A lead tube offers superior flexibility and corrosion resistance compared to a PVC tube, making it ideal for plumbing applications that require durability and adaptability. Unlike PVC tubes, lead tubes can withstand higher temperatures and pressures without cracking or becoming brittle over time. Choosing a lead tube ensures long-term reliability in environments where chemical exposure and mechanical stress are common.
Table of Comparison
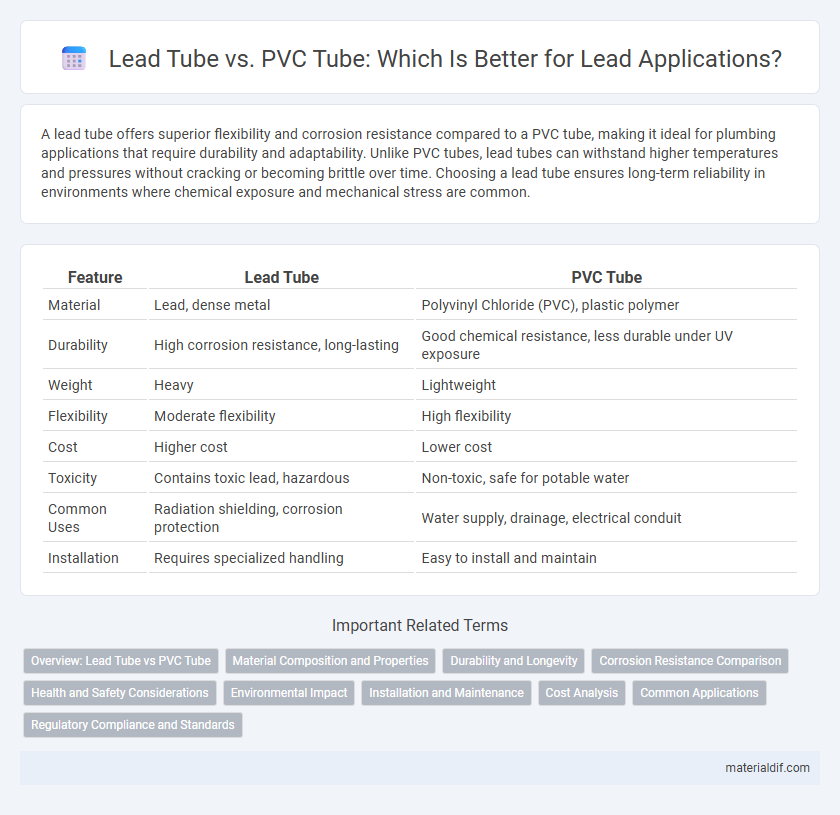
| Feature | Lead Tube | PVC Tube |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Lead, dense metal | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), plastic polymer |
| Durability | High corrosion resistance, long-lasting | Good chemical resistance, less durable under UV exposure |
| Weight | Heavy | Lightweight |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility | High flexibility |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost |
| Toxicity | Contains toxic lead, hazardous | Non-toxic, safe for potable water |
| Common Uses | Radiation shielding, corrosion protection | Water supply, drainage, electrical conduit |
| Installation | Requires specialized handling | Easy to install and maintain |
Overview: Lead Tube vs PVC Tube
Lead tubes offer superior resistance to corrosion and high temperatures, making them ideal for industrial applications requiring durability and chemical stability. PVC tubes are lightweight, cost-effective, and easy to install, commonly used in plumbing and irrigation due to their flexibility and resistance to chemicals and environmental factors. Choosing between lead and PVC tubes depends on application-specific needs, balancing lead's robustness against PVC's affordability and versatility.
Material Composition and Properties
Lead tubes consist primarily of dense, malleable lead metal, offering excellent corrosion resistance and high radiation shielding properties but pose environmental and health risks due to lead toxicity. PVC tubes are made from polyvinyl chloride, a durable plastic material that provides lightweight, chemical resistance, and insulation but lacks the shielding and weight characteristics of lead. The choice between lead and PVC tubes depends on the application's need for flexibility, toxicity concerns, and physical or chemical resistance requirements.
Durability and Longevity
Lead tubes exhibit exceptional durability due to their resistance to corrosion and ability to withstand extreme pressure, making them ideal for long-term applications. PVC tubes, while lightweight and cost-effective, tend to degrade faster under UV exposure and high temperatures, which can reduce their lifespan. Choosing lead tubes ensures prolonged service life in harsh environments, whereas PVC tubes may require more frequent replacements.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Lead tubes exhibit superior corrosion resistance compared to PVC tubes, especially in environments with acidic or alkaline conditions, due to lead's natural oxide layer that protects against rust. PVC tubes, while resistant to many chemicals and non-corrosive metals, can degrade under prolonged UV exposure or specific solvents. This makes lead tubes more suitable for harsh chemical applications, whereas PVC tubes are preferred for general-purpose water and gas distribution systems.
Health and Safety Considerations
Lead tubes pose significant health risks due to lead's toxicity, which can cause severe neurological damage and other chronic health issues through prolonged exposure or ingestion. PVC tubes are generally safer for health, as they do not contain toxic heavy metals, but concerns remain regarding the release of harmful chemicals like phthalates and dioxins during manufacturing or disposal. Proper handling, installation, and adherence to safety regulations are essential to mitigate health and environmental hazards associated with both lead and PVC tubing.
Environmental Impact
Lead tubes pose significant environmental hazards due to lead's toxicity and potential to contaminate soil and water systems, leading to long-term ecological damage and health risks. In contrast, PVC tubes, while also raising environmental concerns because of their plastic composition and challenges with disposal and recycling, generally have a lower toxicity profile and are less likely to leach harmful substances into the environment. Choosing between lead and PVC tubes requires considering the environmental impact of lead contamination versus the sustainability issues related to plastic waste management.
Installation and Maintenance
Lead tubes offer superior flexibility and ease of installation in confined spaces compared to rigid PVC tubes, which require precise cutting and joining methods. Maintenance of lead tubes is generally simpler due to their resistance to corrosion and capacity to withstand high temperatures, while PVC tubes may crack or degrade under UV exposure and require periodic inspection. The weight and softness of lead tubes facilitate adjustments and repairs, making them preferable for complex plumbing systems where frequent modifications are anticipated.
Cost Analysis
Lead tubes typically have a higher initial cost compared to PVC tubes due to raw material expenses and manufacturing complexity. PVC tubes offer cost advantages with lower production and installation expenses, making them more budget-friendly for large-scale plumbing and construction projects. Long-term maintenance costs for lead tubes can also increase overall expenditure due to corrosion and health-related regulations, while PVC tubes provide durable, low-maintenance alternatives.
Common Applications
Lead tubes are commonly used in plumbing for water and gas applications due to their corrosion resistance and malleability, making them suitable for old building restorations and radiation shielding in medical environments. PVC tubes are widely applied in irrigation systems, drainage, and electrical conduit installations because of their lightweight, durability, and chemical resistance. Both materials serve critical roles in different sectors, with lead tubes favored for specialized industrial use and PVC tubes preferred in residential and commercial infrastructure.
Regulatory Compliance and Standards
Lead tubes are strictly regulated due to their toxicity and are often prohibited in potable water systems by agencies such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA). PVC tubes comply with international standards including ASTM D1785 and NSF/ANSI 61, ensuring safe use in drinking water and meeting stringent health and safety regulations. Regulatory compliance favors PVC tubes for most modern plumbing applications due to their non-toxic nature and certification under established safety standards.
Lead tube vs PVC tube Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com