Soft leads provide greater comfort and flexibility for dogs, reducing strain during walks and allowing smoother control for handlers. Hard leads offer superior durability and control, making them ideal for training and managing strong or energetic dogs. Choosing between soft and hard leads depends on your dog's behavior, training needs, and walking environment.
Table of Comparison
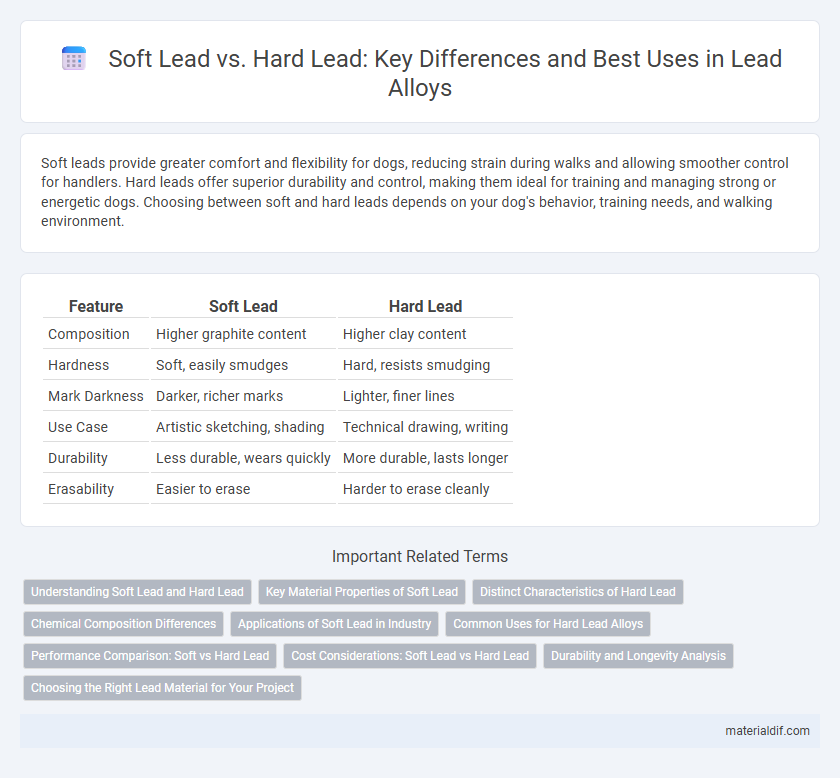
| Feature | Soft Lead | Hard Lead |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Higher graphite content | Higher clay content |
| Hardness | Soft, easily smudges | Hard, resists smudging |
| Mark Darkness | Darker, richer marks | Lighter, finer lines |
| Use Case | Artistic sketching, shading | Technical drawing, writing |
| Durability | Less durable, wears quickly | More durable, lasts longer |
| Erasability | Easier to erase | Harder to erase cleanly |
Understanding Soft Lead and Hard Lead
Soft lead refers to graphite pencils that contain higher clay content, making the lead softer and producing darker, smoother lines ideal for shading and artistic work. Hard lead pencils have more graphite and less clay, resulting in lighter, more precise lines suited for technical drawing and detailed writing. The difference between soft and hard lead affects durability, line quality, and application versatility, crucial for selecting the right pencil for specific tasks.
Key Material Properties of Soft Lead
Soft lead exhibits low hardness and high malleability due to its face-centered cubic crystal structure, enabling easy deformation under stress. Its low melting point around 327.5degC allows for efficient casting and soldering applications. High density and excellent corrosion resistance make soft lead ideal for use in batteries, radiation shielding, and flexible components.
Distinct Characteristics of Hard Lead
Hard leads are characterized by their high graphite content, resulting in a firmer texture that produces lighter, finer lines ideal for technical drawing and detailed work. Their increased durability resists smudging and maintains precise edges, making them preferred in architectural and engineering applications. Unlike soft leads, hard leads require more pressure to mark paper but offer superior accuracy and control.
Chemical Composition Differences
Soft lead primarily consists of nearly pure lead with minimal impurities, allowing it to remain malleable and easy to shape. Hard lead contains a higher proportion of antimony and sometimes arsenic, which significantly increases its hardness and improves durability for applications such as ammunition and battery grids. The addition of these alloying elements alters the crystal structure, resulting in enhanced mechanical strength compared to pure soft lead.
Applications of Soft Lead in Industry
Soft lead, characterized by its high purity and low hardness, is extensively used in applications requiring malleability and corrosion resistance, such as radiation shielding in medical and nuclear industries. Its excellent pliability enables effective use in cable sheathing, soldering materials, and batteries, particularly in lead-acid batteries for automotive and backup power systems. In contrast to hard lead, soft lead's ductility enhances its performance in protective coatings and soundproofing materials across various industrial sectors.
Common Uses for Hard Lead Alloys
Hard lead alloys are primarily used in applications requiring enhanced strength and durability, such as in battery grids, radiation shielding, and cable sheathing. These alloys typically contain tin, antimony, or arsenic to improve hardness and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for heavy-duty industrial environments. Their ability to maintain structural integrity under stress distinguishes them from soft lead alloys commonly used for soldering or cushioning.
Performance Comparison: Soft vs Hard Lead
Soft lead offers superior flexibility and easier machinability compared to hard lead, making it ideal for applications requiring frequent shaping or modification. Hard lead provides enhanced durability and higher resistance to deformation under mechanical stress, resulting in longer-lasting performance in heavy-duty uses. Performance comparison shows soft lead excels in adaptability and ease of use, while hard lead is preferable for tasks demanding strength and structural integrity.
Cost Considerations: Soft Lead vs Hard Lead
Soft lead, commonly used in pencils and cosmetics, generally incurs lower production costs due to simpler processing and abundant raw materials. Hard lead, preferred in industrial applications like soldering and radiation shielding, demands higher expenses from alloying and refining metals such as tin and antimony. Choosing between soft and hard lead hinges on balancing functionality with cost efficiency, where soft lead offers budget-friendly options and hard lead provides durability for specialized uses.
Durability and Longevity Analysis
Soft leads, composed of higher graphite content, exhibit greater flexibility and reduced brittleness, resulting in enhanced durability during frequent use and writing pressure variations. Hard leads, with increased clay composition, provide sharper lines but are more prone to breakage, thus limiting their longevity under constant mechanical stress. Analyzing durability, soft leads generally outperform hard leads in longevity due to their ability to withstand repeated application without frequent sharpening or fragmentation.
Choosing the Right Lead Material for Your Project
Choosing the right lead material depends on the specific requirements of your project, where soft lead offers flexibility and easy shaping, ideal for applications like radiation shielding and plumbing. Hard lead provides greater structural integrity and durability, making it suitable for applications requiring resistance to deformation, such as lead-acid battery plates and industrial equipment. Understanding the material properties and intended use ensures optimal performance and longevity in your lead-related projects.
Soft Lead vs Hard Lead Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com