Lead sheathing offers superior corrosion resistance and flexibility compared to copper sheathing, making it ideal for long-term protection of underground pipes and cables. While copper sheathing provides excellent electrical conductivity and durability, it tends to corrode in certain soil conditions, reducing its effectiveness. Choosing lead sheathing ensures enhanced longevity and reliable insulation in harsh environments where metal degradation is a concern.
Table of Comparison
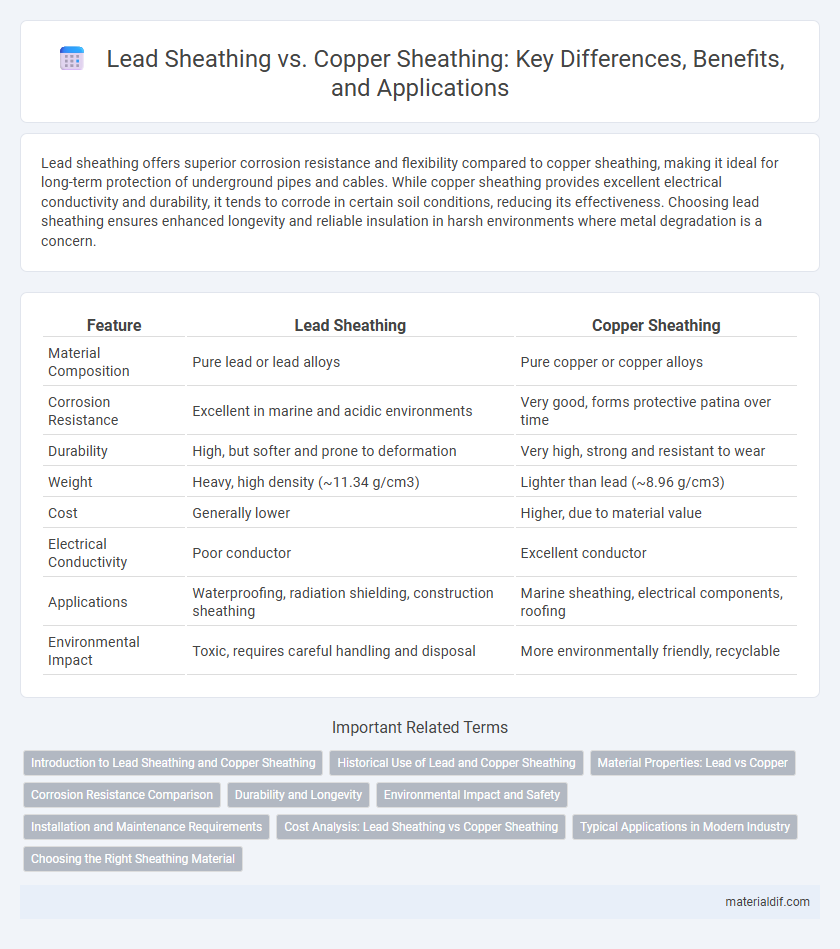
| Feature | Lead Sheathing | Copper Sheathing |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Pure lead or lead alloys | Pure copper or copper alloys |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent in marine and acidic environments | Very good, forms protective patina over time |
| Durability | High, but softer and prone to deformation | Very high, strong and resistant to wear |
| Weight | Heavy, high density (~11.34 g/cm3) | Lighter than lead (~8.96 g/cm3) |
| Cost | Generally lower | Higher, due to material value |
| Electrical Conductivity | Poor conductor | Excellent conductor |
| Applications | Waterproofing, radiation shielding, construction sheathing | Marine sheathing, electrical components, roofing |
| Environmental Impact | Toxic, requires careful handling and disposal | More environmentally friendly, recyclable |
Introduction to Lead Sheathing and Copper Sheathing
Lead sheathing offers superior corrosion resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for protecting underground cables and pipelines in harsh environments. Copper sheathing provides excellent electrical conductivity and durability, often used in applications requiring both mechanical protection and efficient grounding. Choosing between lead and copper sheathing depends on factors such as environmental conditions, electrical requirements, and budget constraints.
