Lead foam offers superior density and soundproofing qualities compared to polyurethane foam, making it ideal for applications requiring enhanced noise reduction and vibration control. While polyurethane foam excels in flexibility and lightweight cushioning, lead foam provides greater durability and fire resistance. Choosing between lead foam and polyurethane foam depends on balancing priorities such as weight, thermal insulation, and acoustic performance.
Table of Comparison
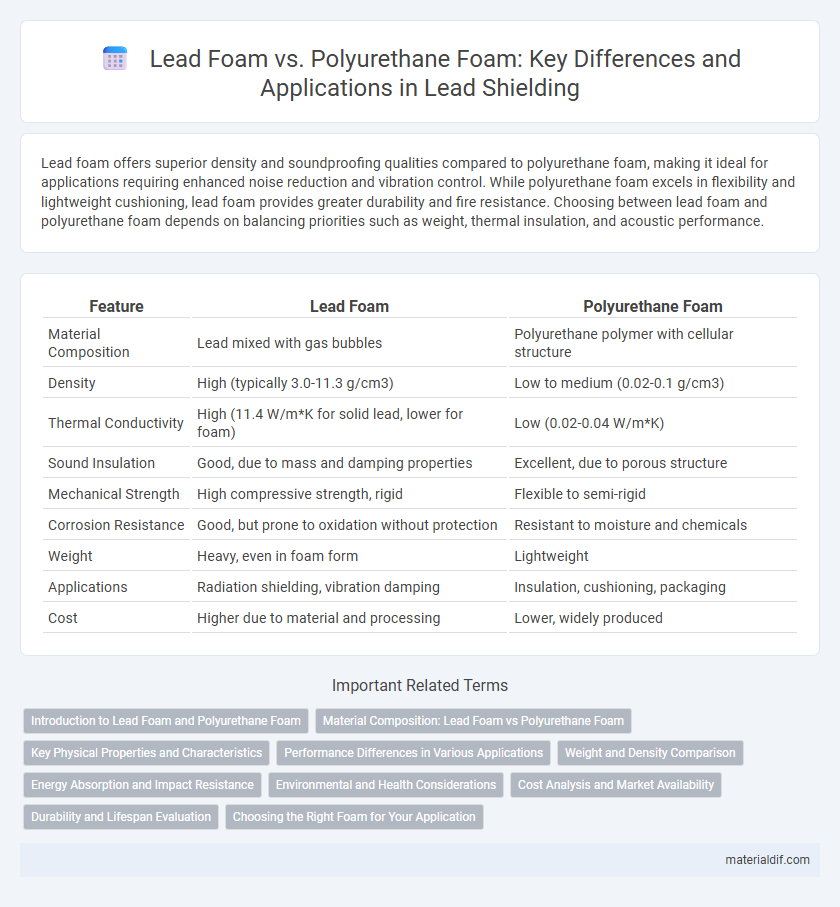
| Feature | Lead Foam | Polyurethane Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Lead mixed with gas bubbles | Polyurethane polymer with cellular structure |
| Density | High (typically 3.0-11.3 g/cm3) | Low to medium (0.02-0.1 g/cm3) |
| Thermal Conductivity | High (11.4 W/m*K for solid lead, lower for foam) | Low (0.02-0.04 W/m*K) |
| Sound Insulation | Good, due to mass and damping properties | Excellent, due to porous structure |
| Mechanical Strength | High compressive strength, rigid | Flexible to semi-rigid |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good, but prone to oxidation without protection | Resistant to moisture and chemicals |
| Weight | Heavy, even in foam form | Lightweight |
| Applications | Radiation shielding, vibration damping | Insulation, cushioning, packaging |
| Cost | Higher due to material and processing | Lower, widely produced |
Introduction to Lead Foam and Polyurethane Foam
Lead foam is a lightweight, porous metal material characterized by its unique combination of high density and excellent sound and vibration dampening properties, making it ideal for specialized applications in aerospace and automotive industries. Polyurethane foam, a versatile polymeric material, offers superior cushioning, thermal insulation, and flexibility, commonly used in furniture, packaging, and construction sectors. Both foams serve distinct purposes where lead foam excels in strength and thermal management, while polyurethane foam provides cost-effective, lightweight insulation and comfort solutions.
