Industrial lead is primarily used in applications such as batteries, shielding, and construction, where cost-effectiveness and general performance are prioritized. Medical-grade lead undergoes stringent purification and testing to ensure biocompatibility and safety, making it suitable for use in protective gear and radiation shielding in healthcare environments. The distinction between industrial and medical-grade lead lies in their purity standards and specific regulatory requirements tailored to their respective uses.
Table of Comparison
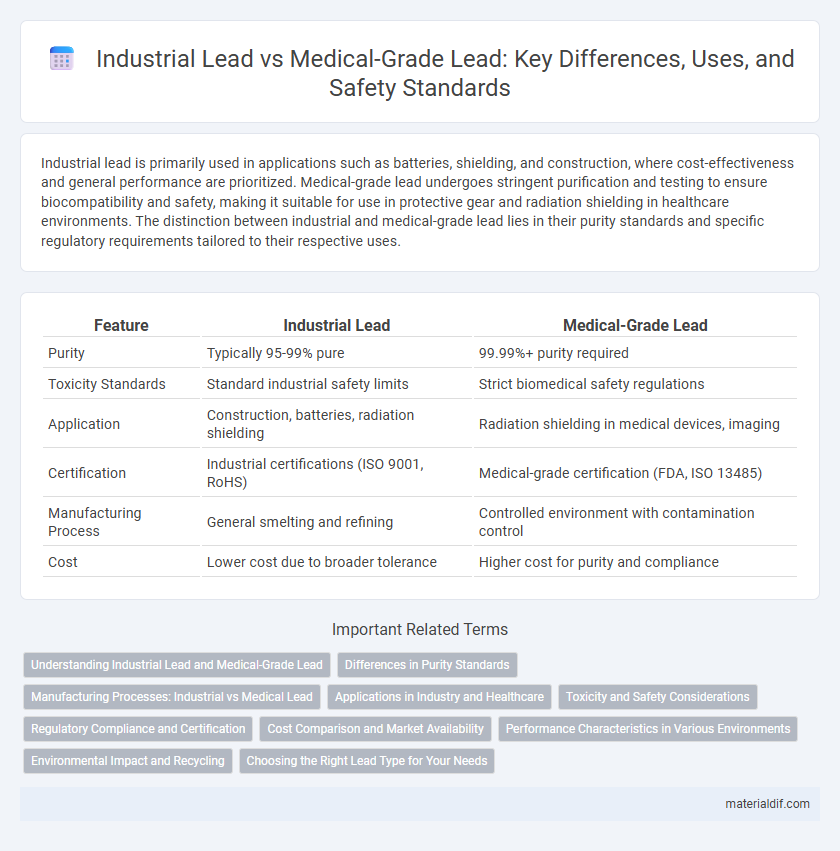
| Feature | Industrial Lead | Medical-Grade Lead |
|---|---|---|
| Purity | Typically 95-99% pure | 99.99%+ purity required |
| Toxicity Standards | Standard industrial safety limits | Strict biomedical safety regulations |
| Application | Construction, batteries, radiation shielding | Radiation shielding in medical devices, imaging |
| Certification | Industrial certifications (ISO 9001, RoHS) | Medical-grade certification (FDA, ISO 13485) |
| Manufacturing Process | General smelting and refining | Controlled environment with contamination control |
| Cost | Lower cost due to broader tolerance | Higher cost for purity and compliance |
Understanding Industrial Lead and Medical-Grade Lead
Industrial lead is primarily used in batteries, radiation shielding, and construction, characterized by lower purity and tolerance for impurities compared to medical-grade lead. Medical-grade lead undergoes stringent refining processes to achieve high purity essential for safe use in medical radiation shielding and diagnostic equipment. Understanding the distinct purity levels and applications helps in selecting the appropriate lead type for industrial or medical purposes, ensuring both performance and safety.
