Recycled metal reduces environmental impact by conserving natural resources and lowering energy consumption compared to virgin metal production. It helps minimize mining waste and greenhouse gas emissions, promoting sustainable manufacturing practices. While virgin metal offers high purity and consistent quality, advances in recycling technology enable recycled metal to meet stringent industry standards effectively.
Table of Comparison
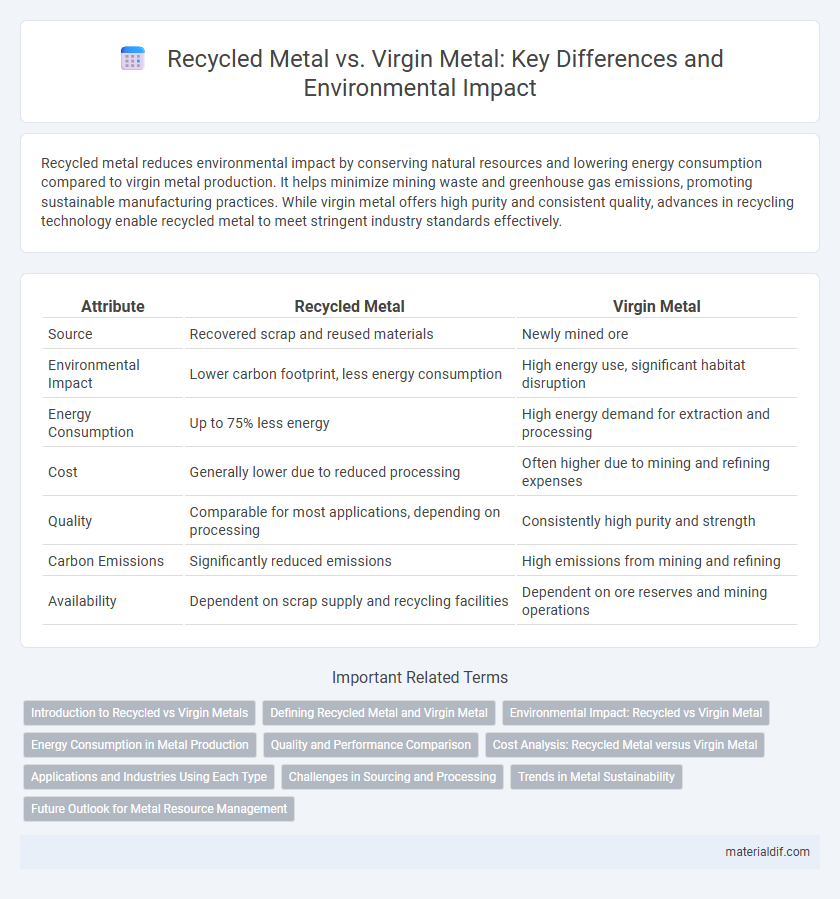
| Attribute | Recycled Metal | Virgin Metal |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Recovered scrap and reused materials | Newly mined ore |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint, less energy consumption | High energy use, significant habitat disruption |
| Energy Consumption | Up to 75% less energy | High energy demand for extraction and processing |
| Cost | Generally lower due to reduced processing | Often higher due to mining and refining expenses |
| Quality | Comparable for most applications, depending on processing | Consistently high purity and strength |
| Carbon Emissions | Significantly reduced emissions | High emissions from mining and refining |
| Availability | Dependent on scrap supply and recycling facilities | Dependent on ore reserves and mining operations |
Introduction to Recycled vs Virgin Metals
Recycled metal is derived from scrap materials that have been reprocessed for reuse, significantly reducing the need for raw ore extraction and minimizing environmental impact. Virgin metal refers to metal produced directly from mined ore, ensuring high purity and consistent quality but involving higher energy consumption and ecological disturbance. Comparing the two, recycled metals offer sustainable alternatives with substantial energy savings, while virgin metals remain essential for applications requiring utmost material integrity.
