CNC machining offers precision and flexibility in producing metal pet components, enabling intricate designs and rapid prototyping with tight tolerances. Die casting provides high-volume production efficiency with excellent surface finish and dimensional consistency, ideal for large-scale metal pet manufacturing. Choosing between CNC machining and die casting depends on production volume, design complexity, and cost considerations.
Table of Comparison
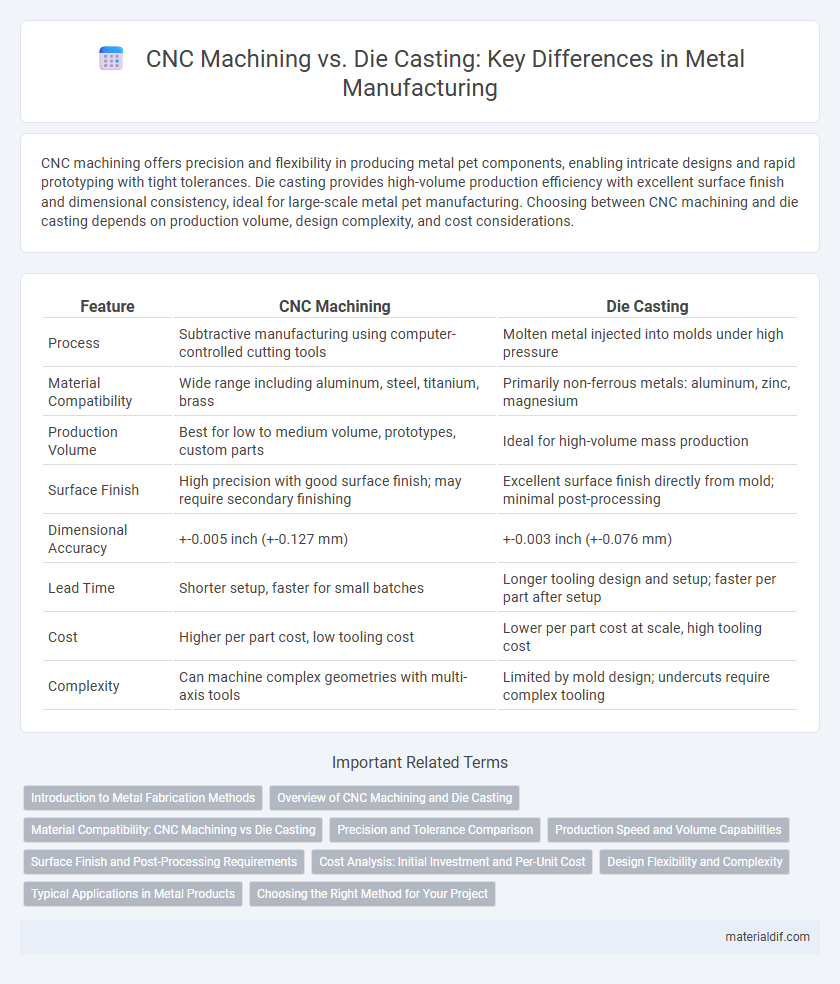
| Feature | CNC Machining | Die Casting |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Subtractive manufacturing using computer-controlled cutting tools | Molten metal injected into molds under high pressure |
| Material Compatibility | Wide range including aluminum, steel, titanium, brass | Primarily non-ferrous metals: aluminum, zinc, magnesium |
| Production Volume | Best for low to medium volume, prototypes, custom parts | Ideal for high-volume mass production |
| Surface Finish | High precision with good surface finish; may require secondary finishing | Excellent surface finish directly from mold; minimal post-processing |
| Dimensional Accuracy | +-0.005 inch (+-0.127 mm) | +-0.003 inch (+-0.076 mm) |
| Lead Time | Shorter setup, faster for small batches | Longer tooling design and setup; faster per part after setup |
| Cost | Higher per part cost, low tooling cost | Lower per part cost at scale, high tooling cost |
| Complexity | Can machine complex geometries with multi-axis tools | Limited by mold design; undercuts require complex tooling |
Introduction to Metal Fabrication Methods
CNC machining offers precision metal fabrication through computer-controlled cutting, shaping, and drilling, ideal for complex and custom parts with tight tolerances. Die casting involves forcing molten metal into molds under high pressure, enabling mass production of intricate shapes with excellent surface finishes. Both methods complement metal fabrication by balancing flexibility, accuracy, and production volume.
