Electroplating enhances metal surfaces by depositing a thin layer of metal to improve corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal, while electropolishing removes a thin layer of metal to smooth and brighten the surface. Electroplating adds material, creating a protective coating, whereas electropolishing refines the surface by eliminating imperfections and reducing roughness. Both processes improve metal durability and appearance but serve distinct functions in metal finishing applications.
Table of Comparison
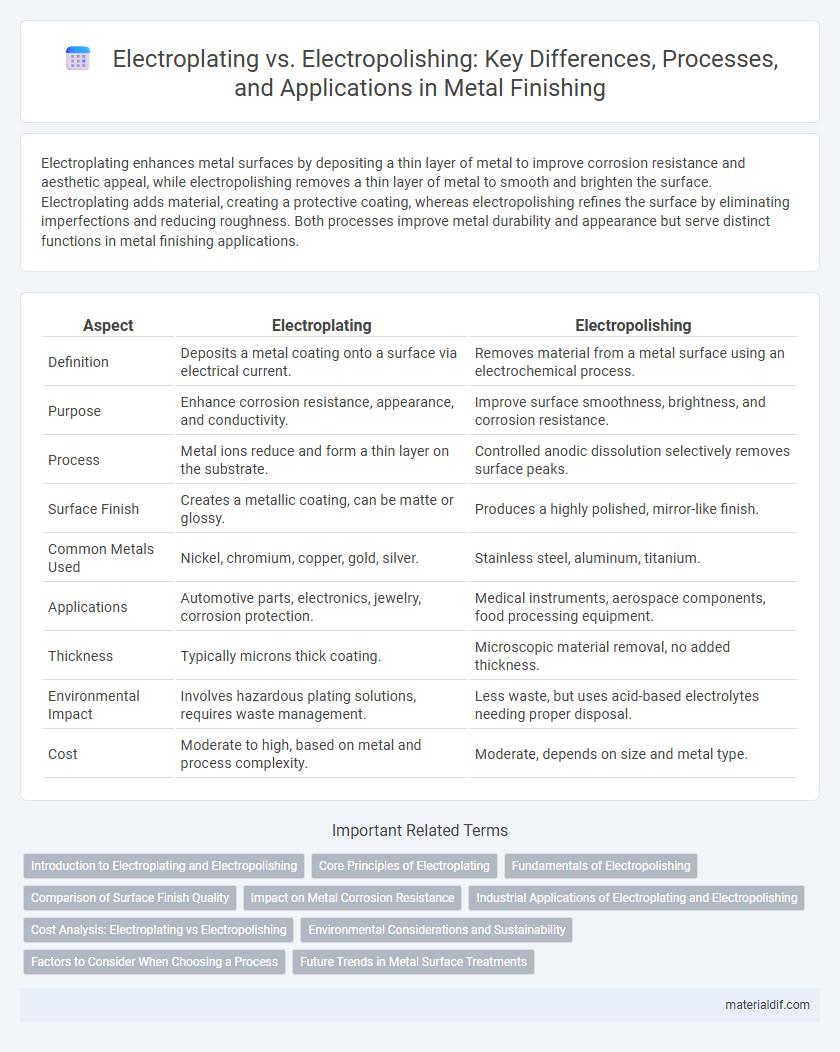
| Aspect | Electroplating | Electropolishing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Deposits a metal coating onto a surface via electrical current. | Removes material from a metal surface using an electrochemical process. |
| Purpose | Enhance corrosion resistance, appearance, and conductivity. | Improve surface smoothness, brightness, and corrosion resistance. |
| Process | Metal ions reduce and form a thin layer on the substrate. | Controlled anodic dissolution selectively removes surface peaks. |
| Surface Finish | Creates a metallic coating, can be matte or glossy. | Produces a highly polished, mirror-like finish. |
| Common Metals Used | Nickel, chromium, copper, gold, silver. | Stainless steel, aluminum, titanium. |
| Applications | Automotive parts, electronics, jewelry, corrosion protection. | Medical instruments, aerospace components, food processing equipment. |
| Thickness | Typically microns thick coating. | Microscopic material removal, no added thickness. |
| Environmental Impact | Involves hazardous plating solutions, requires waste management. | Less waste, but uses acid-based electrolytes needing proper disposal. |
| Cost | Moderate to high, based on metal and process complexity. | Moderate, depends on size and metal type. |
Introduction to Electroplating and Electropolishing
Electroplating involves depositing a thin layer of metal onto a conductive surface using an electric current, enhancing corrosion resistance, appearance, and wear properties. Electropolishing is an electrochemical process that removes a thin layer of material from a metal surface, improving cleanliness, smoothness, and brightness. Both techniques utilize controlled electrical currents but serve different purposes in metal finishing and surface treatment.
