Lead paint contains toxic lead compounds that pose serious health risks, especially to children, causing neurological damage and developmental delays. Lead-free paint eliminates these hazards by using non-toxic ingredients, making it a safer choice for homes, schools, and playgrounds. Choosing lead-free paint promotes a healthier environment and complies with modern safety regulations.
Table of Comparison
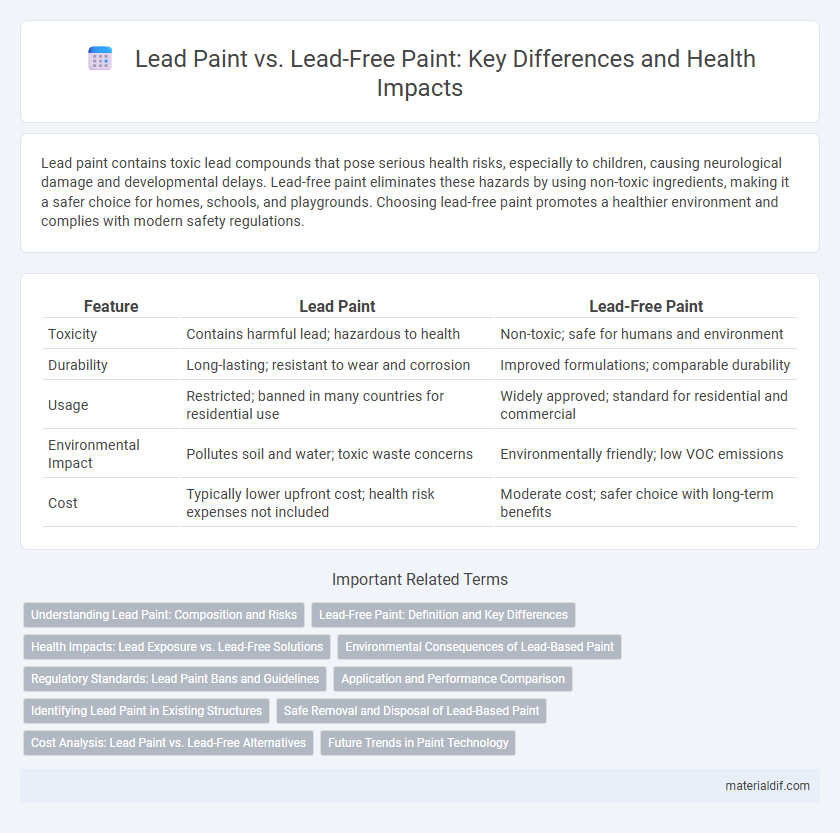
| Feature | Lead Paint | Lead-Free Paint |
|---|---|---|
| Toxicity | Contains harmful lead; hazardous to health | Non-toxic; safe for humans and environment |
| Durability | Long-lasting; resistant to wear and corrosion | Improved formulations; comparable durability |
| Usage | Restricted; banned in many countries for residential use | Widely approved; standard for residential and commercial |
| Environmental Impact | Pollutes soil and water; toxic waste concerns | Environmentally friendly; low VOC emissions |
| Cost | Typically lower upfront cost; health risk expenses not included | Moderate cost; safer choice with long-term benefits |
Understanding Lead Paint: Composition and Risks
Lead paint contains lead compounds, primarily lead(II) carbonate, which provide durability and opacity but pose significant health hazards. Exposure to lead paint dust or chips can cause lead poisoning, affecting neurological development, especially in children. Lead-free paint uses alternative pigments and binders to eliminate these toxic risks while maintaining performance and aesthetic quality.
Lead-Free Paint: Definition and Key Differences
Lead-free paint is a type of coating formulated without lead compounds, reducing health risks associated with lead exposure such as neurological damage and respiratory issues. Unlike traditional lead paint, lead-free paint uses safer pigments and binders, making it compliant with modern environmental regulations and suitable for residential and commercial use. Key differences include the absence of toxic lead, improved environmental safety, and a preference in construction and renovation projects to protect human health.
Health Impacts: Lead Exposure vs. Lead-Free Solutions
Lead paint contains toxic lead compounds that pose serious health risks, including neurological damage, especially in children and pregnant women. Exposure to lead paint can result in developmental delays, cognitive impairments, and cardiovascular problems due to the bioaccumulation of lead in the body. Lead-free paint options eliminate these health hazards by using non-toxic pigments and materials, making them a safer choice for residential and commercial environments.
Environmental Consequences of Lead-Based Paint
Lead-based paint contains toxic heavy metals that persist in the environment, contaminating soil and water sources for decades. The deterioration of lead paint releases hazardous dust and chips, posing significant health risks to humans and wildlife through bioaccumulation. Lead-free paint alternatives eliminate these environmental toxins, reducing pollution and supporting safer ecosystems.
Regulatory Standards: Lead Paint Bans and Guidelines
Regulatory standards for lead paint have become increasingly strict, with many countries imposing comprehensive bans on lead-based paints due to their toxic impact on human health and the environment. Agencies like the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) enforce limits on lead content, mandating lead-free alternatives for consumer products, especially in residential and children's environments. Compliance with these guidelines ensures safer indoor air quality and reduces the risk of lead poisoning, supporting global public health initiatives.
Application and Performance Comparison
Lead paint, historically favored for its durability and moisture resistance, offers superior adhesion and long-lasting finish on metal and wood surfaces, making it ideal for industrial and marine applications. Lead-free paint, formulated with safer pigments and binders, provides comparable performance in indoor residential settings, emphasizing low toxicity and environmental compliance while maintaining adequate coverage and drying times. Advances in lead-free formulations now match lead paint's resistance to cracking and peeling, ensuring sustainable protection without the health hazards associated with lead exposure.
Identifying Lead Paint in Existing Structures
Lead paint in existing structures can be identified through professional testing methods such as X-ray fluorescence (XRF) analyzers or laboratory analysis of paint samples. Visual clues like deteriorating paint with a distinctive pastel color or multiple layers of paint may also indicate the presence of lead-based paint. Homeowners and contractors should prioritize certified lead inspection services to ensure accurate detection and compliance with safety regulations.
Safe Removal and Disposal of Lead-Based Paint
Safe removal and disposal of lead-based paint require specialized techniques such as wet sanding, chemical stripping, or using a HEPA vacuum to minimize lead dust exposure. Certified professionals should conduct the process following EPA's Renovation, Repair, and Painting (RRP) Rule to ensure containment and prevent contamination of the environment. Proper disposal involves placing lead-painted debris in sealed, labeled containers and transporting them to hazardous waste facilities compliant with EPA and local regulations.
Cost Analysis: Lead Paint vs. Lead-Free Alternatives
Lead paint typically incurs lower initial costs compared to lead-free alternatives, making it a seemingly budget-friendly option for short-term projects. However, lead-free paints, while more expensive upfront, reduce health risks and long-term remediation expenses associated with lead poisoning and environmental cleanup. Evaluating total lifecycle costs reveals that lead-free paint offers greater economic benefits by minimizing future liabilities and regulatory compliance costs.
Future Trends in Paint Technology
Future trends in paint technology emphasize the shift from lead paint to lead-free paint formulations, driven by health regulations and environmental concerns. Innovations in nanotechnology and bio-based materials are enhancing the durability and eco-friendliness of lead-free paints, reducing toxic emissions during application and drying. Market projections indicate a growing demand for sustainable, non-toxic coatings in both residential and industrial sectors, accelerating the phase-out of lead-based paints worldwide.
Lead Paint vs Lead-Free Paint Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com