Historical Use of Lead and Copper Sheathing
Lead sheathing has been used historically for ship hull protection due to its corrosion resistance and malleability, dating back to Roman times. Copper sheathing emerged in the 18th century as a superior alternative, effectively preventing biofouling and wood-boring pests, thus enhancing vessel durability and speed. The shift from lead to copper sheathing marked a significant advancement in maritime technology driven by copper's longer lifespan and better antifouling properties.
Material Properties: Lead vs Copper
Lead sheathing offers superior corrosion resistance and malleability, making it ideal for long-term protection in harsh environments, especially against soil and water corrosion. Copper sheathing provides excellent electrical conductivity and higher tensile strength, enhancing durability and resistance to mechanical damage. While lead is denser and heavier, copper's thermal conductivity supports efficient heat dissipation in various industrial applications.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Lead sheathing offers superior corrosion resistance in marine environments due to its inertness and ability to form a protective oxide layer, which prevents further degradation. Copper sheathing also provides good corrosion resistance but is more susceptible to galvanic corrosion when in contact with different metals, especially in saltwater conditions. Overall, lead sheathing maintains structural integrity longer in aggressive environments, making it preferable for long-term protection against corrosion.
Durability and Longevity
Lead sheathing offers superior durability and longevity compared to copper sheathing due to its high resistance to corrosion, especially in acidic or marine environments. Copper sheathing, while corrosion-resistant, can suffer from oxidation and dezincification over time, reducing its lifespan in harsh conditions. The malleability and density of lead sheathing provide extended protection for structures, often exceeding 100 years, whereas copper sheathing typically lasts around 50-70 years under similar conditions.
Environmental Impact and Safety
Lead sheathing offers superior corrosion resistance and longevity but poses significant environmental and health risks due to lead toxicity and potential groundwater contamination. Copper sheathing presents a more eco-friendly alternative, being less toxic and recyclable, while still providing effective protection against marine organisms and corrosion. Safety considerations favor copper since it reduces hazardous exposure for workers and ecosystems compared to lead.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Lead sheathing offers excellent corrosion resistance and requires minimal maintenance, but its installation demands specialized skills due to lead's heavy weight and malleability. Copper sheathing, while easier to install because of its lighter weight and flexibility, needs regular inspection and maintenance to prevent patina and corrosion from environmental exposure. Both materials require careful handling to ensure durability and protection, yet lead's longevity often offsets the initial complexity of its installation.
Cost Analysis: Lead Sheathing vs Copper Sheathing
Lead sheathing typically offers a lower initial material cost compared to copper sheathing, making it a cost-effective choice for large-scale projects. However, copper sheathing provides greater durability and lower maintenance expenses over time, often resulting in a better long-term investment despite its higher upfront price. Cost analysis must consider both the immediate material expenses and the lifecycle costs associated with repair, longevity, and environmental impact.
Typical Applications in Modern Industry
Lead sheathing is commonly used for corrosion protection in underground and marine cable installations due to its excellent resistance to moisture and chemicals, making it ideal for harsh environments. Copper sheathing, favored in electrical applications, provides superior conductivity and mechanical strength, often utilized in power distribution and telecommunications where durability and performance are critical. Modern industry selects sheathing materials based on environmental conditions, electrical requirements, and longevity demands, with lead excelling in protective roles and copper enhancing electrical integrity.
Choosing the Right Sheathing Material
Choosing the right sheathing material between lead and copper depends on factors such as corrosion resistance, durability, and cost. Lead sheathing offers excellent protection against moisture and chemicals, making it ideal for underground cables, while copper sheathing provides superior electrical conductivity and mechanical strength suited for overhead applications. Evaluating the environmental conditions and specific project requirements ensures optimal performance and longevity of the cable installation.
Lead sheathing vs copper sheathing Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com