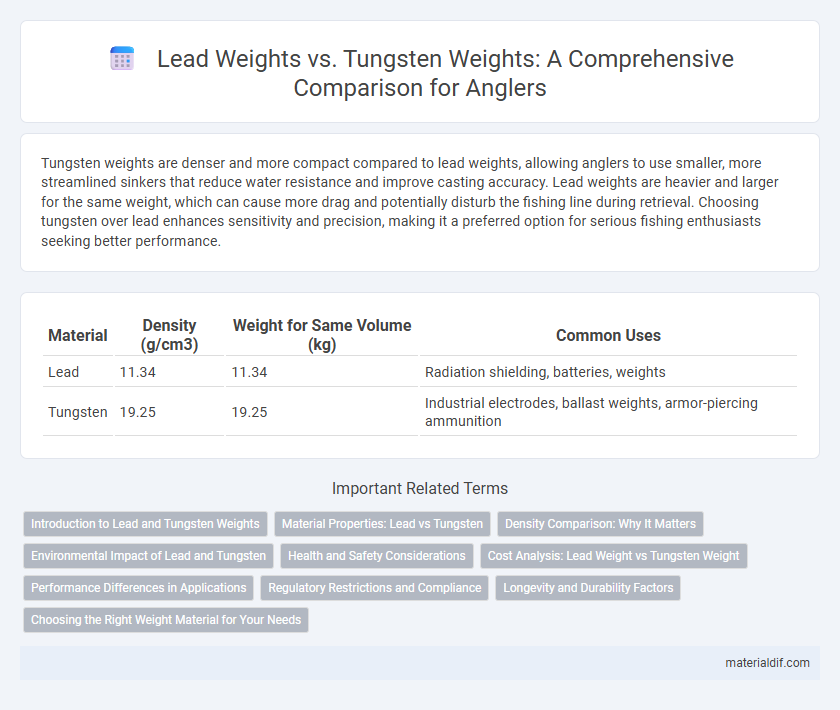
Tungsten weights are denser and more compact compared to lead weights, allowing anglers to use smaller, more streamlined sinkers that reduce water resistance and improve casting accuracy. Lead weights are heavier and larger for the same weight, which can cause more drag and potentially disturb the fishing line during retrieval. Choosing tungsten over lead enhances sensitivity and precision, making it a preferred option for serious fishing enthusiasts seeking better performance.
Table of Comparison
| Material | Density (g/cm3) | Weight for Same Volume (kg) | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lead | 11.34 | 11.34 | Radiation shielding, batteries, weights |
| Tungsten | 19.25 | 19.25 | Industrial electrodes, ballast weights, armor-piercing ammunition |
Introduction to Lead and Tungsten Weights
Lead and tungsten weights are commonly used in fishing and industrial applications due to their density and durability. Lead has a density of about 11.34 g/cm3, making it effective yet heavier compared to tungsten, which has a density of approximately 19.25 g/cm3, allowing for smaller, more compact weights. Tungsten weights offer superior performance by providing increased sensitivity and reduced size, ideal for precision tasks where lead's bulkier weight can be a limitation.
Material Properties: Lead vs Tungsten
Lead has a density of approximately 11.34 g/cm3, making it significantly less dense than tungsten, which has a density of about 19.25 g/cm3, resulting in tungsten weights being more compact and heavier for the same volume. Tungsten exhibits higher hardness and melting point compared to lead, making it more durable and heat-resistant for applications requiring material robustness. Lead's softness and lower melting point limit its use in high-stress environments, whereas tungsten's superior material properties make it ideal for precision weights and high-performance components.
Density Comparison: Why It Matters
Lead has a density of approximately 11.34 g/cm3, while tungsten is significantly denser at about 19.25 g/cm3, making tungsten nearly 70% heavier by volume. This density difference affects the weight and size of weights or projectiles, where tungsten can achieve the same mass as lead in a smaller volume. Understanding this density comparison is crucial for applications requiring compactness or precision in weight distribution.
Environmental Impact of Lead and Tungsten
Lead is significantly heavier than tungsten, with a density of 11.34 g/cm3 compared to tungsten's 19.25 g/cm3, influencing their applications in weighted products. The environmental impact of lead is severe due to its toxicity, persistence in ecosystems, and bioaccumulation, causing soil and water contamination and health hazards to humans and wildlife. Tungsten is considered a safer alternative with lower toxicity and reduced environmental risks, making it increasingly preferred in industries aiming to minimize ecological damage.
Health and Safety Considerations
Lead weight is significantly denser than tungsten weight, making it heavier and more toxic, posing substantial health risks due to lead's neurotoxic effects. Tungsten weight is a safer alternative as it is non-toxic and environmentally friendly, reducing health hazards during handling and use. Proper precautions and regulations are critical when using lead weights to prevent lead poisoning and contamination in occupational and recreational settings.
Cost Analysis: Lead Weight vs Tungsten Weight
Lead weights generally cost significantly less than tungsten weights due to the abundant availability and lower processing expenses associated with lead. Tungsten weights, while denser and more compact, have higher production costs that translate into a premium price, often two to three times that of comparable lead weights. Evaluating the cost-effectiveness depends on usage requirements, with lead offering budget-friendly solutions and tungsten providing durable, space-efficient options.
Performance Differences in Applications
Lead weighs approximately 11.34 g/cm3, while tungsten is significantly denser at about 19.25 g/cm3, impacting performance in applications like fishing sinkers, where tungsten's higher density allows smaller, more compact weights for improved casting distance and sensitivity. Tungsten's hardness and environmental non-toxicity enhance durability and regulatory compliance compared to softer, toxic lead, making it preferable in precision sports and environmental-sensitive regions. The higher cost of tungsten can be offset by performance gains when precise weight distribution and reduced size yield superior results in competitive and technical uses.
Regulatory Restrictions and Compliance
Lead, commonly used for its density and cost-effectiveness, faces increasing regulatory restrictions due to its toxicity and environmental impact, leading to stringent compliance requirements in various industries. Tungsten, a safer and non-toxic alternative with comparable weight and density, is gaining preference to meet these regulatory standards while ensuring performance. Manufacturers must carefully assess weight equivalency and regulatory compliance when substituting lead with tungsten to adhere to global environmental laws and avoid penalties.
Longevity and Durability Factors
Lead weights are commonly used in fishing due to their density and affordability, but tungsten weights offer superior longevity and durability because tungsten is significantly harder and more resistant to deformation. While lead is softer and prone to wear or damage over time, tungsten maintains its shape and effectiveness through repeated use, providing consistent performance for longer durations. The corrosion resistance of tungsten also enhances its durability in various water conditions compared to lead, which can deteriorate or leach harmful substances.
Choosing the Right Weight Material for Your Needs
Lead is denser than many materials but less dense than tungsten, making tungsten weights smaller and more compact for the same mass. When choosing the right weight material, consider tungsten's superior density for precision and durability in applications like fishing or ballasts. Lead offers affordability and malleability but poses environmental and health risks, making tungsten a preferred eco-friendly alternative.
Lead weight vs Tungsten weight Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com