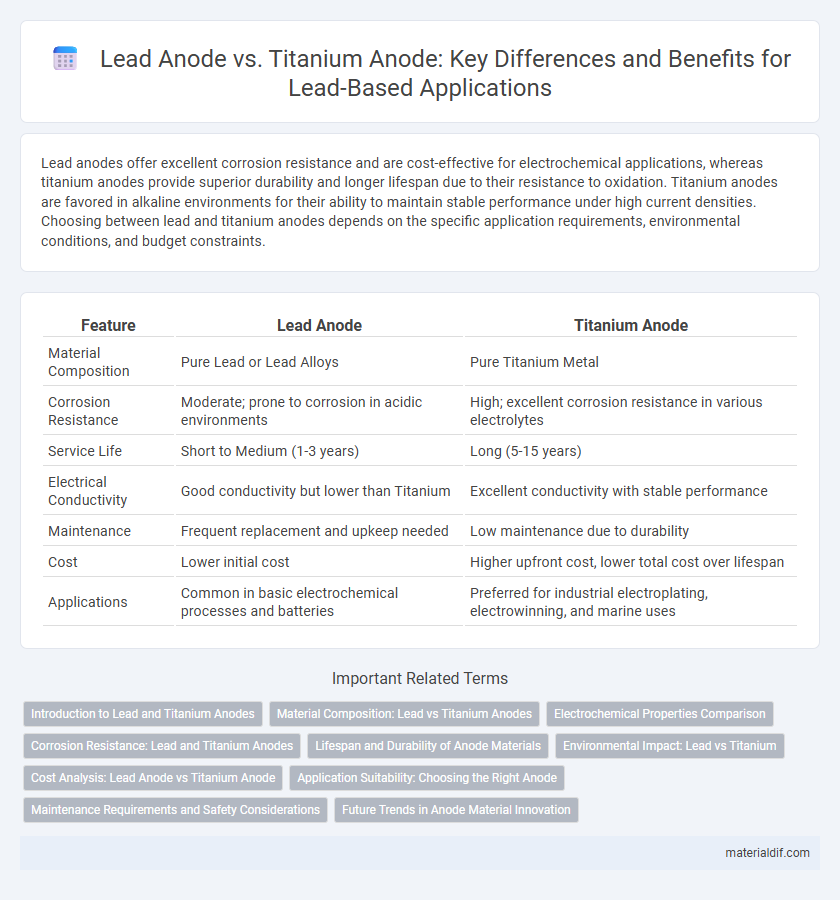
Lead anodes offer excellent corrosion resistance and are cost-effective for electrochemical applications, whereas titanium anodes provide superior durability and longer lifespan due to their resistance to oxidation. Titanium anodes are favored in alkaline environments for their ability to maintain stable performance under high current densities. Choosing between lead and titanium anodes depends on the specific application requirements, environmental conditions, and budget constraints.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Lead Anode | Titanium Anode |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Pure Lead or Lead Alloys | Pure Titanium Metal |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate; prone to corrosion in acidic environments | High; excellent corrosion resistance in various electrolytes |
| Service Life | Short to Medium (1-3 years) | Long (5-15 years) |
| Electrical Conductivity | Good conductivity but lower than Titanium | Excellent conductivity with stable performance |
| Maintenance | Frequent replacement and upkeep needed | Low maintenance due to durability |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher upfront cost, lower total cost over lifespan |
| Applications | Common in basic electrochemical processes and batteries | Preferred for industrial electroplating, electrowinning, and marine uses |
Introduction to Lead and Titanium Anodes
Lead anodes are commonly used in electroplating and battery applications due to their excellent corrosion resistance and conductivity. Titanium anodes, known for their strength and durability, are often coated with mixed metal oxides to enhance performance in harsh environments such as seawater electrolysis. The choice between lead and titanium anodes depends on factors like cost, lifespan, and chemical compatibility in the intended electrochemical process.
