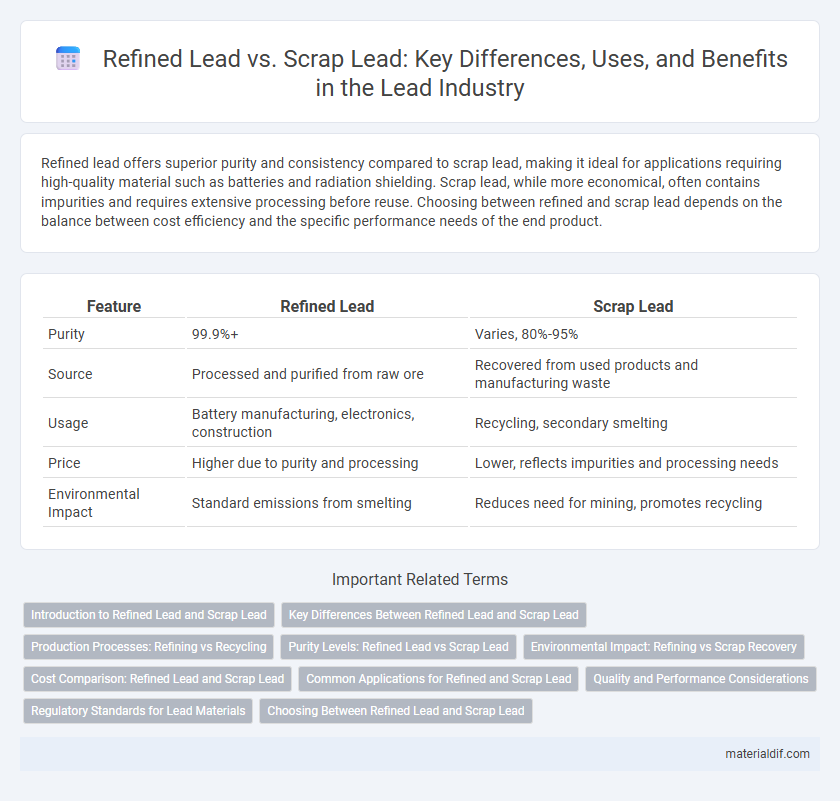
Refined lead offers superior purity and consistency compared to scrap lead, making it ideal for applications requiring high-quality material such as batteries and radiation shielding. Scrap lead, while more economical, often contains impurities and requires extensive processing before reuse. Choosing between refined and scrap lead depends on the balance between cost efficiency and the specific performance needs of the end product.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Refined Lead | Scrap Lead |
|---|---|---|
| Purity | 99.9%+ | Varies, 80%-95% |
| Source | Processed and purified from raw ore | Recovered from used products and manufacturing waste |
| Usage | Battery manufacturing, electronics, construction | Recycling, secondary smelting |
| Price | Higher due to purity and processing | Lower, reflects impurities and processing needs |
| Environmental Impact | Standard emissions from smelting | Reduces need for mining, promotes recycling |
Introduction to Refined Lead and Scrap Lead
Refined lead is purified lead obtained through processes such as smelting and electrolysis, used extensively in batteries, radiation shielding, and cable sheathing. Scrap lead consists of lead-containing materials discarded from manufacturing, batteries, and other products, often recycled to recover valuable lead content. Understanding the distinction between refined and scrap lead is crucial for optimizing recycling efficiency and ensuring environmental compliance.
Key Differences Between Refined Lead and Scrap Lead
Refined lead is a high-purity metal produced through smelting and refining processes, typically achieving purity levels above 99%, making it suitable for batteries, radiation shielding, and alloys. Scrap lead consists of recycled or waste materials containing impurities, requiring further processing to be reused effectively. The key differences lie in their purity, processing requirements, and end-use applications, with refined lead ready for direct industrial use while scrap lead serves as a raw material for refining.
Production Processes: Refining vs Recycling
Refined lead undergoes a complex refining process involving smelting, purification, and alloying to achieve high purity levels essential for battery manufacturing and industrial applications. Scrap lead, on the other hand, is collected from used products and recycled through melting and chemical treatment to remove impurities, reducing environmental impact while conserving raw materials. Production processes for refined lead emphasize quality control and material consistency, whereas scrap lead recycling prioritizes sustainability and resource recovery.
Purity Levels: Refined Lead vs Scrap Lead
Refined lead typically contains purity levels above 99.9%, making it ideal for industrial applications requiring minimal impurities such as battery manufacturing and radiation shielding. Scrap lead, by contrast, often ranges from 85% to 98% purity due to contamination from alloys, oxidation, and other metals, necessitating further processing to achieve refined standards. The purity difference significantly affects performance, recyclability, and processing costs in lead-based products.
Environmental Impact: Refining vs Scrap Recovery
Refined lead undergoes processing that reduces impurities, enabling its use in high-quality batteries and electronics, but this refining process consumes significant energy and emits pollutants. Scrap lead recovery involves recycling existing lead materials, significantly lowering environmental footprint by minimizing raw ore extraction and reducing waste in landfills. Prioritizing scrap lead recovery supports circular economy practices and mitigates the ecological damage associated with traditional lead refining methods.
Cost Comparison: Refined Lead and Scrap Lead
Refined lead typically incurs higher production costs due to advanced processing and purification methods compared to scrap lead, which is sourced from recycled materials with minimal refinement. Scrap lead offers a cost advantage by reducing raw material expenses and energy consumption, making it a more economical choice for manufacturers prioritizing budget efficiency. However, refined lead provides higher purity and consistent quality, justifying its premium price in applications demanding strict material standards.
Common Applications for Refined and Scrap Lead
Refined lead is widely used in the manufacturing of batteries, particularly lead-acid batteries for vehicles and backup power systems, due to its high purity and excellent conductivity. Scrap lead, often recycled from old batteries and industrial waste, is commonly repurposed in the production of new lead products, including pipes, cables, and radiation shielding materials. Both refined and scrap lead play crucial roles in automotive, construction, and electronics industries by providing cost-effective and sustainable sources of lead material.
Quality and Performance Considerations
Refined lead offers superior purity with minimal impurities, enhancing conductivity and corrosion resistance, which makes it ideal for high-performance applications such as batteries and radiation shielding. Scrap lead often contains contaminants and alloying elements that reduce its quality, leading to inconsistent performance and lower durability in industrial uses. Selecting refined lead over scrap lead ensures reliability, longer lifespan, and adherence to stringent industry standards in critical manufacturing processes.
Regulatory Standards for Lead Materials
Refined lead meets stringent regulatory standards such as RoHS and REACH, ensuring reduced toxic impurities and compliance with environmental safety limits for heavy metals in manufacturing. Scrap lead, often sourced from recycled materials, requires thorough testing to verify it meets these regulations due to potential contamination with hazardous substances. Compliance with regulatory standards guarantees safe handling, reduced environmental impact, and eligibility for use in critical applications like batteries and radiation shielding.
Choosing Between Refined Lead and Scrap Lead
Choosing between refined lead and scrap lead depends on purity requirements and application specifics. Refined lead offers higher purity levels, often exceeding 99.9%, making it ideal for sensitive electronics and battery manufacturing. Scrap lead, typically lower in purity due to contaminants, suits less critical uses such as construction or recycling but requires additional processing to meet standards.
Refined Lead vs Scrap Lead Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com