Titanium Grade 2 offers excellent corrosion resistance and high ductility, making it ideal for applications requiring formability and chemical durability. Titanium Grade 5, also known as Ti-6Al-4V, provides superior strength and hardness due to its alloying elements, suitable for aerospace and high-performance engineering. Choosing between Grade 2 and Grade 5 depends on the balance between strength requirements and corrosion resistance needed for the specific application.
Table of Comparison
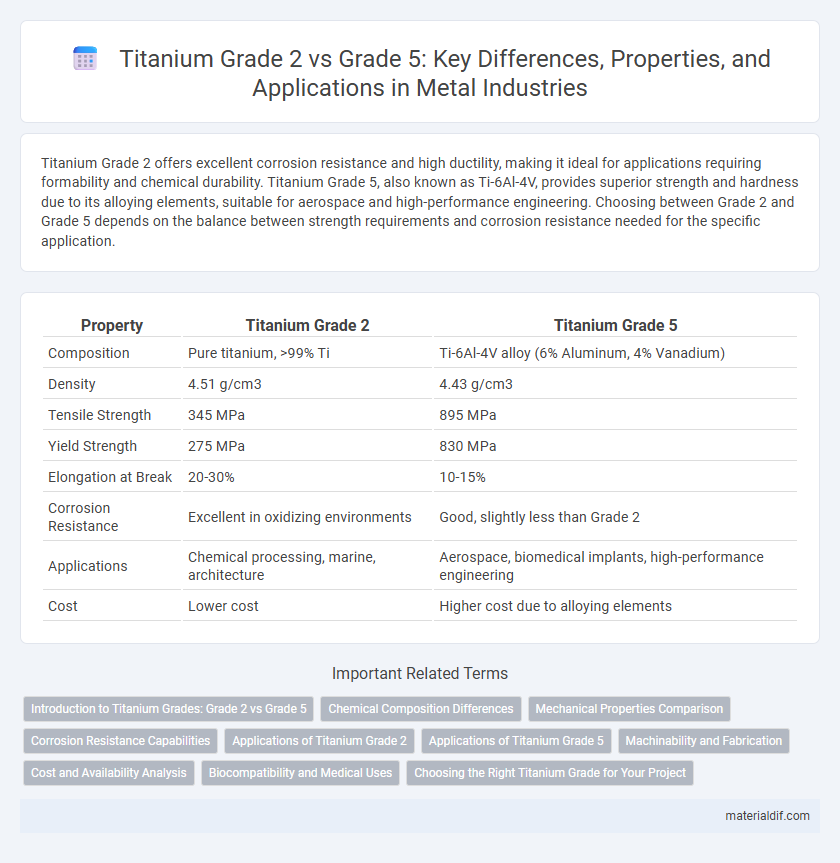
| Property | Titanium Grade 2 | Titanium Grade 5 |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Pure titanium, >99% Ti | Ti-6Al-4V alloy (6% Aluminum, 4% Vanadium) |
| Density | 4.51 g/cm3 | 4.43 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 345 MPa | 895 MPa |
| Yield Strength | 275 MPa | 830 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | 20-30% | 10-15% |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent in oxidizing environments | Good, slightly less than Grade 2 |
| Applications | Chemical processing, marine, architecture | Aerospace, biomedical implants, high-performance engineering |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to alloying elements |
Introduction to Titanium Grades: Grade 2 vs Grade 5
Titanium Grade 2 is commercially pure titanium known for its excellent corrosion resistance and superior ductility, making it ideal for chemical processing and marine applications. Titanium Grade 5, an alloy of titanium with 6% aluminum and 4% vanadium, offers significantly higher strength and fatigue resistance while maintaining good corrosion resistance, widely used in aerospace and medical implants. Understanding the differences in composition and mechanical properties between Grade 2 and Grade 5 is essential for selecting the right titanium grade for specific industrial applications.