Overview of CNC Machining and Die Casting
CNC machining utilizes computer-controlled tools to precisely cut and shape metal parts from solid blocks, offering high accuracy and flexibility for complex geometries. Die casting involves forcing molten metal into molds under high pressure, enabling fast production of intricate shapes with excellent surface finish and dimensional consistency. Both processes serve diverse industries, with CNC machining favored for prototyping and low-volume runs, while die casting excels in mass production of metal components.
Material Compatibility: CNC Machining vs Die Casting
CNC machining offers superior material compatibility, allowing precision work on a wide range of metals including aluminum, steel, titanium, and exotic alloys, ensuring customized part production without material limitations. Die casting is primarily suited for non-ferrous metals like aluminum, zinc, and magnesium, providing high-volume production but limited to materials with good fluidity and lower melting points. Selecting between CNC machining and die casting depends on the specific metal's properties and the desired production volume, balancing flexibility and efficiency.
Precision and Tolerance Comparison
CNC machining delivers superior precision and tighter tolerances, typically achieving +/-0.005 mm, making it ideal for high-accuracy metal components. Die casting generally maintains tolerances around +/-0.1 mm, suitable for mass production but less precise than CNC. The choice between CNC machining and die casting depends on the required tolerance levels and application complexity in metal manufacturing.
Production Speed and Volume Capabilities
CNC machining offers high precision for low to medium production volumes but typically requires longer cycle times compared to die casting. Die casting excels in producing large volumes rapidly due to its automated injection process, significantly reducing per-part production time. For mass production demanding quick turnaround, die casting outperforms CNC machining in speed and volume efficiency.
Surface Finish and Post-Processing Requirements
CNC machining delivers superior surface finish with tight tolerances, reducing the need for extensive post-processing compared to die casting. Die casting often produces parts with rougher surfaces and may require additional polishing, sanding, or machining to meet precise aesthetic or functional standards. Surface finish quality directly impacts post-processing costs and time, making CNC machining more efficient for high-precision metal components.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Per-Unit Cost
CNC machining demands a higher initial investment due to expensive equipment and programming but offers lower per-unit costs for small to medium production runs because of minimal tooling expenses. Die casting requires significant upfront costs in mold creation and setup, making it cost-effective primarily for high-volume production with low per-unit expenses. Evaluating project volume and precision needs is critical for optimizing overall manufacturing costs between CNC machining and die casting.
Design Flexibility and Complexity
CNC machining offers exceptional design flexibility, enabling precise production of complex geometries with tight tolerances and intricate details that die casting may struggle to achieve. Die casting excels in producing high volumes of metal parts with consistent features but is limited by mold design constraints, restricting complexity and quick design changes. For prototypes or customized components requiring intricate shapes, CNC machining remains the preferred method due to its adaptability and ability to accommodate design modifications without extensive tooling costs.
Typical Applications in Metal Products
CNC machining is commonly used for producing complex, high-precision metal components such as aerospace parts, automotive prototypes, and medical devices due to its accuracy and versatility. Die casting excels in manufacturing large volumes of metal products with consistent quality, including engine blocks, housings, and intricate hardware components. Both methods serve critical roles in metal fabrication, with CNC machining favoring customization and die casting prioritizing mass production efficiency.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Project
CNC machining offers precise, customizable metal parts ideal for low to medium production volumes, while die casting provides high-volume manufacturing with complex shapes and excellent surface finishes. Selecting the right method depends on factors such as production scale, material type, tolerances, and cost-effectiveness. Evaluating project requirements ensures optimal performance, lead times, and budget alignment in metal fabrication.
CNC Machining vs Die Casting Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com