Differences in Purity Standards
Industrial lead typically contains impurities such as antimony, arsenic, and sulfur, resulting in a purity level around 97-99%. Medical-grade lead undergoes stringent purification processes to achieve a purity of 99.99% or higher, minimizing trace contaminants that could affect patient safety. These higher purity standards in medical-grade lead ensure biocompatibility and reduce the risk of adverse reactions in medical applications.
Manufacturing Processes: Industrial vs Medical Lead
Industrial lead is produced using cost-efficient manufacturing processes prioritizing bulk output, often incorporating higher impurity levels suitable for construction and shielding applications. In contrast, medical-grade lead undergoes stringent refining and quality control measures, ensuring biocompatibility, low toxicity, and compliance with health regulations critical for patient safety in medical devices and radiation shielding. Advanced purification techniques and trace contaminant testing distinguish medical-grade lead manufacturing from the more lenient protocols applied in industrial lead production.
Applications in Industry and Healthcare
Industrial lead is primarily utilized in manufacturing batteries, radiation shielding, and construction materials due to its durability and cost-effectiveness. Medical-grade lead, distinguished by its higher purity and stringent safety standards, is essential for protective equipment in radiology, diagnostic imaging, and radiation therapy environments. Both types of lead play critical roles in their respective fields by offering corrosion resistance and effective radiation attenuation tailored to specific industrial or healthcare applications.
Toxicity and Safety Considerations
Industrial lead contains higher levels of impurities and poses significant toxicity risks due to the presence of hazardous contaminants, making it unsuitable for medical applications. Medical-grade lead undergoes stringent purification processes to minimize toxic impurities, ensuring biocompatibility and enhanced safety in clinical environments. Strict regulatory standards govern the use of medical-grade lead to prevent lead poisoning and ensure patient and healthcare worker safety.
Regulatory Compliance and Certification
Industrial lead is governed by general environmental and workplace safety regulations such as OSHA and EPA standards, while medical-grade lead must meet stringent certifications like FDA approval and ISO 13485 compliance to ensure biocompatibility and patient safety. Medical-grade lead requires rigorous quality control and traceability to adhere to health regulations in medical devices, whereas industrial lead primarily adheres to performance standards for shielding and contamination control. Compliance with these regulatory frameworks ensures industrial lead is suitable for construction and manufacturing, while medical-grade lead is certified for use in radiation shielding within healthcare environments.
Cost Comparison and Market Availability
Industrial lead generally costs less than medical-grade lead due to lower purity requirements and less stringent manufacturing standards, making it more economically viable for large-scale construction and shielding applications. Medical-grade lead, used primarily for radiation shielding in healthcare settings, commands a higher price driven by its certified purity, regulatory compliance, and superior material consistency. Market availability for industrial lead is broader and more accessible globally, while medical-grade lead is produced in limited quantities and distributed through specialized suppliers to meet healthcare industry regulations.
Performance Characteristics in Various Environments
Industrial lead exhibits high corrosion resistance and durability in harsh environments, making it suitable for construction and battery applications. Medical-grade lead offers superior purity and biocompatibility, ensuring safety and performance in healthcare settings such as radiation shielding. While industrial lead prioritizes robustness and cost-efficiency, medical-grade lead optimizes for non-toxicity and precision in controlled environments.
Environmental Impact and Recycling
Industrial lead, commonly used in batteries and construction materials, poses significant environmental hazards due to its toxicity and persistence in ecosystems, often leading to soil and water contamination. Medical-grade lead, utilized in radiation shielding, is subject to stricter regulations and recycling protocols to minimize environmental impact while ensuring safety and material integrity. Advanced recycling techniques for both types prioritize containment and recovery, reducing hazardous waste and promoting sustainable lead reuse.
Choosing the Right Lead Type for Your Needs
Industrial lead is commonly used for shielding in construction and radiation protection due to its cost-effectiveness and durability, while medical-grade lead offers superior purity and strict quality control essential for patient safety in healthcare settings. Selecting the right lead type depends on application requirements, such as compliance with medical standards, exposure levels, and environmental conditions. Understanding these distinctions ensures optimal performance, safety, and regulatory adherence for your specific needs.
Industrial lead vs Medical-grade lead Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com