Chemical Composition Differences
Titanium Grade 2 is commercially pure titanium with a chemical composition of at least 99% titanium, containing minimal amounts of oxygen, nitrogen, and iron, which enhance its corrosion resistance and ductility. Titanium Grade 5, also known as Ti-6Al-4V, contains approximately 6% aluminum and 4% vanadium, significantly increasing its strength and heat resistance compared to Grade 2. The presence of aluminum and vanadium in Grade 5 alters its mechanical properties, making it more suitable for aerospace and high-performance applications than the more malleable and corrosion-resistant Grade 2.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Titanium Grade 2 exhibits a tensile strength of approximately 350 MPa and excellent ductility with elongation around 20%, favoring applications requiring corrosion resistance and formability. Titanium Grade 5, an alloy containing 6% aluminum and 4% vanadium, offers superior mechanical properties with tensile strength reaching up to 950 MPa and a lower elongation near 10%, making it ideal for high-stress environments. The significant difference in yield strength and fatigue resistance between these grades drives their selection in aerospace, medical, and marine industries.
Corrosion Resistance Capabilities
Titanium Grade 2 exhibits superior corrosion resistance in highly oxidizing environments due to its nearly pure titanium composition, making it ideal for chemical processing and marine applications. Titanium Grade 5, an alloy of titanium with aluminum and vanadium, offers good corrosion resistance but can be more susceptible to pitting and crevice corrosion in chloride-rich environments. Evaluating the operating environment's specific conditions is crucial when selecting between Grade 2 and Grade 5 titanium for corrosion-critical applications.
Applications of Titanium Grade 2
Titanium Grade 2 is widely used in chemical processing, aerospace, and marine industries due to its excellent corrosion resistance and good strength-to-weight ratio. Its applications include heat exchangers, pressure vessels, and desalination plants, where exposure to aggressive environments demands reliable durability. Compared to Titanium Grade 5, which is stronger and often used in high-stress applications, Grade 2 is preferred for components requiring superior corrosion resistance and weldability.
Applications of Titanium Grade 5
Titanium Grade 5, also known as Ti-6Al-4V, is extensively used in aerospace, medical implants, and automotive industries due to its high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance. It outperforms Titanium Grade 2 in structural applications requiring superior mechanical properties and enhanced fatigue resistance. Typical applications include aircraft engine components, surgical instruments, and high-performance automotive parts.
Machinability and Fabrication
Titanium Grade 2 offers superior machinability and is easier to fabricate due to its lower strength and higher ductility compared to Titanium Grade 5, which is an alloy known for its high strength but reduced machinability. Grade 5's increased toughness requires specialized tooling and slower machining speeds, impacting fabrication efficiency. Manufacturing processes favor Grade 2 when complex shapes and extensive welding are involved, whereas Grade 5 is preferred for applications demanding higher strength-to-weight ratios despite fabrication challenges.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Titanium Grade 2 offers a lower-cost option with higher availability due to its simpler alloy composition, primarily consisting of commercially pure titanium. Titanium Grade 5, an alloy with aluminum and vanadium, is more expensive and less readily available because of its advanced manufacturing requirements and superior mechanical properties. Cost analysis shows Grade 2 is preferred for budget-sensitive applications, while Grade 5 suits high-performance demands despite higher expenses and limited supply.
Biocompatibility and Medical Uses
Titanium Grade 2 exhibits superior biocompatibility due to its commercially pure nature, making it ideal for implants like dental fixtures and bone plates where minimal allergic reactions are crucial. In contrast, Titanium Grade 5, an alloy containing aluminum and vanadium, offers higher strength but slightly reduced biocompatibility, commonly used in load-bearing orthopedic implants such as hip and knee replacements. Both grades resist corrosion in bodily fluids, but Grade 2's pure composition ensures better tissue integration and lower cytotoxicity in medical applications.
Choosing the Right Titanium Grade for Your Project
Titanium Grade 2 offers excellent corrosion resistance and ductility, making it ideal for chemical processing and marine applications where flexibility and purity are critical. Titanium Grade 5 combines strength and lightweight properties due to its alloy composition of 6% aluminum and 4% vanadium, preferred for aerospace, medical implants, and high-performance engineering. Selecting the right titanium grade depends on balancing mechanical strength requirements with corrosion resistance and cost considerations specific to your project's demands.
Titanium Grade 2 vs Titanium Grade 5 Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com