Material Composition: Lead vs Titanium Anodes
Lead anodes consist primarily of lead alloy, providing excellent corrosion resistance in acidic environments and superior electrical conductivity, making them ideal for electroplating and battery applications. Titanium anodes are composed of a titanium core coated with noble metals such as platinum or mixed metal oxides, offering exceptional durability, high oxygen evolution potential, and resistance to aggressive chemical attack in electrolytic processes. The material composition directly influences the lifespan, efficiency, and specific use cases, with lead anodes favored for cost-effectiveness and titanium anodes preferred for long-term stability in harsh conditions.
Electrochemical Properties Comparison
Lead anodes exhibit higher electrochemical corrosion rates and lower conductivity compared to titanium anodes, impacting efficiency in electrochemical processes. Titanium anodes provide superior corrosion resistance and enhanced electrical conductivity, resulting in longer service life and stable potential distribution. The choice between lead and titanium anodes significantly affects cell voltage, current efficiency, and maintenance frequency in electrochemical applications.
Corrosion Resistance: Lead and Titanium Anodes
Lead anodes exhibit moderate corrosion resistance, often forming a protective oxide layer that slows degradation in acidic and neutral electrolyte environments. Titanium anodes provide superior corrosion resistance due to their stable oxide film, which enhances durability and performance in aggressive and high-temperature electrolytes. This makes titanium anodes ideal for long-term applications requiring minimal maintenance and high efficiency.
Lifespan and Durability of Anode Materials
Lead anodes offer moderate lifespan but are prone to corrosion and degradation in harsh electrolytic environments, limiting their durability over extended use. Titanium anodes, coated with mixed metal oxides, exhibit superior lifespan and exceptional corrosion resistance, ensuring prolonged operational efficiency and reduced maintenance. The inherent corrosion resistance of titanium anodes significantly enhances durability, making them ideal for long-term industrial electrolysis applications.
Environmental Impact: Lead vs Titanium
Lead anodes pose significant environmental risks due to their toxicity and potential to contaminate soil and water during disposal or corrosion. Titanium anodes offer a more eco-friendly alternative with excellent corrosion resistance and minimal leaching, reducing harmful environmental effects. Transitioning to titanium anodes supports sustainable practices by minimizing hazardous waste and lowering the ecological footprint in electrochemical applications.
Cost Analysis: Lead Anode vs Titanium Anode
Lead anodes typically have a lower upfront cost compared to titanium anodes, making them a budget-friendly option for short-term applications. Titanium anodes, while more expensive initially, offer significantly greater durability and corrosion resistance, reducing replacement frequency and long-term maintenance expenses. Cost analysis favors titanium anodes in projects requiring longevity and minimal downtime, whereas lead anodes may be suitable for cost-sensitive, short-duration uses.
Application Suitability: Choosing the Right Anode
Lead anodes offer excellent corrosion resistance in acidic environments, making them ideal for applications such as electroplating and battery manufacturing. Titanium anodes provide superior durability and chemical resistance in harsh conditions like seawater electrolysis and wastewater treatment. Selecting the right anode depends on the specific operating environment, required lifespan, and cost considerations of the application.
Maintenance Requirements and Safety Considerations
Lead anodes require frequent inspection and replacement due to corrosion, increasing maintenance demands compared to titanium anodes, which have superior corrosion resistance and longer service life. Titanium anodes offer enhanced safety by minimizing the risk of lead contamination and reducing hazardous waste associated with lead anode degradation. Proper handling and disposal protocols are critical for lead anodes to mitigate environmental and health risks, whereas titanium anodes have lower environmental impact and simpler maintenance procedures.
Future Trends in Anode Material Innovation
Future trends in anode material innovation emphasize the development of titanium anodes due to their superior corrosion resistance, longer lifespan, and enhanced conductivity compared to traditional lead anodes. Advances in titanium anode coatings and alloys are expected to improve efficiency and reduce maintenance costs in electrochemical applications. Research is increasingly focused on sustainable materials and nano-engineering to optimize performance and environmental impact in industrial anode use.
Lead anode vs Titanium anode Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com