Material Composition: Lead Foam vs Polyurethane Foam
Lead foam, composed primarily of powdered lead fused into a porous matrix, offers high density and excellent radiation shielding properties ideal for specialized industrial applications. Polyurethane foam consists of polymer chains formed from polyols and isocyanates, resulting in lightweight, flexible material widely used for insulation and cushioning. The distinct material compositions dictate their performance differences, with lead foam providing superior structural strength and radiation attenuation, while polyurethane foam excels in thermal insulation and impact absorption.
Key Physical Properties and Characteristics
Lead foam exhibits superior density and soundproofing capabilities compared to polyurethane foam, making it ideal for heavy-duty shielding applications. Its intrinsic high melting point and excellent vibration damping set it apart from polyurethane foam's lower weight and greater flexibility. Polyurethane foam typically excels in thermal insulation and cushioning but lacks the structural robustness and radiation attenuation provided by lead foam.
Performance Differences in Various Applications
Lead foam exhibits superior acoustic and thermal insulation properties compared to polyurethane foam, making it ideal for industrial and construction applications that require soundproofing and heat resistance. Polyurethane foam offers greater flexibility and lighter weight, which enhances its performance in cushioning, packaging, and automotive seat padding. In environments exposed to high temperatures or heavy mechanical stress, lead foam maintains structural integrity better than polyurethane foam, emphasizing its suitability for specialized, high-performance applications.
Weight and Density Comparison
Lead foam exhibits significantly higher density compared to polyurethane foam, resulting in a much heavier material for the same volume. While polyurethane foam typically weighs between 20 to 80 kg/m3, lead foam density ranges around 4000 to 11,000 kg/m3, making it ideal for applications requiring substantial weight and shielding. The substantial weight difference impacts thermal insulation properties and mechanical strength, where polyurethane foam offers lightweight flexibility, whereas lead foam provides robustness and radiation resistance.
Energy Absorption and Impact Resistance
Lead foam exhibits superior energy absorption and impact resistance compared to polyurethane foam due to its higher density and unique cellular structure that effectively dissipates kinetic energy. Polyurethane foam, while lighter and more flexible, provides less resistance to high-impact forces and compressive stresses. The enhanced damping capabilities of lead foam make it ideal for applications requiring robust impact protection and vibration isolation.
Environmental and Health Considerations
Lead foam contains toxic lead particles that pose significant health risks such as lead poisoning and neurological damage, requiring careful handling and disposal. Polyurethane foam is generally safer but may emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during installation, which can affect indoor air quality and cause respiratory irritation if not properly ventilated. Environmentally, polyurethane foam offers better sustainability options with recyclable variants, whereas lead foam's heavy metal content creates long-term soil and water contamination concerns.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Lead foam exhibits higher material and processing costs compared to polyurethane foam, driven by its metal content and specialized manufacturing requirements. Polyurethane foam benefits from widespread market availability and lower production expenses, making it a more cost-effective option for large-scale insulation and cushioning applications. Market trends indicate polyurethane foam dominates due to affordability and accessibility, while lead foam is niche, favored for specific industries needing radiation shielding or structural applications.
Durability and Lifespan Evaluation
Lead foam exhibits superior durability and a longer lifespan compared to polyurethane foam due to its robust metallic structure and resistance to environmental degradation. Polyurethane foam tends to degrade faster under exposure to UV light, moisture, and mechanical stress, reducing its effective service life. The enhanced durability of lead foam makes it a preferred choice in applications requiring long-term structural integrity and resistance to harsh conditions.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Application
Lead foam offers superior density and radiation shielding, making it ideal for industrial and medical applications requiring high protection levels. Polyurethane foam excels in insulation, cushioning, and lightweight structural support, suited for furniture, packaging, and automotive industries. Selecting the right foam depends on balancing factors like thermal conductivity, compressive strength, and specific application requirements.
Lead foam vs Polyurethane foam Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com