Defining Recycled Metal and Virgin Metal
Recycled metal refers to metal materials recovered and processed from scrap or used products, reducing the need for new mining and conserving natural resources. Virgin metal, on the other hand, is extracted directly from ore through mining and refining processes, representing raw, unprocessed metal. The distinction impacts environmental sustainability, energy consumption, and resource management within the metal industry.
Environmental Impact: Recycled vs Virgin Metal
Recycled metal significantly reduces environmental impact by lowering greenhouse gas emissions and conserving natural resources compared to virgin metal extraction, which involves energy-intensive mining and processing. The use of recycled metal minimizes habitat destruction, reduces landfill waste, and decreases water pollution associated with ore mining and smelting. Recycling metals like aluminum and steel can save up to 95% of the energy required for producing metals from virgin ores, contributing to a more sustainable and circular economy.
Energy Consumption in Metal Production
Recycled metal significantly reduces energy consumption compared to virgin metal production, using up to 95% less energy in processes such as aluminum and steel manufacturing. Virgin metal extraction involves energy-intensive mining, refining, and smelting operations that increase carbon emissions and environmental impact. Transitioning to recycled metal lowers energy demand and supports sustainable metal supply chains.
Quality and Performance Comparison
Recycled metal often matches or exceeds virgin metal in quality due to advancements in refining and alloying processes that remove impurities and restore structural integrity. Performance characteristics such as tensile strength, durability, and corrosion resistance in recycled metals remain highly competitive, making them suitable for critical applications in automotive, aerospace, and construction industries. Utilizing recycled metal reduces environmental impact without compromising material reliability, supporting sustainable manufacturing without sacrificing performance standards.
Cost Analysis: Recycled Metal versus Virgin Metal
Recycled metal generally costs 20-40% less than virgin metal due to reduced energy consumption and lower raw material expenses. The production of recycled metal emits up to 75% less greenhouse gases, contributing to long-term financial savings in sustainability initiatives. Price volatility is also typically lower for recycled metal, offering more stable budgeting for manufacturers.
Applications and Industries Using Each Type
Recycled metal is predominantly used in construction, automotive, and packaging industries due to its cost-effectiveness and reduced environmental impact, making it ideal for producing steel beams, car parts, and aluminum cans. Virgin metal finds critical applications in aerospace, electronics, and medical industries where material purity and strength are essential for manufacturing aircraft components, high-performance electronic devices, and surgical instruments. Both recycled and virgin metals serve vital roles, with recycled metal supporting sustainable practices and virgin metal meeting stringent quality and performance standards.
Challenges in Sourcing and Processing
Recycled metal sourcing faces inconsistent supply chains due to variable scrap availability and contamination levels, impacting quality control in processing. Virgin metal extraction involves extensive mining operations that require significant energy and result in environmental degradation, complicating sustainable procurement. Both recycled and virgin metals demand advanced refining technologies to meet industry standards while addressing cost-efficiency and regulatory compliance challenges.
Trends in Metal Sustainability
Recycled metal reduces carbon emissions by up to 85% compared to virgin metal production, driving increased adoption across industries aiming to meet sustainability goals. The global metal recycling market is projected to reach USD 66 billion by 2030, propelled by demand for circular economy practices and government regulations targeting resource conservation. Advances in sorting technology and increased consumer awareness further amplify the preference for recycled metals, positioning them as critical components in future sustainable manufacturing.
Future Outlook for Metal Resource Management
Recycled metal significantly reduces environmental impact by lowering the demand for virgin metal extraction, which depletes natural resources and increases greenhouse gas emissions. Advances in recycling technology and circular economy policies are expected to enhance the efficiency and scale of metal recovery, fostering sustainable resource management. The future outlook for metal resource management emphasizes increased material reuse, reducing raw material dependency while supporting global efforts to combat climate change.
Recycled Metal vs Virgin Metal Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com