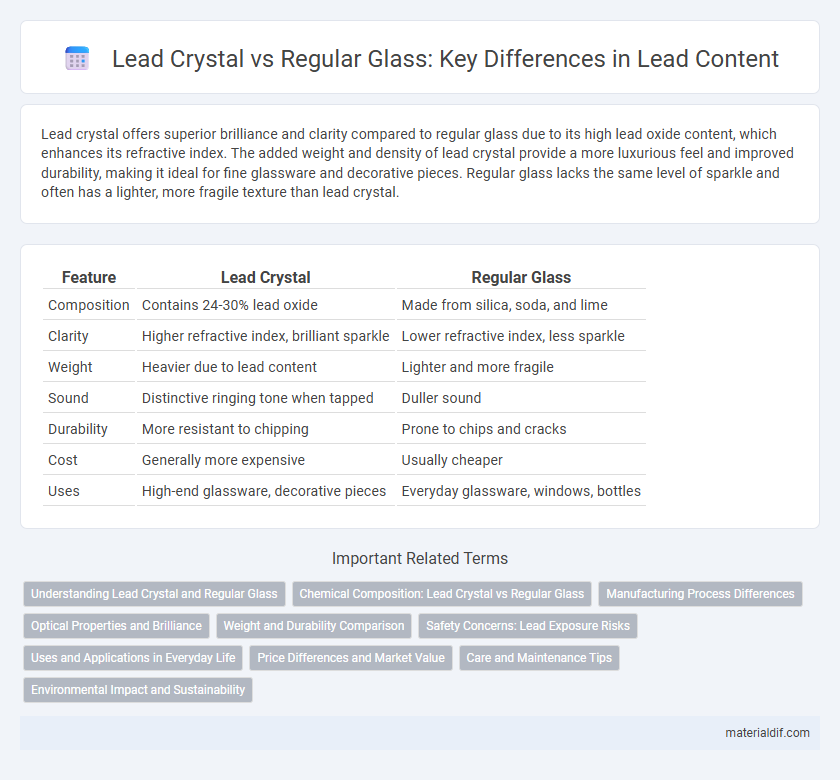
Lead crystal offers superior brilliance and clarity compared to regular glass due to its high lead oxide content, which enhances its refractive index. The added weight and density of lead crystal provide a more luxurious feel and improved durability, making it ideal for fine glassware and decorative pieces. Regular glass lacks the same level of sparkle and often has a lighter, more fragile texture than lead crystal.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Lead Crystal | Regular Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Contains 24-30% lead oxide | Made from silica, soda, and lime |
| Clarity | Higher refractive index, brilliant sparkle | Lower refractive index, less sparkle |
| Weight | Heavier due to lead content | Lighter and more fragile |
| Sound | Distinctive ringing tone when tapped | Duller sound |
| Durability | More resistant to chipping | Prone to chips and cracks |
| Cost | Generally more expensive | Usually cheaper |
| Uses | High-end glassware, decorative pieces | Everyday glassware, windows, bottles |
Understanding Lead Crystal and Regular Glass
Lead crystal contains a significant percentage of lead oxide, typically around 24-30%, which enhances its refractive index, brilliance, and weight compared to regular glass. Regular glass, primarily composed of silica, soda, and lime, lacks lead content and has lower density, making it less sparkly and more brittle than lead crystal. Understanding these compositional differences explains lead crystal's superior clarity, durability, and use in high-end decorative glassware versus the more everyday applications of regular glass.
Chemical Composition: Lead Crystal vs Regular Glass
Lead crystal contains lead oxide typically ranging from 18% to 30%, which enhances its refractive index and brilliance compared to regular glass that primarily consists of silica (silicon dioxide) with minor alkali and alkaline earth metals. The lead oxide in lead crystal lowers the melting point and increases density, resulting in a heavier and more resonant material than regular glass. Regular glass has a simpler chemical structure focused on silicon dioxide, whereas lead crystal incorporates lead to achieve superior clarity and sparkle.
Manufacturing Process Differences
Lead crystal differs from regular glass primarily due to its manufacturing process, which involves adding lead oxide to molten glass, typically between 18-30%, enhancing its weight, brilliance, and clarity. The introduction of lead oxide lowers the melting point, allowing for easier shaping and more intricate designs compared to the silica-based regular glass that has a higher melting temperature. Specialized annealing techniques are employed in lead crystal production to relieve internal stresses and achieve its characteristic clarity and refractive qualities, which are less pronounced in regular glass manufacturing.
Optical Properties and Brilliance
Lead crystal exhibits superior optical properties compared to regular glass due to its high refractive index, which enhances light dispersion and creates a distinctive brilliance and sparkle. The presence of lead oxide in lead crystal increases its density and allows for greater light refraction, producing vivid prisms and a radiant glow. In contrast, regular glass has a lower refractive index, resulting in less brilliance and a more muted appearance.
Weight and Durability Comparison
Lead crystal contains lead oxide, which increases its density, making it significantly heavier than regular glass of the same size. The added lead also enhances durability by providing greater resistance to chipping and cracking, unlike ordinary glass, which is more prone to damage over time. This combination of weight and durability distinguishes lead crystal as a premium material for fine glassware and decorative items.
Safety Concerns: Lead Exposure Risks
Lead crystal contains a significant amount of lead oxide, which can leach lead into beverages or food, posing health risks through prolonged exposure. Regular glass, typically made from silica and soda-lime, does not contain lead and is considered safer for everyday use, especially in storing acidic liquids. Careful handling and limited use of lead crystal items are recommended to minimize potential lead exposure risks.
Uses and Applications in Everyday Life
Lead crystal enhances decorative items, offering brilliance and clarity ideal for luxury glassware, chandeliers, and fine vases, making it a preferred choice for elegant table settings and artistic displays. Regular glass, valued for its durability and cost-effectiveness, is commonly used in everyday containers, windows, and drinkware, providing practicality for routine household and commercial applications. The weighted feel and refractive quality of lead crystal make it favored in high-end settings, while regular glass supports mass production and functional versatility.
Price Differences and Market Value
Lead crystal commands a higher price than regular glass due to its enhanced clarity, brilliance, and weight, which appeal to luxury markets and collectors. The market value of lead crystal remains stable or appreciates over time because of its craftsmanship and brand reputation, while regular glass typically has lower resale value and is priced more affordably for everyday use. Consumers often pay a premium for lead crystal in fineware and decorative items, reflecting its perceived quality and exclusivity.
Care and Maintenance Tips
Lead crystal requires gentle care to prevent damage to its delicate surfaces, making hand washing with mild detergent and warm water essential while avoiding abrasive scrubbers. Regular glass offers greater durability and can often be cleaned in a dishwasher without risk, though fragile glassware may still benefit from gentle handling. Proper drying with a soft lint-free cloth helps maintain the clarity and brilliance of lead crystal, preventing water spots and preserving its unique sparkle.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Lead crystal, containing lead oxide, poses environmental challenges during production and disposal due to lead's toxicity and potential soil and water contamination. Regular glass, typically composed of silica, soda ash, and lime, is more environmentally sustainable as it is easier to recycle and lacks harmful heavy metals. Choosing regular glass over lead crystal reduces ecological risks and supports sustainable manufacturing practices.
Lead crystal vs Regular glass Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com