile strength, perfect for precision parts and indoor projects requiring detailed shaping or painting. Selecting the right steel depends on balancing environmental exposure, strength requirements, and surface finish needs to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Galvanized Steel vs Cold Rolled Steel Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com