Core Principles of Electroplating
Electroplating involves the deposition of a metal coating onto a conductive surface through an electrochemical process, using an electrolyte solution and an electric current to reduce metal ions onto the substrate. This process enhances corrosion resistance, improves surface appearance, and increases wear resistance by creating a uniform metal layer. Key parameters include current density, electrolyte composition, temperature, and plating duration, all critical for achieving optimal coating thickness and adhesion.
Fundamentals of Electropolishing
Electropolishing is an electrochemical process that smooths and brightens metal surfaces by selectively removing microscopic layers of material. Unlike electroplating, which deposits a layer of metal onto a substrate, electropolishing enhances corrosion resistance and surface finish without adding material. The process involves anodic dissolution in an electrolytic bath, producing a uniform, reflective surface ideal for stainless steel and other alloys.
Comparison of Surface Finish Quality
Electropolishing produces a smoother, more reflective surface by selectively removing microscopic peaks and contaminants, resulting in superior corrosion resistance and enhanced aesthetic appeal compared to electroplating. Electroplating adds a metal coating that can improve surface hardness and wear resistance but may leave uneven layers or minor imperfections. The choice between electroplating and electropolishing depends on whether surface texture refinement or protective layering is the primary goal.
Impact on Metal Corrosion Resistance
Electroplating enhances metal corrosion resistance by depositing a protective layer of metals such as nickel, chromium, or zinc, creating a barrier against environmental factors. Electropolishing improves corrosion resistance by selectively removing microscopic surface irregularities and contaminants, resulting in a smooth, passive oxide layer that minimizes oxidation sites. Both methods increase longevity, but electroplating relies on the coating's integrity, whereas electropolishing strengthens the metal's inherent surface properties.
Industrial Applications of Electroplating and Electropolishing
Electroplating enhances corrosion resistance and surface conductivity, making it ideal for automotive, electronics, and aerospace industries where durable coatings improve performance. Electropolishing is widely used in pharmaceutical, food processing, and semiconductor manufacturing due to its precision in removing microscopic surface imperfections and achieving ultra-smooth finishes. Both processes optimize metal surface properties, but electroplating focuses on coating applications while electropolishing primarily improves surface cleanliness and passivation.
Cost Analysis: Electroplating vs Electropolishing
Electroplating typically incurs higher material and waste disposal costs due to the use of metal salts and chemical baths, whereas electropolishing tends to have lower environmental compliance expenses as it mainly involves electrolyte solutions with fewer hazardous byproducts. The energy consumption in electropolishing is generally more efficient, resulting in reduced operational costs compared to the longer processing times and higher power requirements of electroplating. Overall, electropolishing offers a cost advantage in surface finishing applications where reduced maintenance and enhanced corrosion resistance translate to long-term savings.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainability
Electroplating involves depositing metals like nickel, chromium, or cadmium, often producing hazardous waste containing heavy metals and toxic chemicals requiring careful disposal to minimize environmental impact. Electropolishing, an electrochemical process primarily applied to stainless steel, reduces surface roughness and removes contaminants without introducing heavy metals, generating fewer harmful effluents. Choosing electropolishing over electroplating enhances sustainability by lowering chemical waste, reducing toxic byproducts, and enabling better recycling of rinse water and used electrolytes.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Process
Electroplating and electropolishing both enhance metal surfaces but differ in purpose and results, with electroplating adding a metal layer to improve corrosion resistance and aesthetics, while electropolishing removes a thin surface layer to increase smoothness and purity. Key factors to consider when choosing between the two include the desired surface finish, corrosion resistance requirements, and the metal substrate involved, as some metals respond better to one process over the other. Cost-effectiveness and the specific application environment, such as exposure to chemicals or wear, also influence the selection of the appropriate surface treatment method.
Future Trends in Metal Surface Treatments
Advancements in electroplating focus on incorporating eco-friendly coatings and nanoscale precision to enhance corrosion resistance and conductivity in electronic components. Electropolishing evolves with the integration of automated systems and real-time monitoring, improving surface uniformity and reducing processing time for medical implants and aerospace parts. Emerging techniques combine both methods, harnessing synergy effects to create multifunctional metal surfaces with superior durability and aesthetic appeal.
Electroplating vs Electropolishing Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com